前言
pytest 结合 allure 描述用例的时候我们一般使用 @allure.title 和 @allure.description 描述测试用例的标题和详情。
在用例里面也可以动态更新标题和详情,使用allure.dynamic方法实现。
allure.dynamic 动态属性
feature 模块
allure.dynamic.feature(feature_name)
功能点 story
allure.dynamic.story(case_story)
用例标题 title
allure.dynamic.title(case_title)
用例描述:请求URL 请求类型 期望结果 实际结果描述
desc = "<font color='red'>请求URL:</font>{}<Br/>"
"<font color='red'>请求类型:</font>{}<Br/>"
"<font color='red'>期望结果:</font>{}<Br/>"
"<font color='red'>实际结果描述:</font>{}<Br/>".format(url,method,expect,expect_result)
allure.dynamic.description(desc)
description 用例描述
可以在测试主体内部动态更新描述 allure.dynamic.description
import allure
@allure.description("""
This description will be replaced at the end of the test.
""")
def test_dynamic_description():
assert 42 == int(6 * 7)
allure.dynamic.description('A final description.')
最后用例的描述被更新为 'A final description.'

title 用例标题
用例标题也可以被动态更新
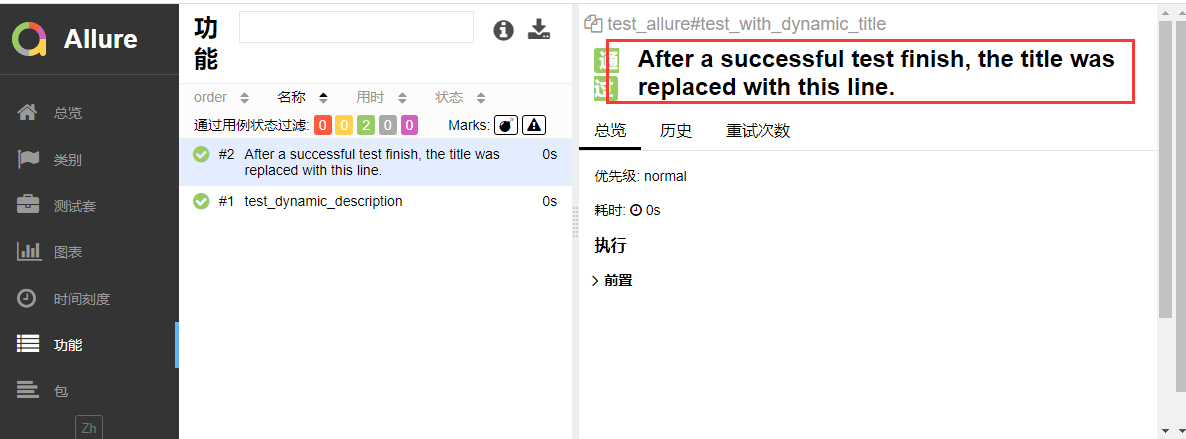
@allure.title("This title will be replaced in a test body")
def test_with_dynamic_title():
assert 2 + 2 == 4
allure.dynamic.title('After a successful test finish, the title was replaced with this line.')
最终用例的title更新为'After a successful test finish, the title was replaced with this line.'
参数化
参数化时候,可以使用@allure.title给用例不同标题
@allure.title("Parameterized test title: adding {param1} with {param2}")
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param1,param2,expected', [
(2, 2, 4),
(1, 2, 5)
])
def test_with_parameterized_title(param1, param2, expected):
assert param1 + param2 == expected
也可以在用例里面使用allure.dynamic.title更新用例的标题
import pytest
import allure
# 作者:上海-悠悠 QQ交流群:779429633
def login(username, password):
'''登录'''
print("输入账号:%s" % username)
print("输入密码:%s" % password)
# 返回
return {"code": 0, "msg": "success!"}
# 测试数据
test_datas = [
({"username": "yoyo1", "password": "123456"}, "success!", "输入正确账号,密码,登录成功"),
({"username": "yoyo2", "password": "123456"}, "failed!", "输入错误账号,密码,登录失败"),
({"username": "yoyo3", "password": "123456"}, "success!", "输入正确账号,密码,登录成功"),
]
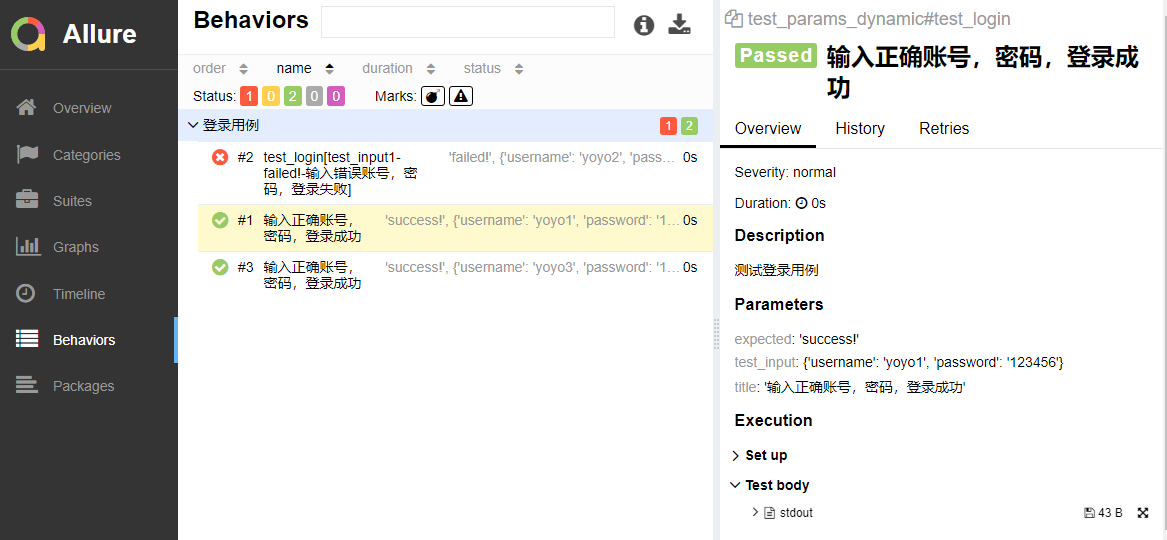
@allure.story("登录用例")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected,title",
test_datas
)
def test_login(test_input, expected, title):
'''测试登录用例'''
# 获取函数返回结果
result = login(test_input["username"], test_input["password"])
# 断言
assert result["msg"] == expected
allure.dynamic.title(title)
最终生成报告效果