纯随机数发生器


编写一个方法,使用以下算法生成指定数目(比如1000个)的随机整数。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 8 9 System.out.print("输入你要获取的个数:"); 10 11 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 12 13 int n = input.nextInt();//获取的随机数的个数 14 15 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 16 17 System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*1000));//输出获取的1-10000的随机数 18 19 } 20 21 }

2)请看以下代码,你发现了有什么特殊之处吗?
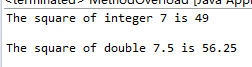
public class MethodOverload { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("The square of integer 7 is " + square(7)); System.out.println(" The square of double 7.5 is " + square(7.5)); } public static int square(int x) { return x * x; } public static double square(double y) { return y * y; } }
运行结果:
满足以下条件的两个或多个方法构成重载关系:
(1)方法名相同
(2)参数类型不同,参数个数不同,或者是参数类型的顺序不同。
3)查看一下JDK中System.out.println()方法,你发现了什么?
JDK中有许多System.out.println()同名的重载方法,方法名都是print()。