1、冒泡排序
伪代码:
i∈[0,N-1) //循环N-1遍
j∈[0,N-1-i) //每遍循环要处理的无序部分
if a[j] > a[j+1]
swap(j,j+1) //两两排序(升序/降序)
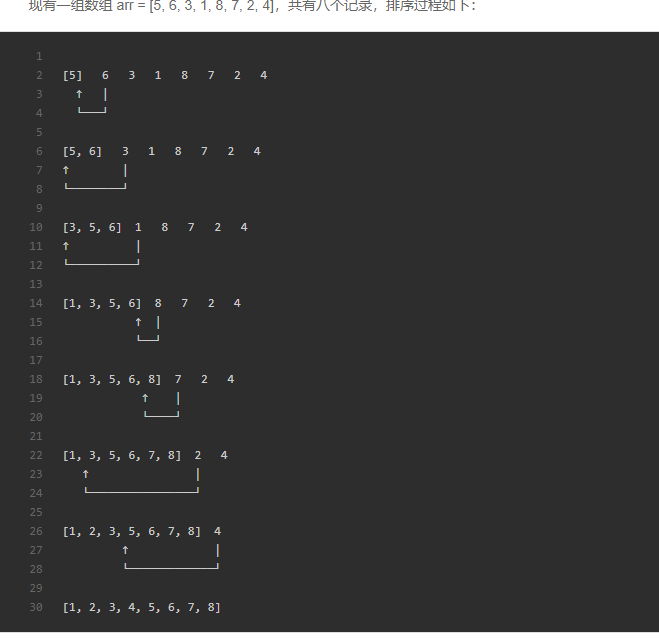
2、插入排序
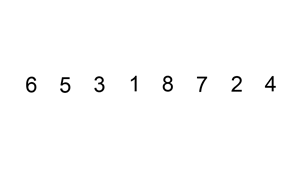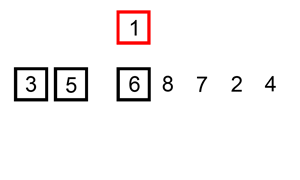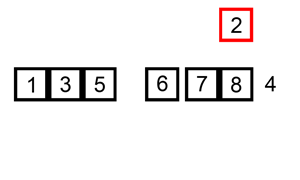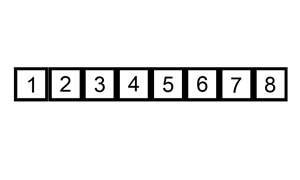
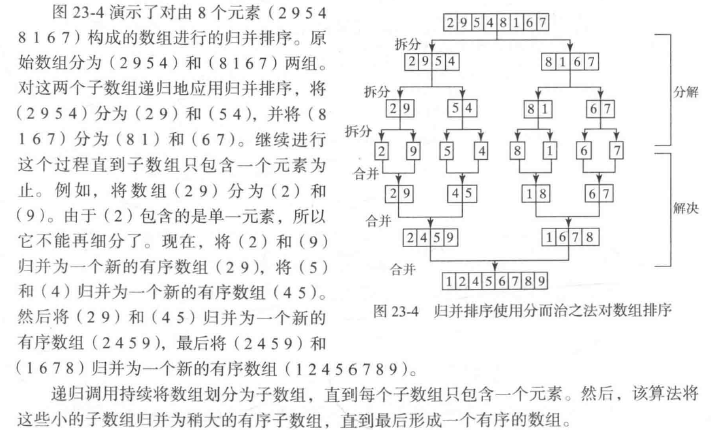
3、归并排序
4、快速排序
步骤为:
- 从数列中挑出一个元素,称为"基准"(pivot),
- 重新排序数列,所有比基准值小的元素摆放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的元素摆在基准后面(相同的数可以到任何一边)。在这个分区结束之后,该基准就处于数列的中间位置。这个称为分区(partition)操作。
- 递归地(recursively)把小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列排序
5、选择排序
每次从数组中选出最小或者最大的,然后依次放在前面
以上排序代码如下:
public class Sort{ public static void main(String [] args) { Integer [] a = {9,8,5,1,3,4}; Double [] b = {5.54,8.2,7.22,15.22,71.0}; // bubbleSort(a); // bubbleSort(b); // InsertSort(a); // InsertSort(b); // mergeSort(a); // mergeSort(b); // quickSort(a); // quickSort(b); selectSort(a); selectSort(b); for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { System.out.print(b[i] + " "); } } //冒泡排序 public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void bubbleSort(T [] a) { for(int i=0; i<a.length-1; i++) { for(int j=0; j<a.length-1-i; j++) { if(a[j].compareTo(a[j+1]) > 0) { swap(a, j, j+1); } } } } //插入排序 public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void InsertSort(T [] a) { for(int i=1; i<a.length; i++) { T currentElement = a[i]; int j; for(j=i-1; j>=0 && a[j].compareTo(currentElement) > 0; j--) { a[j+1] = a[j]; } a[j+1] = currentElement; } } //归并排序 public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void mergeSort(T [] a) { if(a.length > 1) { T [] firstHalf = (T[]) new Comparable[a.length/2]; System.arraycopy(a, 0, firstHalf, 0, a.length/2); mergeSort(firstHalf); int secondHalfLength = a.length - a.length / 2; T [] secondHalf = (T[]) new Comparable[secondHalfLength]; System.arraycopy(a, a.length/2, secondHalf, 0, secondHalfLength); mergeSort(secondHalf); merge(firstHalf, secondHalf, a); } } public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void merge(T [] firstHalf, T [] secondHalf,T [] a) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int current1; int current2; int current3; current1 = current2 = current3 = 0; while(current1 < firstHalf.length && current2 < secondHalf.length) { if(firstHalf[current1].compareTo(secondHalf[current2]) < 0 ) { a[current3++] = firstHalf[current1++]; }else { a[current3++] = secondHalf[current2++]; } } while(current1 < firstHalf.length) { a[current3++] = firstHalf[current1++]; } while(current2 < secondHalf.length) { a[current3++] = secondHalf[current2++]; } } //快速排序 public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void quickSort(T [] a) { qsort(a,0,a.length-1); } private static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void qsort(T[] a, int left, int right) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(left < right) { int pivot = partition(a,left,right); qsort(a, left, pivot-1); qsort(a, pivot+1, right); } } //快速排序 中的 找出 把数组分成两部分的 那个下标 private static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> int partition(T[] a, int left, int right) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub T pivot = a[left]; while(left < right) { while(left < right && a[right].compareTo(pivot)>=0) { right--; } a[left] = a[right]; while(left < right && a[left].compareTo(pivot)<=0) { left++; } a[right] = a[left]; } a[left] = pivot; return left; } public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void selectSort(T [] a){ T min; int minIndex; for(int i=0; i<a.length-1; i++) { min = a[i]; minIndex = i; for(int j=i+1; j<a.length; j++) { if(min.compareTo(a[j])>0) { min = a[j]; minIndex = j; } } swap(a, minIndex, i); } } private static <T> void swap(T[] a, int i, int j) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub T temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } }