Spring AOP面向切面编程,可以用来配置事务、做日志、权限验证、在用户请求时做一些处理等等。用@Aspect做一个切面,就可以直接实现。
1、包结构
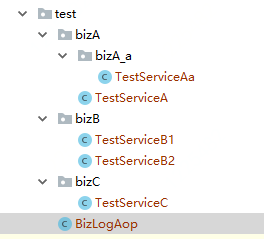
2、切面类
execution解释:
1)execution(), 表达式主体
2)第一个*表示返回类型,*表示所有类型
3)包名,后面两个..表示当前包和当前包所有子包
4)第二个*表示所有类名,*表示所有类
5)*(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。

package com.test; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @author zyydd * @date 2019/12/25 19:53 */ @Aspect @Service public class BizLogAop { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BizLogAop.class); @Around("execution(* com.test.bizA..*.*(..)) || " + "execution(* com.test.bizB.TestServiceB1.*(..)) || " + "execution(* com.test.bizC.TestServiceC.test1(..))") public Object aroundBiz(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { String methodFullName = ""; try { methodFullName = String.format("%s.%s", pjp.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getName(), pjp.getSignature().getName()); logger.info("methodFullName={} 开始调用,参数={}", methodFullName, JSON.toJSON(pjp.getArgs())); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error("BizLogAop类异常", ex); } //调用实际的方法,如果没有异常直接返回结果 Object result = pjp.proceed(pjp.getArgs()); try { logger.info("methodFullName={} 调用完成,返回值={}", methodFullName, JSON.toJSON(result)); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error("BizLogAop类异常", ex); } return result; } }
3、TestService类举例
很简单,通过注解,注册一个service,然后返回一个字符串。

package com.test.bizA; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @author zyydd * @date 2019/12/26 9:35 */ @Service public class TestServiceA { public String test1(){ return "TestServiceA1"; } public String test2(){ return "TestServiceA2"; } }
4、单元测试类

package com.test.bizA.bizA_a; import com.**.web.Application; import com.test.bizA.TestServiceA; import com.test.bizB.TestServiceB1; import com.test.bizB.TestServiceB2; import com.test.bizC.TestServiceC; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; /** * @author laizy * @date 2019/12/26 9:56 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class) @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) public class ServiceTest { public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceTest.class); @Autowired private TestServiceA testServiceA; @Autowired private TestServiceAa testServiceAa; @Autowired private TestServiceB1 testServiceB1; @Autowired private TestServiceB2 testServiceB2; @Autowired private TestServiceC testServiceC; @Test public void testAll() { logger.info(testServiceA.test1()); logger.info(testServiceA.test2()); logger.info(testServiceAa.test()); } @Test public void testOneClass() { logger.info(testServiceB1.test()); logger.info(testServiceB2.test()); } @Test public void testOneMethod() { logger.info(testServiceC.test1()); logger.info(testServiceC.test2()); } }
第一个测试对应execution中第一个表达式:execution(* com.test.bizA..*.*(..)) 即bizA下所有包,所有子包,所有方法都在作用范围内,执行结果:

第二个测试对应execution中第二个表达式:execution(* com.test.bizB.TestServiceB1.*(..)) 即bizB下TestServiceB1类的所有方法都在作用范围内,执行结果:

第三个测试对应execution中第三个表达式:execution(* com.test.bizC.TestServiceC.test1(..)) 即bizC下TestServiceC类的test1方法在作用范围内,执行结果:

