部署视图
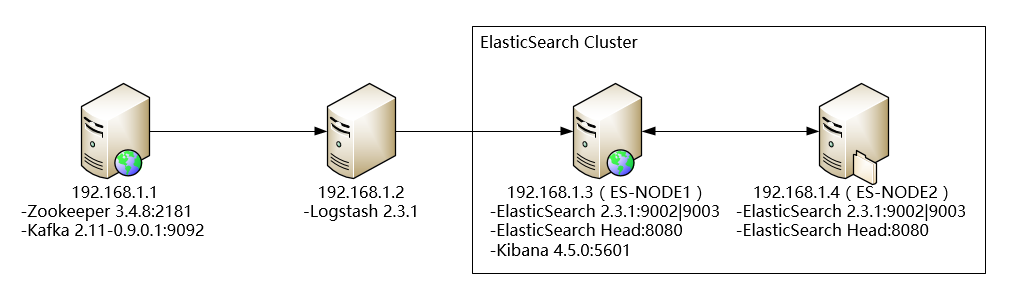
运行环境
CentOS 6.7 x64 (2核4G,硬盘100G)
需要的安装包
Runtime
jdk1.8 : jdk-8u91-linux-x64.gz (http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html )
Kafka
zookeeper : zookeeper-3.4.8.tar.gz(https://zookeeper.apache.org/releases.html )
kafka : kafka_2.11-0.9.0.1.tgz (https://kafka.apache.org/downloads.html)
ELK Stack (https://www.elastic.co//)
logstash : logstash-2.3.1.tar.gz
elasticsearch : elasticsearch-2.3.1.tar.gz
kibana : kibana-4.5.0-linux-x64.tar.gz
环境搭建
由于环境无法连接Internet,所有应用部署都通过离线安装的方式
安装JDK
CentOS 6.7自带的 jdk 是1.7 版本的 ELK官方推荐使用 jdk 8
卸载系统自带 1.7 参考以下命令
# rpm -qa|grep jdk
java-1.6.0-openjdk-1.6.0.0-1.50.1.11.5.el6_3.x86_64
java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.9-2.3.4.1.el6_3.x86_64
# rpm -qa|grep gcj
java-1.4.2-gcj-compat-1.4.2.0-40jpp.115
libgcj-4.1.2-48.el5
# yum -y remove java java-1.6.0-openjdk-1.6.0.0-1.50.1.11.5.el6_3.x86_64
# yum -y remove java java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.9-2.3.4.1.el6_3.x86_64
# yum -y remove java java-1.4.2-gcj-compat-1.4.2.0-40jpp.115
# yum -y remove libgcj-4.1.2-48.el5
安装jdk1.8
解压
tar -zxvf jdk-8u91-linux-x64.gz -C /usr/local/jdk/
配置环境变量
-
使用vim /etc/profile编辑profile文件
-
在/etc/profile底部加入如下内容
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jdk1.8.0_91
PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
CLASSPATH=$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
export PATH JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH
以上,环境变量配置完成。需要注意的是,PATH在配置的时候,一定要把JAVA_HOME/bin放在前面,不然使用java命令时,系统会找到以前的java,再不往下找了。这样java这个可执行文件运行的目录其实不在$JAVA_HOME/bin下,而在其它目录下,会造成很大的问题。
最后使用source /etc/profile让profile文件立即生效。
安装配置kafka
安装配置zookeeper
解压安装包
tar -zxvf zookeeper-3.4.8.tar.gz -C /usr/local/apps/
在conf目录下创建配置文件zoo.cfg
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/usr/local/tmp/zookeeper
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2181
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
#autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
#autopurge.purgeInterval=1
启动脚本 zkStart.sh
#!/bin/bash
nohup /usr/local/apps/zookeeper-3.4.8/bin/zkServer.sh start /usr/local/apps/zookeeper-3.4.8/conf/zoo.cfg > /usr/local/apps/bash/logs/zookeeper.log 2>&1
安装配置kafka
解压安装包
tar -zxvf kafka_2.11-0.9.0.1.tgz -C /usr/local/apps/
修改配置文件 config/server.properties
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
# The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM)
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
############################# Log Basics #############################
# A comma seperated list of directories under which to store log files
log.dirs=/usr/local/tmp/kafka-logs
# The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater
# parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across
# the brokers.
num.partitions=1
# The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown.
# This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array.
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
############################# Log Flush Policy #############################
# Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync
# the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk.
# There are a few important trade-offs here:
# 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication.
# 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush.
# 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to exceessive seeks.
# The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or
# every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis.
# The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk
#log.flush.interval.messages=10000
# The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush
#log.flush.interval.ms=1000
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can
# be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated.
# A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens
# from the end of the log.
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion
log.retention.hours=168
# A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log as long as the remaining
# segments don't drop below log.retention.bytes.
#log.retention.bytes=1073741824
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
log.segment.bytes=1073741824
# The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according
# to the retention policies
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
############################# Zookeeper #############################
# Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details).
# This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk
# server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002".
# You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the
# root directory for all kafka znodes.
zookeeper.connect=192.168.1.1:2181
# Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
启动脚本 kafkaStart.sh
#!/bin/bash
nohup /usr/local/apps/kafka_2.11-0.9.0.1/bin/kafka-server-start.sh /usr/local/apps/kafka_2.11-0.9.0.1/config/server.properties > /usr/local/apps/bash/logs/kafka.log 2>&1 &
安装配置logstash
解压安装包
tar -zxvf logstash-2.3.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/apps/
创建配置文件 conf/logstash-es.conf
#logstash configuration
input {
kafka {
zk_connect => "192.168.1.1:2181"
group_id => "logstash"
topic_id => "test"
reset_beginning => false
consumer_threads => 5
decorate_events => true
}
}
filter{
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.1.3:9200","192.168.1.4:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{type}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "%{type}"
workers => 1
flush_size => 20000
idle_flush_time => 10
template_overwrite => true
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
启动脚本 kafkaStart.sh
#!/bin/bash
nohup /usr/local/apps/logstash-2.3.1/bin/logstash agent -f /usr/local/apps/logstash-2.3.1/conf/logstash-es.conf > /usr/local/apps/bash/logs/logstash.log 2>&1 &
安装配置elasticsearch
解压安装包
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-2.3.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/apps/
修改配置文件 config/elasticsearch.yml
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
# path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
# path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
# bootstrap.mlockall: true
#
# Make sure that the `ES_HEAP_SIZE` environment variable is set to about half the memory
# available on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host:192.168.1.3
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, see the documentation at:
# <http://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-network.html>
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.1.3", "192.168.1.4"]
#
# Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of nodes / 2 + 1):
#
# discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, see the documentation at:
# <http://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-discovery.html>
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
# gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, see the documentation at:
# <http://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-gateway.html>
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Disable starting multiple nodes on a single system:
#
# node.max_local_storage_nodes: 1
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
# action.destructive_requires_name: true
启动脚本 esStart.sh
#!/bin/bash
nohup /usr/local/apps/elasticsearch-2.3.1/bin/elasticsearch > /usr/local/apps/bash/logs/es.log 2>&1 &
安装配置kibana
解压安装包
tar -zxvf kibana-4.5.0-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/apps/
修改配置文件 config/kibana.yml
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This controls which port to use.
# server.port: 5601
# The host to bind the server to.
# server.host: "0.0.0.0"
# If you are running kibana behind a proxy, and want to mount it at a path,
# specify that path here. The basePath can't end in a slash.
# server.basePath: ""
# The maximum payload size in bytes on incoming server requests.
# server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576
# The Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries.
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.1.3:9200"
# preserve_elasticsearch_host true will send the hostname specified in `elasticsearch`. If you set it to false,
# then the host you use to connect to *this* Kibana instance will be sent.
# elasticsearch.preserveHost: true
# Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations
# and dashboards. It will create a new index if it doesn't already exist.
# kibana.index: ".kibana"
# The default application to load.
# kibana.defaultAppId: "discover"
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic auth, these are the user credentials
# used by the Kibana server to perform maintenance on the kibana_index at startup. Your Kibana
# users will still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch (which is proxied through
# the Kibana server)
# elasticsearch.username: "user"
# elasticsearch.password: "pass"
# SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana Server to the browser (PEM formatted)
# server.ssl.cert: /path/to/your/server.crt
# server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key
# Optional setting to validate that your Elasticsearch backend uses the same key files (PEM formatted)
# elasticsearch.ssl.cert: /path/to/your/client.crt
# elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key
# If you need to provide a CA certificate for your Elasticsearch instance, put
# the path of the pem file here.
# elasticsearch.ssl.ca: /path/to/your/CA.pem
# Set to false to have a complete disregard for the validity of the SSL
# certificate.
# elasticsearch.ssl.verify: true
# Time in milliseconds to wait for elasticsearch to respond to pings, defaults to
# request_timeout setting
# elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500
# Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or elasticsearch.
# This must be > 0
# elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000
# Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards.
# Set to 0 to disable.
# elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 0
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch at Kibana startup before retrying
# elasticsearch.startupTimeout: 5000
# Set the path to where you would like the process id file to be created.
# pid.file: /var/run/kibana.pid
# If you would like to send the log output to a file you can set the path below.
# logging.dest: stdout
# Set this to true to suppress all logging output.
# logging.silent: false
# Set this to true to suppress all logging output except for error messages.
# logging.quiet: false
# Set this to true to log all events, including system usage information and all requests.
# logging.verbose: false
启动脚本 kibanaStart.sh
#!/bin/bash
nohup /usr/local/apps/kibana-4.5.0-linux-x64/bin/kibana > /usr/local/apps/bash/logs/kibana.log 2>&1 &