hibernate中可以一次对多个表进行数据插入,这种插入类似
Hibernate的关联映射关系有:
多对一 ---- many-to-one
一对多 ---- one-to-many
一对一 ---- one-to-one
多对多 ---- many-to-many
比较常用的是多对一和一对一关联映射多对一关联映射:
场景:用户和组;从用户角度来看,多个用户属于一个组(多对一关联)
使用Hibernate开发的思路:先建立对象模型,把实体抽取出来。目前两个实体:用户和组两个实体,多个学生拥有同一个地址
,所有用户实体中应该有一个持有组的引用
看实体类:
package com.entity;
/**
* Student entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
public class Student implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer addid;
private Adrress adss;
// Constructors
public Adrress getAdss() {
return adss;
}
public void setAdss(Adrress adss) {
this.adss = adss;
}
/** default constructor */
public Student() {
}
/** full constructor */
public Student(String name, Integer addid) {
this.name = name;
this.addid = addid;
}
// Property accessors
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAddid() {
return this.addid;
}
public void setAddid(Integer addid) {
this.addid = addid;
}
}
package com.entity;
/**
* Adrress entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
public class Adrress implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private Integer idAdrress;
private String detail;
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Adrress() {
}
/** full constructor */
public Adrress(String detail) {
this.detail = detail;
}
// Property accessors
public Integer getIdAdrress() {
return this.idAdrress;
}
public void setIdAdrress(Integer idAdrress) {
this.idAdrress = idAdrress;
}
public String getDetail() {
return this.detail;
}
public void setDetail(String detail) {
this.detail = detail;
}
}
hibernate 映射表的内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.entity.Student" table="student" catalog="test">
<id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="id" />
<generator class="increment"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="Name" length="45" />
</property>
<many-to-one name="adss" column="addid" cascade="save-update" class="com.entity.Adrress"></many-to-one>
<!-- name 属性表示Student类中的属性,column为对应的表中的和adrress表中主键关联的名称,
也就是将address类中的主键的值作为addid的值插入表student中 -->
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Spring中配置了事务,利用的是注解的方式
<bean id="sessionFactoryt"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 也可以这样配 -->
<!-- <property name="configLocation"> <value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value>
</property> -->
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect <!-- 数据库所用的sql语句 -->
</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</prop> <!--启用二级缓存 -->
<prop key="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">false</prop> <!--是否启动查询缓存 -->
<prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</prop> <!--指定缓存类 -->
</props>
</property>
<!-- <property name="packagesToScan" value="com.*" /> 为什么不起作用,别人的就可以 -->
<!-- <property name="mappingResources"> <list> <value>com/entity/Admin.hbm.xml</value>
<value>com/entity/Userinfo.hbm.xml</value> </list> </property> -->
<property name="mappingDirectoryLocations">
<list>
<value>com/entity</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="tm"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactoryt" />
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.dao.imp.UserDao">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactoryt" />
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="tm">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 配置被weave织入的那些方法, 使用的传播行为和隔离级别 -->
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 6.aop:config-->
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"
pointcut="execution(* com.dao.imp.UserDao.*(..))" />
</aop:config>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="tm" />测试代码
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserDao ud1=(UserDao)ctx.getBean("userDao");//改成userDao就是注解方式的代理
System.out.println("OK");
ud1.insert("liu");
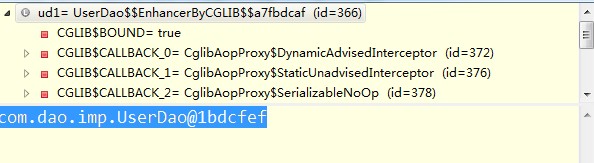
UserDao中的插入数据,因为没有用到接口Spring采用的CGLib代理。
public void insert(String s) {
System.out.println("插入数据!");
// sessionFactory.openSession().save(arg0)
Admin adm = new Admin();
Session sess = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Adrress ad = new Adrress();
ad.setDetail("shan xi");
Student st = new Student();
st.setName("liuyu");
st.setAdss(ad);
sess.save(st);
//Transaction tx = sess.beginTransaction();
//tx.begin();
/*Userinfo user = new Userinfo();
System.out.println("查找数据!");
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
如果成功,就可以看到如下的语句:
插入数据!
Hibernate:
select
max(id)
from
student
Hibernate:
select
max(idAdrress)
from
adrress
插入数据!
Hibernate:
insert
into
test.adrress
(detail, idAdrress)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
test.student
(Name, addid, id)
values
(?, ?, ?)
回到数据库中也可以看到结果。
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/fengxuezhiye/article/details/7369786