同步和异步:
同步就是整个处理过程顺序执行,当各个过程都执行完毕,并返回结果。是一种线性执行的方式,执行的流程不能跨越。
异步与同步相反,在调用发出后,调用者可以继续执行后面的操作,被调用者通过状态通知调用者,或者通过回调函数来通知结果。
1. Asyncio模块
#asyncio import asyncio import time #匿名函数 now = lambda:time.time() start_time = now() async def test1(): print('test1') await asyncio.sleep(3) async def test2(): print('test12') async def test3(): print('test3') await asyncio.sleep(5) async def test4(): print('test4') await asyncio.sleep(6) def main(): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() tasks = [test1(), test2(), test3(), test4()] loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) loop.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main() print(now() - start_time)
执行结果:
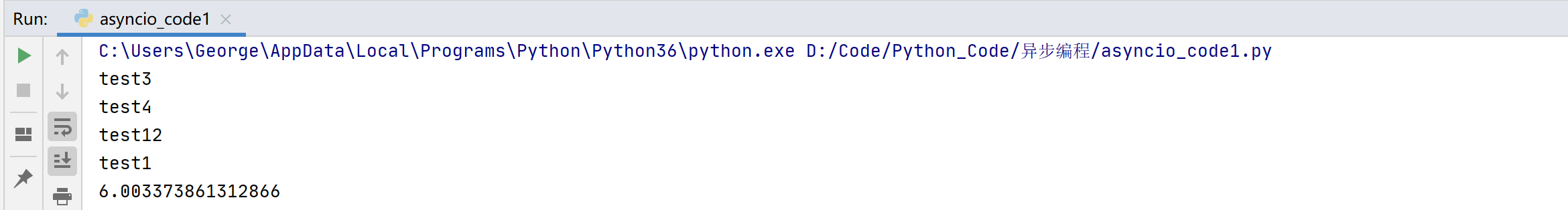
分析:如果是同步的话,需要先执行test1,遇到sleep会一直等待test1执行完成才继续执行下一个方法