Title
A Comparative Illustration of AI Planning-based Web Services Composition
Journal
ACM SIGecom Exchanges
Year
2005
Author
Seog-Chan Oh, Dongwon Lee
Level
Introductory
Comment
根据自动/手动,复杂性,规模对WSC问题进行区分,然后讲述了AI方法对各种不同的WSC问题的适用性,重点研究了AI Planning方法对一般WSC问题的应用。
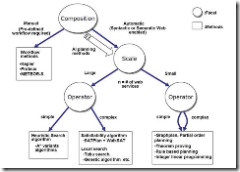
1. 文章结构
Propose the Problem Setting: Find the Restaurant and give the concept of WSC
Classification of WSC Problem
Manual vs. Automatic Workflow Composition
Simple vs. Complex Operator
Small vs. LargeScale
Overview of Matching Approaches
Approach-1: exact match using syntactic equivalence
Approach-2: approximate match using distance functions
Approach-3: semantic match using ontologies
AI-Planning based algorithms for WSC problem
Graphplan based planning
SATPlan based reduction
Integer Linear Programming formulation
Conclusion
2. Claims
Web services based e-service workflow problem can be formulated as AI-planning problem
3. WSC problem classification
(1) Manual vs. Automatic Workflow Composition
Manual approach is not appropriate for large-scale WSC problem.
(2) Simple vs. Complex Operator
Simple WSC: sequential AND Composition
(3) Small vs. Large Scale
Small-scale WSC problem: exhaustive search algorithms
Large-scale problem: approximate algorithms
The automatic composition approach can be complementary to the manual approach such that a few feasible workflows generated from the automatic approach are in turn presented to domain experts who may choose one of them, and refine it further manually.
4. Different WSC problem and the corresponding AI method
(1) WSC without complex operator:
heuristic sub-optimal algorithms (e.g. A *)
(2) Operators are complex and some specific constraint rules must be checked
rule-based expert systems
(3) More General WSC problem
AI planning methods
5. AI-Planning based algorithms for WSC problem
Graphplan and ILP are suitable for planning problem with complex operators in a small-scale.
SATPlan can be used to find sub-optimal compositions for a large-scale problem with complex operator
Appendix
A.1 Definition of WSC (Web Service Composition) Problem
In order to fully satisfy a request r, one has to compose multiple web services, {w1, w2, …, wn } in sequential or parallel way such that:
(1) ∈{w1,w2,…,wn}, wiin can be grounded when wiout is required at a particular state in composition
(2) in Uw1out … Uwnout) ⊇rout
A.2 Background
(1) The general WSC problem can be reduced to the satisfiabiliy problem[Vossen et al. 1999].