原题采用Kmeans方法对西瓜数据集进行聚类。我花了一些时间居然没找到西瓜数据集4.0在哪里,于是直接采用sklearn给的例子来分析一遍,更能说明Kmeans的效果。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier file1 = open('c:quantwatermelon.csv','r') data = [line.strip(' ').split(',') for line in file1] data = np.array(data) #X = [[float(raw[-7]),float(raw[-6]),float(raw[-5]),float(raw[-4]),float(raw[-3]), float(raw[-2])] for raw in data[1:,1:-1]] X = [[float(raw[-3]), float(raw[-2])] for raw in data[1:]] y = [1 if raw[-1]=='1' else 0 for raw in data[1:]] X = np.array(X) y = np.array(y) print(__doc__) from time import time import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn.datasets import load_digits from sklearn.decomposition import PCA from sklearn.preprocessing import scale np.random.seed(42) digits = load_digits() data = scale(digits.data) n_samples, n_features = data.shape n_digits = len(np.unique(digits.target)) labels = digits.target sample_size = 300 print("n_digits: %d, n_samples %d, n_features %d" % (n_digits, n_samples, n_features)) #一共十个不同的类 print(79 * '_') print('% 9s' % 'init' ' time inertia homo compl v-meas ARI AMI silhouette') def bench_k_means(estimator, name, data): t0 = time() estimator.fit(data) print('% 9s %.2fs %i %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f' % (name, (time() - t0), estimator.inertia_, metrics.homogeneity_score(labels, estimator.labels_), metrics.completeness_score(labels, estimator.labels_), metrics.v_measure_score(labels, estimator.labels_), metrics.adjusted_rand_score(labels, estimator.labels_), metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score(labels, estimator.labels_), metrics.silhouette_score(data, estimator.labels_, metric='euclidean', sample_size=sample_size)))
#Homogeneity 和 completeness 表示簇的均一性和完整性。V值是他们的调和平均,值越大,说明效果越好。
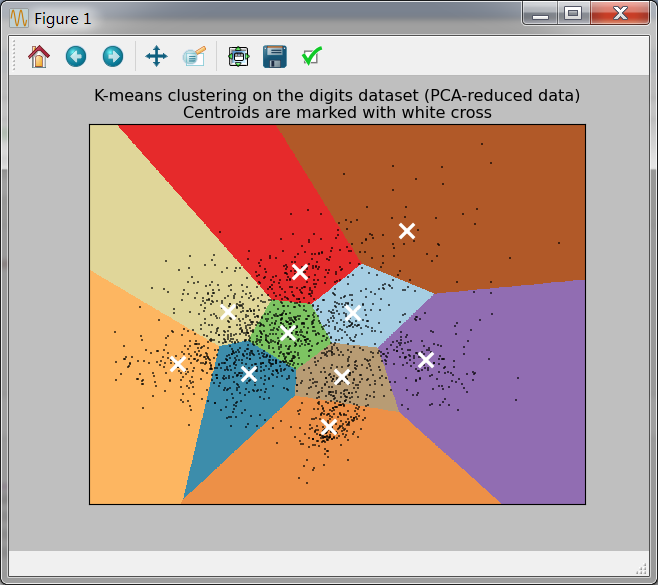
bench_k_means(KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10), name="k-means++", data=data) bench_k_means(KMeans(init='random', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10), name="random", data=data) # in this case the seeding of the centers is deterministic, hence we run the # kmeans algorithm only once with n_init=1 pca = PCA(n_components=n_digits).fit(data) bench_k_means(KMeans(init=pca.components_, n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=1), name="PCA-based", data=data) print(79 * '_') ############################################################################### # Visualize the results on PCA-reduced data reduced_data = PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(data) kmeans = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10) kmeans.fit(reduced_data) # Step size of the mesh. Decrease to increase the quality of the VQ. h = .02 # point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max]. # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each x_min, x_max = reduced_data[:, 0].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 0].max() + 1 y_min, y_max = reduced_data[:, 1].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 1].max() + 1 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) # Obtain labels for each point in mesh. Use last trained model. Z = kmeans.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) plt.figure(1) plt.clf() plt.imshow(Z, interpolation='nearest', extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()), cmap=plt.cm.Paired, aspect='auto', origin='lower') plt.plot(reduced_data[:, 0], reduced_data[:, 1], 'k.', markersize=2) # Plot the centroids as a white X centroids = kmeans.cluster_centers_ plt.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1], marker='x', s=169, linewidths=3, color='w', zorder=10) plt.title('K-means clustering on the digits dataset (PCA-reduced data) ' 'Centroids are marked with white cross') plt.xlim(x_min, x_max) plt.ylim(y_min, y_max) plt.xticks(()) plt.yticks(()) plt.show()
运行文本结果:
n_digits: 10, n_samples 1797, n_features 64 _______________________________________________________________________________ init time inertia homo compl v-meas ARI AMI silhouette k-means++ 0.21s 69432 0.602 0.650 0.625 0.465 0.598 0.146 random 0.20s 69694 0.669 0.710 0.689 0.553 0.666 0.147 PCA-based 0.02s 71820 0.673 0.715 0.693 0.567 0.670 0.150
我们可以看到降维处理后运行时间缩短,而且V值还略高于以上两种方法。
图片结果: