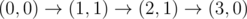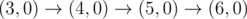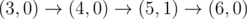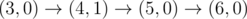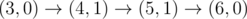题意:
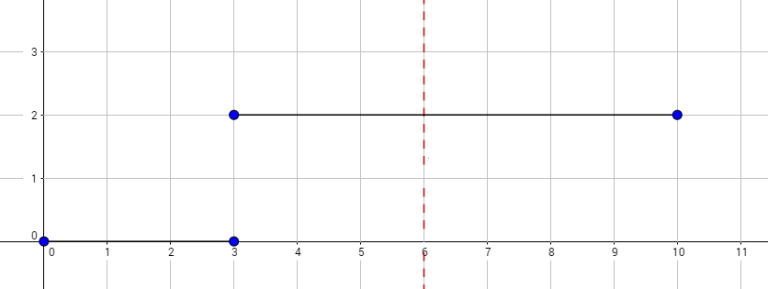
给你一个起点(0,0),和终点(k,0)
假设现在在(x,y),下一步你可以走到(x+1,y)、(x+1,y-1)、(x+1,y+1);
但是不能超过给定的上界线段和正x轴,也就是每一步都要在这两个线段中间
问你有多少种走法,走到终点
题解:
C很小,只有15
每个点向左边走一步,就是, dp[x][y]==》dp[x+1][y]、dp[x+1][y+1]、dp[x+1][y-1],
x最多走10^18步,y最多15,用矩阵快速幂加速求解这个dp方程
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") #define ls i<<1 #define rs ls | 1 #define mid ((ll+rr)>>1) #define pii pair<int,int> #define MP make_pair typedef long long LL; const long long INF = 1e18+1LL; const double Pi = acos(-1.0); const int N = 1e4+10, M = 1e3+20, inf = 2e9; LL mod = 1e9+7; LL a[N],b[N]; int c[N],n; struct Matix { LL arr[20][20]; }E,first,dp[500]; Matix mul(Matix a,Matix b,LL hang ,LL lie) { Matix ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(int i=0;i<=hang;i++) { for(int t=0;t<=lie;t++) for(int j=0;j<=lie;j++) { ans.arr[i][t]+=(a.arr[i][j]*b.arr[j][t])%mod, ans.arr[i][t]%=mod; } } return ans; } Matix multi (Matix a, Matix b,int hang,int lie,int lie2) { Matix ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(int i = 0; i < hang; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < lie2; j++) { ans.arr[i][j] = 0; for(int k = 0; k < lie; k++) ans.arr[i][j] += (a.arr[i][k] * b.arr[k][j])%mod, ans.arr[i][j] %= mod; } } return ans; } Matix pow(Matix ans,Matix a,LL x,int cc) { while(x) { if(x&1) ans=multi(ans,a,1,cc+1,cc+1); a=mul(a,a,cc,cc); x/=2; } return ans; } LL K; int main() { scanf("%d%lld",&n,&K); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { scanf("%lld%lld%d",&a[i],&b[i],&c[i]); } dp[0].arr[0][0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { memset(first.arr,0,sizeof(first.arr)); for(int j = 0; j <= c[i]; ++j) first.arr[0][j] = dp[i-1].arr[0][j]; memset(E.arr,0,sizeof(E.arr)); int sum = 2; for(int j = 0; j <= c[i]; ++j) { if(sum) E.arr[0][j] = 1,sum--; } int fir = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= c[i]; ++j) { for(int k = fir; k <= min(fir+2,c[i]); ++k) { E.arr[j][k] = 1; } fir++; } dp[i] = pow(first,E,min(b[i],K) - a[i],c[i]); // dp[i] = multi(first,E,1,c[i]+1,c[i]+1); } printf("%lld ",(dp[n].arr[0][0]+mod)%mod); return 0; }