介绍
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004059167
在专业的网络世界中,经常使用到Virtual Routing and Forwarding(VRF),比如Cisco,Alcatel-Lucent, Juniper 等。对于L2 switch,自从上世纪90年代就开始使用VLAN,一个物理交换机上可以使用多个广播域,如今大多数交换机都支持4K vlan。
这个概念被引入到L3,如今很多网络设备支持VRF。这意味着,单个物理设备上可运行多个虚拟路由(L3 转发实例)。
在linux中,VRF被叫做“network namespace”。
每个network namespace拥有其对应的路由表(routing table)& 其对应的iptables,并且运行程序运行其中。 为什么有人使用它?比如一个运行在linux上的 Firewall,将firewall的所有服务端口分配给一个network namespace,这样,默认的network namespace 和 Firewall network namespace就运行着不同的路由表。像SSH这样的application运行在默认的network namespace,但是不在Firewall network namespace。
下面展示了其基本用法。
Basic network namespace commands
基本命令为“ip”,有些用户使用它来代替废弃的 ifconfig,route,netstat... 必须为root用户来使用它,这样才能更改network stack的配置。下面是ip命令和其他命令的映射:
ifconfig --> ip addr or just ip a ifconfig <interface> up/down --> ip link set dev <interface> up/down ifconfig <interface> <ip> netmask <netmask> --> ip addr add <ip>/<masklen> dev <interface> netstat -rn --> ip route or just ip r route add -net <net> netmask <netmask> gw <gateway> --> ip r add <net>/<netmasklen> via <gateway>
Check your Linux for namespace support
使用前,先检查系统是否支持。
Creating a network namespace
# add a new namespace ip netns add <network namespace name> #Example: ip netns add nstest
Listing all existing network namespaces in the system
# list all namespaces ip netns list #will show the namespace from above nstest
Deleting a network namespace
ip netns delete <network namespace name>
Executing a command in a network namespace
下面展示了使程序运行在network namespace中的“黑魔法”。
# execute a command in a namespace ip netns exec <network namespace name> <command> #Example using the namespace from above: ip netns exec nstest ip addr
展示了在此network namespace中的所有的ip interface
lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
一个脏技巧是在network namespace中运行shell:
ip netns exec <network namespace name> bash
现在,你已经“trapped”入namespace中了,exit退出。
Exploring the network namespace
当我们已经创建了network namespace,第一个task是bring up其中的lo interface。应该注意到的是,在创建了network namespace后,lo interface的状态是down。如果忽略了这个,可能会发生一些奇怪的事。
# set the link of lo in the namespace to up ip netns exec nstest ip link set dev lo up # list all interfaces and the state in the namespace ip netns exec nstest ip link
现在lo interface状态为up,现在,是时候将network namespace链接到外部空间。
Adding interfaces to a network namespace
将一个物理interface分配给network namespace是不可能的,而是使用 virtual interface来实现。所以,我们先创建一个virtual interface,同样使用 ip command:
ip link add veth-a type veth peer name veth-b
上述命令创建了两个virtual interface,分别为veth-a & veth-b,他们之间通过一个virtual cable链接。ip link命令显示了在默认namespace下这两个interface的信息。
ip link veth-b: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 link/ether 72:01:ad:c5:67:84 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff veth-a: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 link/ether 8e:8b:bd:b1:88:e5 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
下面我们将其中的一个interface添加入之前我们创建的namespace nstest:
ip link set veth-b netns nstest
现在veth-b不在默认的namespace下了,而出现在了nstest 中,使用如下命令验证:
# list all interfaces in the namespace nstest ip netns exec nstest ip link lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 veth-b: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 link/ether 72:01:ad:c5:67:84 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
现在,在network namespace nstest中,就拥有了两个interface。
Assign ip addresses to the veth interfaces
现在是时候为这个veth interface分配ip并且使他的状态为up。
# default namespace ip addr add 10.0.0.1/24 dev veth-a ip link set dev veth-a up # # namespace nstest ip netns exec nstest ip addr add 10.0.0.2/24 dev veth-b ip netns exec nstest ip link set dev veth-b up
可通过“ip link”查看interface状态是否为up,使用“ip addr”查看interface的ip 地址,使用“ip route”查看其路由。
现在可以在default namespace中,通过veth-a来ping通 位于 nstest中的veth-b。
ping 10.0.0.2 PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.054 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.034 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.039 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_req=4 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms
以及在nstest network namespace中,通过veth-b来ping通 veth-a:
ip netns exec nstest ping 10.0.0.1 PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.064 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.039 ms
Demo
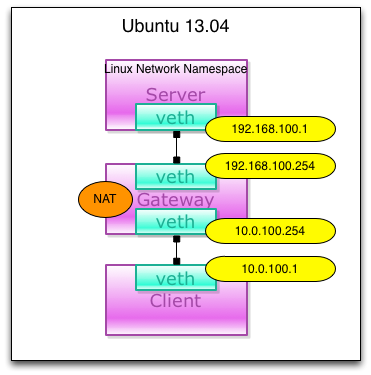
下面一起来实现一个demo,最终实现如下的case:
首先,先建立对应的namespace:
$ sudo ip netns add server
$ sudo ip netns add gateway
$ sudo ip netns add client
$ ip netns list
client
gateway
server
然后,启用gateway namespace中的ip forward功能,注意,操作全是在root权限下执行:
$ ip netns exec gateway sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
下面我们来创建两对veth,用来连接不同的namespace:
$ ip link add svr-veth type veth peer name svrgw-veth $ ip link add cli-veth type veth peer name cligw-veth $ ip link show | grep veth 3: svrgw-veth: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 4: svr-veth: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 5: cligw-veth: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000 6: cli-veth: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000
将veth对的两端加入对应的namespace中,这样在默认的default namespace中就看不到他们了:
$ ip link set svr-veth netns server $ ip link set svrgw-veth netns gateway $ ip link set cligw-veth netns gateway $ ip link set cli-veth netns client $ ip link show | grep veth
在指定的namespace上可以看到对应的interface:
$ ip netns exec server ip link show | grep veth 4: svr-veth: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT qlen 1000
为各个veth分配ip:
$ ip netns exec server ifconfig svr-veth 192.168.100.1 $ ip netns exec gateway ifconfig svrgw-veth 192.168.100.254 $ ip netns exec gateway ifconfig cligw-veth 10.0.100.254 $ ip netns exec client ifconfig cli-veth 10.0.100.1
在各个veth对中,通过ping来检查连通性:
$ ip netns exec gateway ping 192.168.100.1 -I 192.168.100.254 PING 192.168.100.1 (192.168.100.1) from 192.168.100.254 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.044 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms ^C --- 192.168.100.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1999ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.036/0.040/0.044/0.003 ms $ ip netns exec gateway ping 10.0.100.1 -I 10.0.100.254 PING 10.0.100.1 (10.0.100.1) from 10.0.100.254 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.100.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.107 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.100.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.037 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.100.1: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.037 ms ^C --- 10.0.100.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1998ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.037/0.060/0.107/0.033 ms
接下来设定路由,将各namespace中的默认路由指向对应的veth ip:
$ sudo ip netns exec client route add default gw 10.0.100.254 $ sudo ip netns exec client netstat -rn Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 0.0.0.0 10.0.100.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 cli-veth 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 U 0 0 0 cli-veth $ ip netns exec server route add default gw 192.168.100.254 $ ip netns exec server netstat -rn Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 svr-veth 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 svr-veth
最后我们尝试从client namespace 到 server namespace的网络连通性,通过ping命令来测试:
$ ip netns exec client ping 192.168.100.1 -I 10.0.100.1 PING 192.168.100.1 (192.168.100.1) from 10.0.100.1 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=63 time=0.106 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=63 time=0.076 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.100.1: icmp_req=3 ttl=63 time=0.050 ms ^C --- 192.168.100.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1999ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.050/0.077/0.106/0.024 ms
一个稍微复杂的网络环境
创建虚拟网络环境并且连接网线
ip netns add net0 ip netns add net1 ip netns add bridge ip link add type veth ip link set dev veth0 name net0-bridge netns net0 ip link set dev veth1 name bridge-net0 netns bridge ip link add type veth ip link set dev veth0 name net1-bridge netns net1 ip link set dev veth1 name bridge-net1 netns bridge |
在bridge中创建并且设置br设备
ip netns exec bridge brctl addbr br ip netns exec bridge ip link set dev br up ip netns exec bridge ip link set dev bridge-net0 up ip netns exec bridge ip link set dev bridge-net1 up ip netns exec bridge brctl addif br bridge-net0 ip netns exec bridge brctl addif br bridge-net1 |
然后配置两个虚拟环境的网卡
ip netns exec net0 ip link set dev net0-bridge up ip netns exec net0 ip address add 10.0.1.1/24 dev net0-bridge |
ip netns exec net1 ip link set dev net1-bridge up ip netns exec net1 ip address add 10.0.1.2/24 dev net1-bridge |
测试
$ ip netns exec net0 ping -c 3 10.0.1.2 PING 10.0.1.2 (10.0.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.121 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.072 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.069 ms --- 10.0.1.2 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1999ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.069/0.087/0.121/0.025 ms
|