一. 方法(函数)
1:函数的概念?函数的格式?格式的解释说明
函数也叫做方法,是用来完成特定功能的代码块
修饰符 + 返回值(没有返回值的话是void) + 方法名 + 参数列表
2:函数的调用
A:明确返回值类型的函数调用
返回值类型为基本数据类型,返回值是什么类型,返回值类型就是什么类型 用return返回
B:void类型的函数调用
没有返回值,当需要在控制台输出打印时,为void型
3:函数的练习:
A:求两个数据之和
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070901 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一个数a:"); int a = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入一个数b:"); int b = sc.nextInt(); int sum = getSum(a,b); System.out.println("你输入的两个数的和为:" + sum); } /* 1.返回值类型 int 2.参数类型 int a,int b */ public static int getSum(int a,int b){ return a + b; } }
B:判断两个数据是否相等
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070902 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一个数a:"); int a = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入一个数b:"); int b = sc.nextInt(); isEqual(a,b); } /* 1.返回值类型 void (需要在控制台输出打印) 2.参数类型 int a,int b */ public static void isEqual(int a,int b){ if (a == b) { System.out.println("你输入的这两个数相等"); }else{ System.out.println("你输入的这两个数不等"); } } }
C:获取两个数中较大的值
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070903 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一个数a:"); int a = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入一个数b:"); int b = sc.nextInt(); int max = getMax(a,b); System.out.println("你输入的这两个数中较大的为:" + max); } /* 1.返回值类型 int 2.参数类型 int a,int b */ public static int getMax(int a,int b){ return (a > b)?a:b; } }
D:打印m行n列的星形矩形
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070904 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入行数a:"); int a = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入列数b:"); int b = sc.nextInt(); getStar(a,b); } /* 1.返回值类型 void 2.参数类型 int a,int b */ public static void getStar(int a,int b){ for (int i = 0;i < a ;i++ ) { for (int j = 0;j < b; j++) { System.out.print("* "); } System.out.println(); } } }
E:打印nn乘法表
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070905{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入行数n:"); int n = sc.nextInt(); getMultiply(n); } /* 1.返回值类型 void 2.参数类型 int a,int b */ public static void getMultiply(int a){ for (int i = 1;i <=a ;i++ ) { for (int j = 1;j <=i; j++) { System.out.print(j + "*" + i + "=" + j*i + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }
4:什么是函数重载?以及函数重载的练习?把讲过的案例练习一次即可
在同一个类中的及格不同方法,它们的方法名相同,但是参数不同(参数类型,参数个数)
===============================================================
===============================================================
二. 内存图
画图操作:
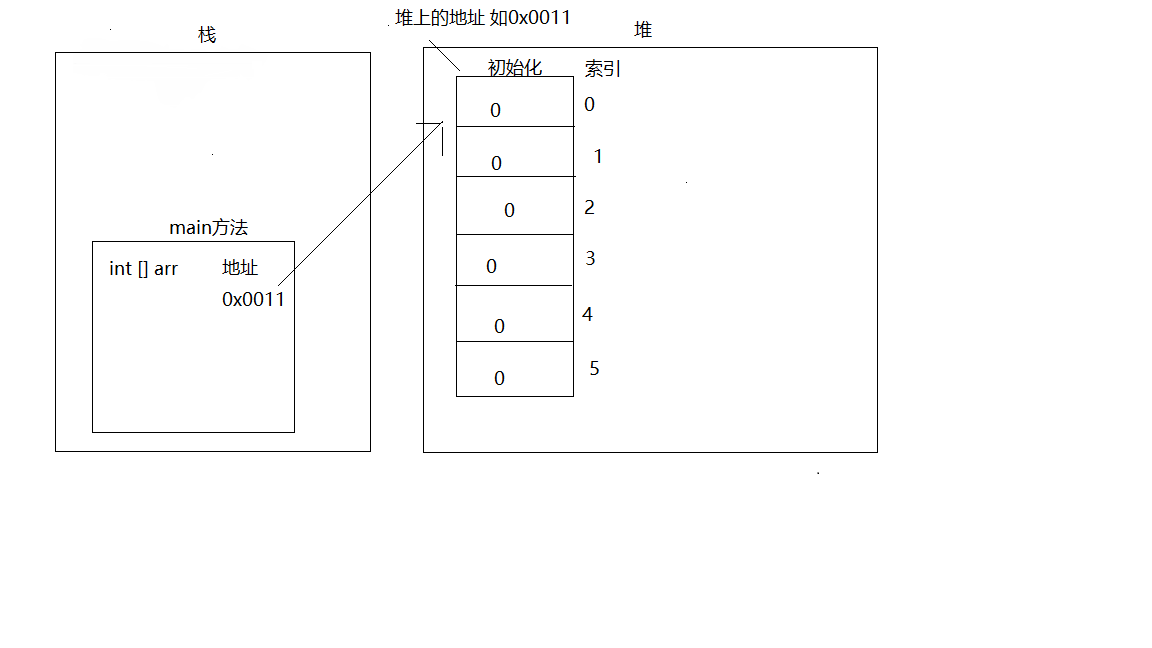
1.一个数组的内存图
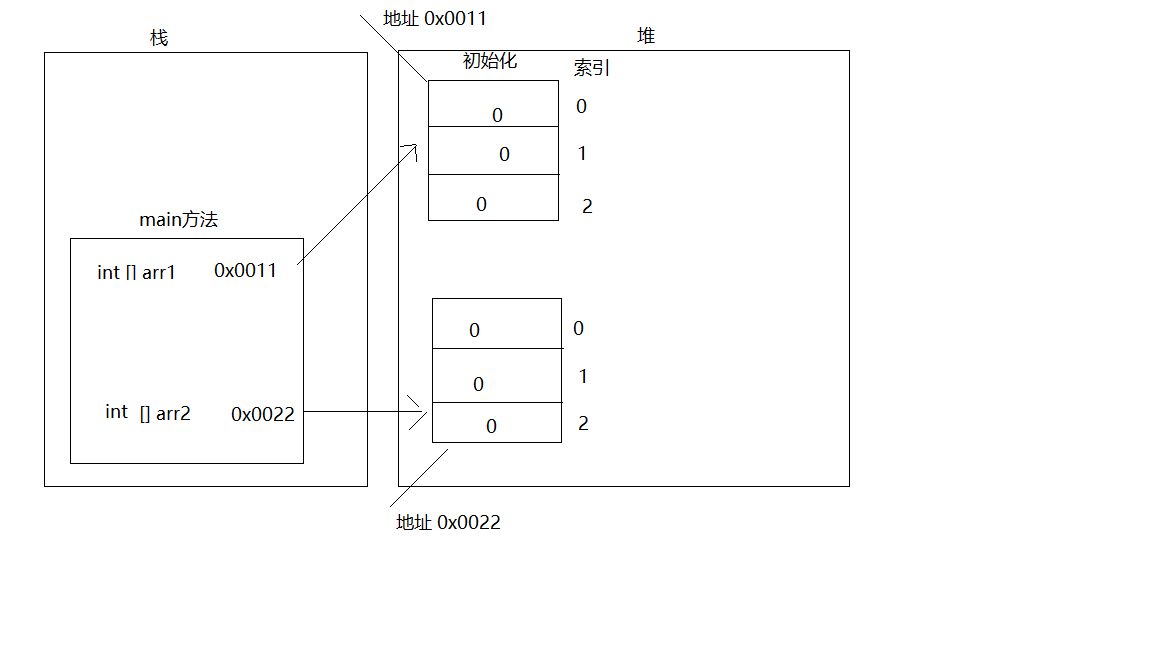
2.两个数组的内存图
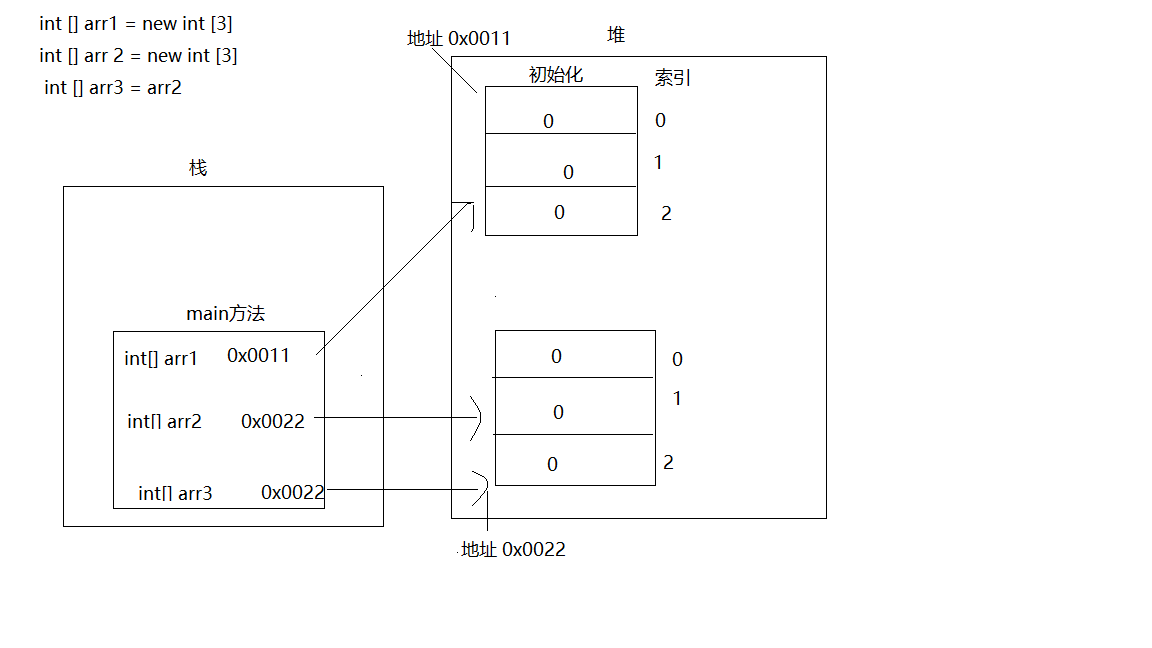
3.三个引用两个数组的内存图
三.数组
1:数组的概念?有什么特点?
存储同一种类型数据多个元素的集合,可以看作是一个容器
存储的是同一类型
2:一维数组的定义格式?
数据类型(int) + [] +数组名 = new 数据类型[]
3:数组操作的两个小问题
一是数组索引越界异常,原因是索引超过数组个数
一是空指针异常 数组已经不再指向堆了,为null
4:数组常见操作:
数组遍历(依次输出数组中的每一个元素)
运用for循环
for(int i = 0;i < arr.lenth;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
数组获取最值(获取数组中的最大值最小值)
int max = arr[0];
for(int i = 1;i < arr.length;i++){
if(max < arr[i]){
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
数组元素逆序 (就是把元素对调)
for(int i = 0;i <arr.length;i++){
int temp;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i]= arr[arr.length-i-1];
arr[arr.length-i-1]=arr[i];
}
数组查表法(根据键盘录入索引,查找对应星期)
import java.util.Scanner; class Practise070906{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一个数(1~7)"); int n = sc.nextInt(); getIndex(n); System.out.println("你要查找的是星期" + getIndex(n)); } /* 1.返回值类型 char 2.参数类型 int a */ public static char getIndex(int a){ char[] arr = new char[]{' ','一','二','三','四','五','六','日'}; return arr[a]; } }
数组元素查找(查找指定元素第一次在数组中出现的索引)
public static int getIndex(int arr,int value){ for(int i = 0;i <arr.length;i++){ if(arr[i] == value){ return i; } } return -1; }
5:二维数组定义格式?
数据类型[][] arr = new 数据类型[] []
看懂针对每种格式的内存图解?
6:案例
A:二维数组遍历
for(int i = 0;i <arr.length ;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < arr[i].length;j++){ System.out.print(arr[i][j]); } System.out.println(); }
B:公司年销售额求和
某公司按照季度和月份统计的数据如下:单位(万元)
第一季度:22,66,44
第二季度:77,33,88
第三季度:25,45,65
第四季度:11,66,99
int[][] arr = new int[][]{{22,66,44},{77,33,88},{25,45,65},{11,66,99}}; int sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < arr[i].length;j++){ sum +=arr[i][j]; } } System.out.println(sum);
7:参数传递问题
基本数据类型参数传递,不改变原参数值,因为参数传递一直在栈中进行,调用结束后会弹出,因此不变
引用数据类型参数传递会改变原值,因为方法调用后尽管弹栈,但堆内存中还在,还通过地址继续引用