前言
golang作为常驻进程, 请求第三方服务或者资源(http, mysql, redis等)完毕后, 需要手动关闭连接, 否则连接会一直存在;
连接池是用来管理连接的, 请求之前从连接池里获取连接, 请求完毕后再将连接归还给连接池;
连接池做了连接的建立, 复用以及回收工作;
本文件仅介绍http请求的连接池http.Transport;
net/http 的工作流程
http请求示例代码
func main() {
url := "http://localhost:8080/login?name=zhouwei1&password=123456"
// 1.创建client, 这里使用的默认值
client := http.DefaultClient
// 2.创建请求
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, url, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 3.发送请求
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 4.关闭
if resp != nil && resp.Body != nil {
defer resp.Body.Close()
}
data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("请求成功, data: %s
", data)
}
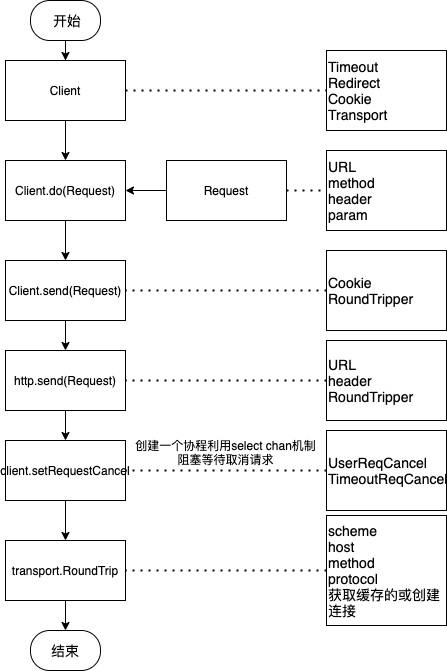
http请求流程
- 创建http.Client对象
client - 创建http.Request对象
req - 发送请求
client.do(req) - 关闭
resp.Body.Close()
即使直接调用client.Get()或client.Post(), 内部同样创建了request, 且最终总是通过client.Do()方法调用私有的client.do()方法, 执行请求;
http请求核心类
- http.Client
- http.Request
- http.Transport
http.Client
该类主要功能:
- Cookie
- Timeout
- Redirect
- Transport
type Client struct {
Transport RoundTripper
CheckRedirect func(req *Request, via []*Request) error
Jar CookieJar
Timeout time.Duration
}
http.Request
type Request struct {
Method string
URL *url.URL
Proto string // "HTTP/1.0"
ProtoMajor int // 1
ProtoMinor int // 0
Header Header
Body io.ReadCloser
GetBody func() (io.ReadCloser, error)
ContentLength int64
TransferEncoding []string
// true: 不重用此tcp连接
Close bool
Host string
Form url.Values
PostForm url.Values
MultipartForm *multipart.Form
Trailer Header
RemoteAddr string
RequestURI string
TLS *tls.ConnectionState
Cancel <-chan struct{}
Response *Response
ctx context.Context
}
http.Transport
- Transport用来缓存连接, 以供将来重用, 而不是根据需要创建
- Transport是并发安全的
- Transport仅是用来发送HTTP或HTTPS的低级功能, 像cookie和redirect等高级功能是http.Client实现的
type Transport struct {
// 操作空闲连接池(idleConn)的锁
idleMu sync.Mutex
// true: 关闭所有空闲连接; false: 不关闭
wantIdle bool
// 空闲连接池(最近使用完的连接)
idleConn map[connectMethodKey][]*persistConn
// 等待空闲连接的队列, 基于chan实现
idleConnCh map[connectMethodKey]chan *persistConn
// 双向队列
idleLRU connLRU
// 请求锁
reqMu sync.Mutex
// 请求取消器(如: 超时取消)
reqCanceler map[*Request]func(error)
// altProto的锁
altMu sync.Mutex
// 存储的map[string]RoundTripper, key为URI的scheme(如http, https)
altProto atomic.Value
// 连接数量锁
connCountMu sync.Mutex
// 每台主机连接的数量
connPerHostCount map[connectMethodKey]int
// 每台主机可用的连接
connPerHostAvailable map[connectMethodKey]chan struct{}
// Proxy指定一个函数来返回给定Request的代理
// 代理类型由URL scheme确定。支持http, https等。 默认为http
// 如果Proxy为空或返回空的url,则不使用任何代理。
Proxy func(*Request) (*url.URL, error)
// DialContext指定用于创建未加密的TCP连接的拨号功能。
// 如果DialContext为nil(并且下面不建议使用的Dial也为nil),则传输使用程序包net进行拨号。
// DialContext与RoundTrip的调用同时运行。
// 当较早的连接在以后的DialContext完成之前处于空闲状态时,
// 发起拨号的RoundTrip调用可能会使用先前拨打的连接结束。
DialContext func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// Dial指定用于创建未加密的TCP连接的拨号功能。
// 拨号与RoundTrip的呼叫同时运行。
// 当较早的连接在之后的拨号完成之前变为空闲时,发起拨号的RoundTrip呼叫可能会使用先前拨打的连接结束。
// 不推荐使用:改用DialContext,它使传输器在不再需要拨号时立即取消它们。
// 如果两者都设置,则DialContext优先。
Dial func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// DialTLS指定用于为非代理HTTPS请求创建TLS连接的可选拨号功能。
// 如果DialTLS为nil,则使用Dial和TLSClientConfig。
// 如果设置了DialTLS,则Dial Hook不用于HTTPS请求,
// 并且TLSClientConfig和TLSHandshakeTimeout将被忽略。
// 假定返回的net.Conn已通过TLS握手。
DialTLS func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// TLSClientConfig指定要与tls.Client一起使用的TLS配置。
// 如果为nil,则使用默认配置。
// 如果为非nil,则默认情况下可能不会启用HTTP / 2支持。
TLSClientConfig *tls.Config
// TLSHandshakeTimeout指定等待TLS握手的最大时间。 零表示没有超时。
TLSHandshakeTimeout time.Duration
// true: 将禁用HTTP保持活动状态,并且仅将与服务器的连接用于单个HTTP请求。
// 这与类似命名的TCP保持活动无关。
DisableKeepAlives bool
// true: 当请求不包含现有的Accept-Encoding值时,
// 阻止传输使用“ Accept-Encoding:gzip”请求标头请求压缩。
// 如果传输本身请求gzip并获得gzip压缩的响应,则会在Response.Body中对其进行透明解码。
// 但是,如果用户明确请求gzip,则不会自动将其解压缩。
DisableCompression bool
// MaxIdleConns控制所有主机之间的最大空闲(保持活动)连接数。 零表示无限制。
MaxIdleConns int
// MaxIdleConnsPerHost控制最大空闲(保持活动)连接以保留每个主机。
// 如果为零,则使用DefaultMaxIdleConnsPerHost=2。
MaxIdleConnsPerHost int
// MaxConnsPerHost可以选择限制每个主机的连接总数,包括处于拨号,活动和空闲状态的连接。
// 超出限制时,拨号将阻塞。
// 零表示无限制。
// 对于HTTP / 2,当前仅控制一次创建的新连接数,而不是总数。
// 实际上,使用HTTP / 2的主机只有大约一个空闲连接。
MaxConnsPerHost int
// IdleConnTimeout是空闲(保持活动状态)连接在关闭自身之前将保持空闲状态的最长时间。
// 零表示无限制。
IdleConnTimeout time.Duration
//(如果非零)指定在完全写入请求(包括其body(如果有))之后等待服务器的响应头的时间。
// 该时间不包括读取响应正文的时间。
ResponseHeaderTimeout time.Duration
//(如果非零)指定如果请求具有“期望:100-连续”标头,
// 则在完全写入请求标头之后等待服务器的第一个响应标头的时间。
// 零表示没有超时,并导致正文立即发送,而无需等待服务器批准。
// 此时间不包括发送请求标头的时间。
ExpectContinueTimeout time.Duration
// TLSNextProto指定在TLS NPN / ALPN协议协商之后,传输方式如何切换到备用协议(例如HTTP / 2)。
// 如果传输使用非空协议名称拨打TLS连接,并且TLSNextProto包含该键的映射条目(例如“ h2”),
// 则将以请求的权限(例如“ example.com”或“ example .com:1234“)和TLS连接。
// 该函数必须返回RoundTripper,然后再处理请求。
// 如果TLSNextProto不为nil,则不会自动启用HTTP / 2支持。
TLSNextProto map[string]func(authority string, c *tls.Conn) RoundTripper
// 可以选择指定在CONNECT请求期间发送到代理的header。
ProxyConnectHeader Header
// 指定对服务器的响应标头中允许的响应字节数的限制。
// 零表示使用默认限制。
MaxResponseHeaderBytes int64
// nextProtoOnce防止TLSNextProto和h2transport的初始化(通过OnceSetNextProtoDefaults)
nextProtoOnce sync.Once
// 如果http2已连接,则为非null
h2transport h2Transport
}
源码分析
1. Client.do
该方法主要实现了:
- 参数检查
- 默认值设置
- 多跳请求
- 计算超时时间点deadline
- 调用c.send(req, deadline)
func (c *Client) do(req *Request) (retres *Response, reterr error) {
...
reqs = append(reqs, req)
var err error
var didTimeout func() bool
if resp, didTimeout, err = c.send(req, deadline); err != nil {
// c.send() always closes req.Body
reqBodyClosed = true
if !deadline.IsZero() && didTimeout() {
err = &httpError{
err: err.Error() + " (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)",
timeout: true,
}
}
return nil, uerr(err)
}
var shouldRedirect bool
redirectMethod, shouldRedirect, includeBody = redirectBehavior(req.Method, resp, reqs[0])
if !shouldRedirect {
return resp, nil
}
req.closeBody()
}
2. Client.send
该方法主要实现了:
- Cookie的装载
- Transport对象的获取
- 调用send(req, c.transport(), deadline)
func (c *Client) send(req *Request, deadline time.Time) (resp *Response, didTimeout func() bool, err error) {
if c.Jar != nil {
for _, cookie := range c.Jar.Cookies(req.URL) {
req.AddCookie(cookie)
}
}
resp, didTimeout, err = send(req, c.transport(), deadline)
if err != nil {
return nil, didTimeout, err
}
if c.Jar != nil {
if rc := resp.Cookies(); len(rc) > 0 {
c.Jar.SetCookies(req.URL, rc)
}
}
return resp, nil, nil
}
Transport的默认值
var DefaultTransport RoundTripper = &Transport{
Proxy: ProxyFromEnvironment,
DialContext: (&net.Dialer{
Timeout: 30 * time.Second,
KeepAlive: 30 * time.Second,
DualStack: true,
}).DialContext,
MaxIdleConns: 100,
IdleConnTimeout: 90 * time.Second,
TLSHandshakeTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
ExpectContinueTimeout: 1 * time.Second,
}
3. http.send
该方法主要实现了:
- 参数校验: URL, header, RoundTripper
- 超时取消: setRequestCancel(req, rt, deadline)
- 请求事务: rt.RoundTrip(req)
func send(ireq *Request, rt RoundTripper, deadline time.Time) (resp *Response, didTimeout func() bool, err error) {
...
// 请求是否超时的监控
stopTimer, didTimeout := setRequestCancel(req, rt, deadline)
// 真正发送请求
resp, err = rt.RoundTrip(req)
if err != nil {
stopTimer()
if resp != nil {
log.Printf("RoundTripper returned a response & error; ignoring response")
}
if tlsErr, ok := err.(tls.RecordHeaderError); ok {
// If we get a bad TLS record header, check to see if the
// response looks like HTTP and give a more helpful error.
// See golang.org/issue/11111.
if string(tlsErr.RecordHeader[:]) == "HTTP/" {
err = errors.New("http: server gave HTTP response to HTTPS client")
}
}
return nil, didTimeout, err
}
if !deadline.IsZero() {
resp.Body = &cancelTimerBody{
stop: stopTimer,
rc: resp.Body,
reqDidTimeout: didTimeout,
}
}
return resp, nil, nil
}
4. client.setRequestCancel
该方法主要实现了:
创建一个协程利用select chan机制阻塞等待取消请求
func setRequestCancel(req *Request, rt RoundTripper, deadline time.Time) (stopTimer func(), didTimeout func() bool) {
...
doCancel := func() {
// The newer way (the second way in the func comment):
close(cancel)
type canceler interface {
CancelRequest(*Request)
}
switch v := rt.(type) {
case *Transport, *http2Transport:
// Do nothing. The net/http package's transports
// support the new Request.Cancel channel
case canceler:
v.CancelRequest(req)
}
}
stopTimerCh := make(chan struct{})
var once sync.Once
stopTimer = func() { once.Do(func() { close(stopTimerCh) }) }
timer := time.NewTimer(time.Until(deadline))
var timedOut atomicBool
go func() {
select {
case <-initialReqCancel: // 用户传来的取消请求
doCancel()
timer.Stop()
case <-timer.C: // 超时取消请求
timedOut.setTrue()
doCancel()
case <-stopTimerCh:
timer.Stop()
}
}()
return stopTimer, timedOut.isSet
}
5. Transport.RoundTrip
该方法主要实现了
- 参数校验: scheme, host, method, protocol...
- 获取缓存的或新建的连接
func (t *Transport) roundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error) {
...
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
req.closeBody()
return nil, ctx.Err()
default:
}
// treq gets modified by roundTrip, so we need to recreate for each retry.
treq := &transportRequest{Request: req, trace: trace}
cm, err := t.connectMethodForRequest(treq)
if err != nil {
req.closeBody()
return nil, err
}
// 获取缓存的或新建的连接
pconn, err := t.getConn(treq, cm)
if err != nil {
t.setReqCanceler(req, nil)
req.closeBody()
return nil, err
}
var resp *Response
if pconn.alt != nil {
// HTTP/2 path.
t.decHostConnCount(cm.key()) // don't count cached http2 conns toward conns per host
t.setReqCanceler(req, nil) // not cancelable with CancelRequest
resp, err = pconn.alt.RoundTrip(req)
} else {
resp, err = pconn.roundTrip(treq)
}
if err == nil {
return resp, nil
}
if !pconn.shouldRetryRequest(req, err) {
// Issue 16465: return underlying net.Conn.Read error from peek,
// as we've historically done.
if e, ok := err.(transportReadFromServerError); ok {
err = e.err
}
return nil, err
}
testHookRoundTripRetried()
// Rewind the body if we're able to.
if req.GetBody != nil {
newReq := *req
var err error
newReq.Body, err = req.GetBody()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req = &newReq
}
}
}
6. Transport.getConn
- 首先从连接池中获取连接
t.getIdleConn(cm), 获取成功即返回 - 拨号创建新连接
- 如果达到了最大数量则阻塞, 等待空闲
func (t *Transport) getConn(treq *transportRequest, cm connectMethod) (*persistConn, error) {
req := treq.Request
trace := treq.trace
ctx := req.Context()
if trace != nil && trace.GetConn != nil {
trace.GetConn(cm.addr())
}
// 从连接池中取空闲的连接
if pc, idleSince := t.getIdleConn(cm); pc != nil {
if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil {
trace.GotConn(pc.gotIdleConnTrace(idleSince))
}
// set request canceler to some non-nil function so we
// can detect whether it was cleared between now and when
// we enter roundTrip
t.setReqCanceler(req, func(error) {})
return pc, nil
}
// 连接池中没有空闲的连接, 创建新连接
// 拨号
type dialRes struct {
pc *persistConn
err error
}
dialc := make(chan dialRes)
cmKey := cm.key()
// Copy these hooks so we don't race on the postPendingDial in
// the goroutine we launch. Issue 11136.
testHookPrePendingDial := testHookPrePendingDial
testHookPostPendingDial := testHookPostPendingDial
handlePendingDial := func() {
testHookPrePendingDial()
go func() {
if v := <-dialc; v.err == nil {
t.putOrCloseIdleConn(v.pc)
} else {
t.decHostConnCount(cmKey)
}
testHookPostPendingDial()
}()
}
cancelc := make(chan error, 1)
t.setReqCanceler(req, func(err error) { cancelc <- err })
// 如果没有空闲的连接或已达到最大数量会阻塞
if t.MaxConnsPerHost > 0 {
select {
case <-t.incHostConnCount(cmKey):
// count below conn per host limit; proceed
case pc := <-t.getIdleConnCh(cm):
if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil {
trace.GotConn(httptrace.GotConnInfo{Conn: pc.conn, Reused: pc.isReused()})
}
return pc, nil
case <-req.Cancel:
return nil, errRequestCanceledConn
case <-req.Context().Done():
return nil, req.Context().Err()
case err := <-cancelc:
if err == errRequestCanceled {
err = errRequestCanceledConn
}
return nil, err
}
}
go func() {
// 拨号建立连接
pc, err := t.dialConn(ctx, cm)
dialc <- dialRes{pc, err}
}()
idleConnCh := t.getIdleConnCh(cm)
select {
case v := <-dialc: // 拨号成功
// Our dial finished.
if v.pc != nil {
if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil && v.pc.alt == nil {
trace.GotConn(httptrace.GotConnInfo{Conn: v.pc.conn})
}
return v.pc, nil
}
// Our dial failed. See why to return a nicer error
// value.
t.decHostConnCount(cmKey)
select {
case <-req.Cancel:
// It was an error due to cancelation, so prioritize that
// error value. (Issue 16049)
return nil, errRequestCanceledConn
case <-req.Context().Done():
return nil, req.Context().Err()
case err := <-cancelc:
if err == errRequestCanceled {
err = errRequestCanceledConn
}
return nil, err
default:
// It wasn't an error due to cancelation, so
// return the original error message:
return nil, v.err
}
case pc := <-idleConnCh:
// Another request finished first and its net.Conn
// became available before our dial. Or somebody
// else's dial that they didn't use.
// But our dial is still going, so give it away
// when it finishes:
handlePendingDial()
if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil {
trace.GotConn(httptrace.GotConnInfo{Conn: pc.conn, Reused: pc.isReused()})
}
return pc, nil
case <-req.Cancel:
handlePendingDial()
return nil, errRequestCanceledConn
case <-req.Context().Done():
handlePendingDial()
return nil, req.Context().Err()
case err := <-cancelc:
handlePendingDial()
if err == errRequestCanceled {
err = errRequestCanceledConn
}
return nil, err
}
}
7. roundTrip
func (pc *persistConn) roundTrip(req *transportRequest) (resp *Response, err error) {
testHookEnterRoundTrip()
if !pc.t.replaceReqCanceler(req.Request, pc.cancelRequest) {
pc.t.putOrCloseIdleConn(pc)
return nil, errRequestCanceled
}
pc.mu.Lock()
pc.numExpectedResponses++
headerFn := pc.mutateHeaderFunc
pc.mu.Unlock()
if headerFn != nil {
headerFn(req.extraHeaders())
}
// Ask for a compressed version if the caller didn't set their
// own value for Accept-Encoding. We only attempt to
// uncompress the gzip stream if we were the layer that
// requested it.
requestedGzip := false
if !pc.t.DisableCompression &&
req.Header.Get("Accept-Encoding") == "" &&
req.Header.Get("Range") == "" &&
req.Method != "HEAD" {
// Request gzip only, not deflate. Deflate is ambiguous and
// not as universally supported anyway.
// See: https://zlib.net/zlib_faq.html#faq39
//
// Note that we don't request this for HEAD requests,
// due to a bug in nginx:
// https://trac.nginx.org/nginx/ticket/358
// https://golang.org/issue/5522
//
// We don't request gzip if the request is for a range, since
// auto-decoding a portion of a gzipped document will just fail
// anyway. See https://golang.org/issue/8923
requestedGzip = true
req.extraHeaders().Set("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
}
var continueCh chan struct{}
if req.ProtoAtLeast(1, 1) && req.Body != nil && req.expectsContinue() {
continueCh = make(chan struct{}, 1)
}
if pc.t.DisableKeepAlives && !req.wantsClose() {
req.extraHeaders().Set("Connection", "close")
}
gone := make(chan struct{})
defer close(gone)
defer func() {
if err != nil {
pc.t.setReqCanceler(req.Request, nil)
}
}()
const debugRoundTrip = false
// Write the request concurrently with waiting for a response,
// in case the server decides to reply before reading our full
// request body.
startBytesWritten := pc.nwrite
writeErrCh := make(chan error, 1)
pc.writech <- writeRequest{req, writeErrCh, continueCh}
resc := make(chan responseAndError)
pc.reqch <- requestAndChan{
req: req.Request,
ch: resc,
addedGzip: requestedGzip,
continueCh: continueCh,
callerGone: gone,
}
var respHeaderTimer <-chan time.Time
cancelChan := req.Request.Cancel
ctxDoneChan := req.Context().Done()
for {
testHookWaitResLoop()
select {
case err := <-writeErrCh:
if debugRoundTrip {
req.logf("writeErrCh resv: %T/%#v", err, err)
}
if err != nil {
pc.close(fmt.Errorf("write error: %v", err))
return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, err)
}
if d := pc.t.ResponseHeaderTimeout; d > 0 {
if debugRoundTrip {
req.logf("starting timer for %v", d)
}
timer := time.NewTimer(d)
defer timer.Stop() // prevent leaks
respHeaderTimer = timer.C
}
case <-pc.closech:
if debugRoundTrip {
req.logf("closech recv: %T %#v", pc.closed, pc.closed)
}
return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, pc.closed)
case <-respHeaderTimer:
if debugRoundTrip {
req.logf("timeout waiting for response headers.")
}
pc.close(errTimeout)
return nil, errTimeout
case re := <-resc:
if (re.res == nil) == (re.err == nil) {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("internal error: exactly one of res or err should be set; nil=%v", re.res == nil))
}
if debugRoundTrip {
req.logf("resc recv: %p, %T/%#v", re.res, re.err, re.err)
}
if re.err != nil {
return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, re.err)
}
return re.res, nil
case <-cancelChan:
pc.t.CancelRequest(req.Request)
cancelChan = nil
case <-ctxDoneChan:
pc.t.cancelRequest(req.Request, req.Context().Err())
cancelChan = nil
ctxDoneChan = nil
}
}
}