首先查看一下CentOS版本
查看网络配置
我用虚拟机能上网的。
安装dhcp服务
yum install dhcp -y

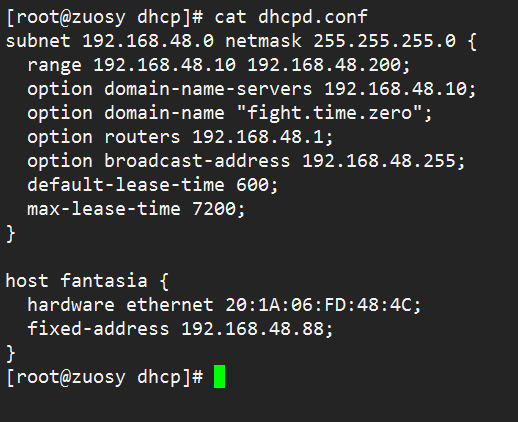
配置dhcp服务器的配置文件
cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf

它告诉你去 /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.sample 里面去找一个例子
直接重定向 简单粗暴

打开文件后里面的内容是:
1 # dhcpd.conf 2 # 3 # Sample configuration file for ISC dhcpd 4 # 5 6 # option definitions common to all supported networks... 7 option domain-name "example.org"; 8 option domain-name-servers ns1.example.org, ns2.example.org; 9 10 default-lease-time 600; 11 max-lease-time 7200; 12 13 # Use this to enble / disable dynamic dns updates globally. 14 #ddns-update-style none; 15 16 # If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local 17 # network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented. 18 #authoritative; 19 20 # Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also 21 # have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection). 22 log-facility local7; 23 24 # No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the 25 # DHCP server to understand the network topology. 26 27 subnet 10.152.187.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { 28 } 29 30 # This is a very basic subnet declaration. 31 32 subnet 10.254.239.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 { 33 range 10.254.239.10 10.254.239.20; 34 option routers rtr-239-0-1.example.org, rtr-239-0-2.example.org; 35 } 36 37 # This declaration allows BOOTP clients to get dynamic addresses, 38 # which we don't really recommend. 39 40 subnet 10.254.239.32 netmask 255.255.255.224 { 41 range dynamic-bootp 10.254.239.40 10.254.239.60; 42 option broadcast-address 10.254.239.31; 43 option routers rtr-239-32-1.example.org; 44 } 45 46 # A slightly different configuration for an internal subnet. 47 subnet 10.5.5.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 { 48 range 10.5.5.26 10.5.5.30; 49 option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org; 50 option domain-name "internal.example.org"; 51 option routers 10.5.5.1; 52 option broadcast-address 10.5.5.31; 53 default-lease-time 600; 54 max-lease-time 7200; 55 } 56 57 # Hosts which require special configuration options can be listed in 58 # host statements. If no address is specified, the address will be 59 # allocated dynamically (if possible), but the host-specific information 60 # will still come from the host declaration. 61 62 host passacaglia { 63 hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95; 64 filename "vmunix.passacaglia"; 65 server-name "toccata.fugue.com"; 66 } 67 68 # Fixed IP addresses can also be specified for hosts. These addresses 69 # should not also be listed as being available for dynamic assignment. 70 # Hosts for which fixed IP addresses have been specified can boot using 71 # BOOTP or DHCP. Hosts for which no fixed address is specified can only 72 # be booted with DHCP, unless there is an address range on the subnet 73 # to which a BOOTP client is connected which has the dynamic-bootp flag 74 # set. 75 host fantasia { 76 hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5; 77 fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com; 78 } 79 80 # You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation 81 # based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients 82 # in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all 83 # other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet. 84 85 class "foo" { 86 match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW"; 87 } 88 89 shared-network 224-29 { 90 subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { 91 option routers rtr-224.example.org; 92 } 93 subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { 94 option routers rtr-29.example.org; 95 } 96 pool { 97 allow members of "foo"; 98 range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250; 99 } 100 pool { 101 deny members of "foo"; 102 range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230; 103 } 104 }
然后删除 删成这个样子:

为了方便把这部分贴出来
subnet 10.5.5.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 { range 10.5.5.26 10.5.5.30; option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org; option domain-name "internal.example.org"; option routers 10.5.5.1; option broadcast-address 10.5.5.31; default-lease-time 600; max-lease-time 7200; } host fantasia { hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5; fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com; }
然后就开始配置吧 假设在一个局域网192.168.48.0配置 分配给host的ip范围是192.168.48.10 192.168.48.200 然后开始搞起
网络接口配置:
vim /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd
DHCPDARGS=eth0
配置一下本地虚拟机的网络

这个样子,我的XShell也就断了
然后虚拟机配置一下桥接模式,这样我的Windows就和虚拟机在一个局域网下了

成功了嘿嘿嘿。
但是在这里还是要说以下细节的
本地的Windows网卡要设置自动获取ip自动获取dns
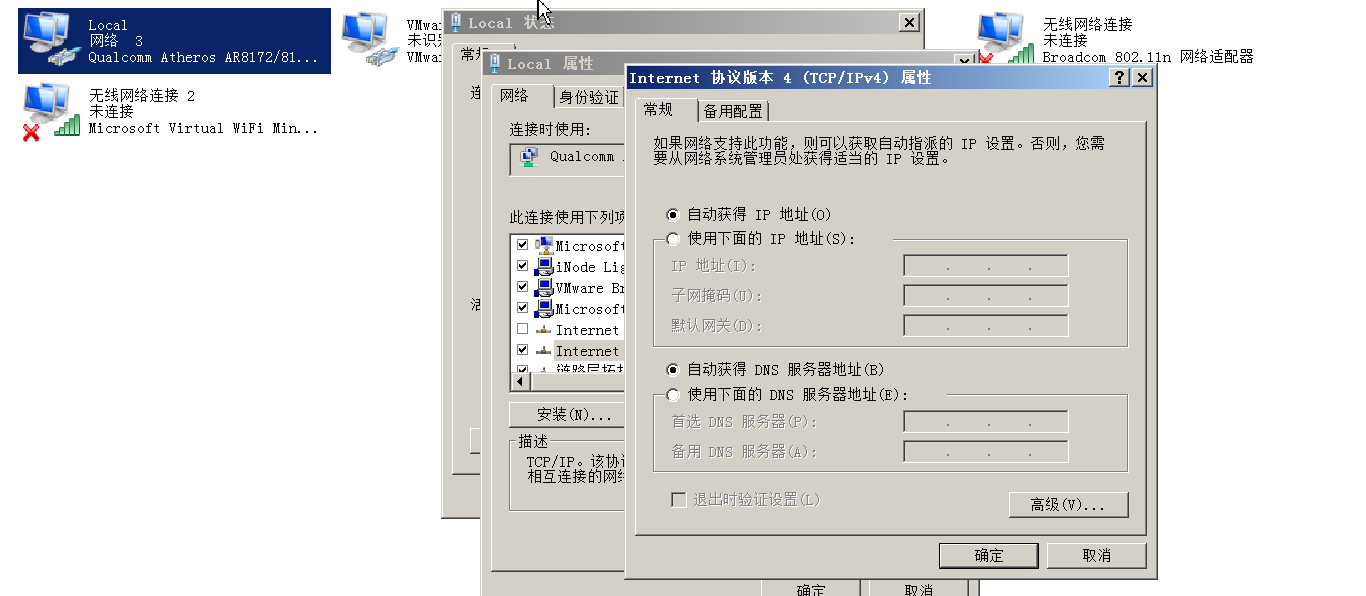
然后要重启一下网卡才能生效,这样最简单粗暴了。