组件基础
基本示例
这里有一个 Vue 组件的示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="components-demo"> <button-counter></button-counter> </div> <script> // 定义一个名为 button-counter 的新组件 Vue.component('button-counter', { data: function() { return { count: 0 } }, template: '<button v-on:click="count++">You clicked me {{ count }} times.</button>' }) new Vue({ el: '#components-demo' }) </script> </body> </html>
组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,且带有一个名字:在这个例子中是在一个通过 new Vue 创建的 Vue 根实例中,把这个组件作为自定义元素来使用。
因为组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与 new Vue 接收相同的选项,例如 data 、 computed 、 watch 、 methods 以及生命周期钩子等。仅有的例外是像 el 这样根实例特有的选项。
data必须是一个函数
当我们定义这个 <button-counter> 组件时,你可能会发现它的 data 并不是像这样直接提供一个对象:
data: { count: 0 }
取而代之的是,一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数,因此每个实例可以维护一份被返回对象的独立的拷贝:
data: function () { return { count: 0 } }
组件的组织
通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织:
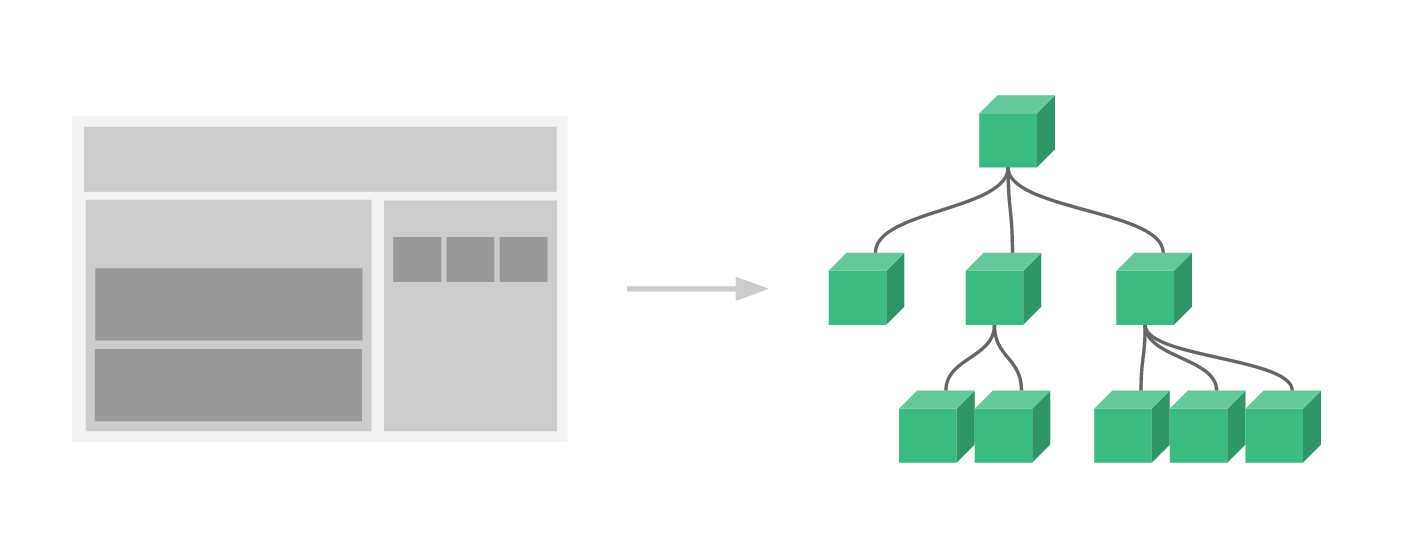
例如,你可能会有页头、侧边栏、内容区等组件,每个组件又包含了其它的像导航链接、博文之类的组件。
为了能在模板中使用,这些组件必须先注册以便 Vue 能够识别。这里有两种组件的注册类型:全局注册和局部注册。至此,我们的组件都只是通过 Vue.component 全局注册的。
Vue.component('my-component-name', {
// ... options ...
})
全局注册的组件可以用在其被注册之后的任何 (通过 new Vue ) 新创建的 Vue 根实例,也包括其组件树中的所有子组件的模板中。
通过Prop向子组件传递数据
Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义特性。当一个值传递给一个 prop 特性的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个属性。为了给下面组件传递一个标题,我们可以用一个 props 选项将其包含在该组件可接受的 prop 列表中:
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: ['title'],
template: '<h3>{{ title }}</h3>'
})
一个组件默认可以拥有任意数量的 prop ,任何值都可以传递给任何 prop 。在上述模板中,你会发现我们能够在组件实例中访问这个值,就像访问 data 中的值一样。
一个 prop 被注册之后,你就可以像这样把数据作为一个自定义特性传递进来:
<blog-post title="My journey with Vue"></blog-post> <blog-post title="Blogging with Vue"></blog-post> <blog-post title="Why Vue is so fun"></blog-post>
效果:

然而在一个典型的应用中,你可能在 data 里有一个博文的数组:
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: ['id','title'],
template: '<h3>{{ id }}:{{ title }}</h3>'
})
new Vue({
el: '#blog-post-demo',
data: {
posts: [
{ id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue' },
{ id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue' },
{ id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun' }
]
}
})
并想要为每篇博文渲染一个组件:
<blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:id="post.id" v-bind:title="post.title"></blog-post>
如上所示,你会发现我们可以使用 v-bind 来动态传递 prop 。这在你一开始不清楚要渲染的具体内容,比如从一个 API 获取博文列表的时候,是非常有用的。
单个根元素
当构建一个 <blog-post> 组件时,你的模板最终会包含的东西远不止一个标题,最最起码,会包含这篇博文的正文:
<h3>{{ title }}</h3> <div v-html="content"></div>
然而如果你在模板中尝试这样写,Vue 会显示一个错误,并解释道 every component must have a single root element (每个组件必须只有一个根元素) 。你可以将模板的内容包裹在一个父元素内,来修复这个问题,例如:
<div class="blog-post"> <h3>{{ title }}</h3> <div v-html="content"></div> </div>
看起来当组件变得越来越复杂的时候,我们的博文不只需要标题和内容,还需要发布日期、评论等等。为每个相关的信息定义一个 prop 会变得很麻烦:
<blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:key="post.id" v-bind:title="post.title" v-bind:content="post.content" v-bind:publishedAt="post.publishedAt" v-bind:comments="post.comments" ></blog-post>
所以是时候重构一下这个组件了,让它变成接受一个单独的 post prop :
<blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:key="post.id" v-bind:post="post" ></blog-post>
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: ['post'],
template: `
<div class="blog-post">
<h3>{{ post.title }}</h3>
<div v-html="post.content"></div>
</div>
`
})
通过事件向父级组件发送消息
在我们开发 <blog-post> 组件时,它的一些功能可能要求我们和父级组件进行沟通。例如我们可能会引入一个可访问性的功能来放大博文的字号,同时让页面的其它部分保持默认的字号。
在其父组件中,我们可以通过添加一个 postFontSize 数据属性来支持这个功能,它可以在模板中用来控制所有博文的字号:
<div id="blog-posts-events-demo"> <div :style="{ fontSize: postFontSize + 'em' }"> <blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:key="post.id" v-bind:post="post" ></blog-post> </div> </div>
现在我们在每篇博文正文之前添加一个按钮来放大字号:
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: ['post'],
template: `
<div class="blog-post">
<h3>{{ post.title }}</h3>
<button @click="$emit('enlarge-text')">
Enlarge text
</button>
<div v-html="post.content"></div>
</div>
`
});
new Vue({
el: '#blog-posts-events-demo',
data: {
posts: [
{ id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue' },
{ id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue' },
{ id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun' }
],
postFontSize: 1
}
});
当点击这个按钮时,我们需要告诉父级组件放大所有博文的文本。幸好 Vue 实例提供了一个自定义事件的系统来解决这个问题。我们可以调用内建的 $emit 方法并传入事件的名字,来向父级组件触发一个事件:
<button v-on:click="$emit('enlarge-text')"> Enlarge text </button>
然后我们可以用 v-on 在博文组件上监听这个事件,就像监听一个原生 DOM 事件一样:
<blog-post ... v-on:enlarge-text="postFontSize += 0.1" ></blog-post>
-
使用事件抛出一个值
有的时候用一个事件来抛出一个特定的值是非常有用的。例如我们可能想让 <blog-post> 组件决定它的文本要放大多少。这时可以使用 $emit 的第二个参数来提供这个值:
<button v-on:click="$emit('enlarge-text', 0.1)"> Enlarge text </button>
然后当在父级组件监听这个事件的时候,我们可以通过 $event 访问到被抛出的这个值:
<blog-post ... v-on:enlarge-text="postFontSize += $event" ></blog-post>
或者,如果这个事件处理函数是一个方法:
<blog-post ... v-on:enlarge-text="onEnlargeText" ></blog-post>
那么这个值将会作为第一个参数传入这个方法:
methods: { onEnlargeText: function (enlargeAmount) { this.postFontSize += enlargeAmount } }
-
在组件上使用v-model
自定义事件也可以用于创建支持 v-model 的自定义输入组件。记住:等价于:<input v-model="searchText">
当用在组件上时, v-model 则会这样:<input v-bind:value="searchText" v-on:input="searchText = $event.target.value" >
<custom-input v-bind:value="searchText" v-on:input="searchText = $event" ></custom-input>
- 为了让它正常工作,这个组件内的 <input> 必须:
- 将其 value 特性绑定到一个名叫 value 的 prop 上
- 在其 input 事件被触发时,将新的值通过自定义的 input 事件抛出
写成代码之后是这样的:
现在 v-model 就应该可以在这个组件上完美地工作起来了:Vue.component('custom-input', { props: ['value'], template: ` <input v-bind:value="value" v-on:input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)" > ` }) 例:
例:<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id='demo'> <custom-input v-bind:value="searchText" v-on:input="searchText = $event"></custom-input> <custom-input v-model='searchText'></custom-input> {{searchText}} </div> <script> Vue.component('custom-input', { props: ['value'], template: ` <input v-bind:value="value" v-on:input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)" > ` }); var vm = new Vue({ el: "#demo", data: { searchText: '' } }) </script> </body> </html>
通过插槽分发内容
和 HTML 元素一样,我们经常需要向一个组件传递内容,像这样:
<alert-box> Something bad happened. </alert-box>
可能会渲染出这样的东西:
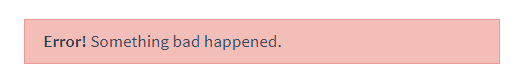
幸好,Vue 自定义的 元素让这变得非常简单:
Vue.component('alert-box', {
template: `
<div class="demo-alert-box">
<strong>Error!</strong>
<slot></slot>
</div>
`
})
如你所见,我们只要在需要的地方加入插槽就行了——就这么简单!

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="components-demo"> <alert-box>通过插件传入</alert-box> </div> <script> Vue.component('alert-box', { template: ` <div class="demo-alert-box"> <strong>组件自己内容</strong> <h3><slot></slot></h3> </div> ` }) new Vue({ el: '#components-demo' }) </script> </body> </html>
动态组件
有的时候,在不同组件之间进行动态切换是非常有用的,比如在一个多标签的界面里:

上述内容可以通过 Vue 的元素加一个特殊的 is 特性来实现:
<!-- 组件会在 `currentTabComponent` 改变时改变 --> <component v-bind:is="currentTabComponent"></component>
在上述示例中, currentTabComponent 可以包括已注册组件的名字:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script> <style> .tab-button { padding: 6px 10px; border-top-left-radius: 3px; border-top-right-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid #ccc; cursor: pointer; background: #f0f0f0; margin-bottom: -1px; margin-right: -1px; } .tab-button:hover { background: #e0e0e0; } .tab-button.active { background: #e0e0e0; } .tab { border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="dynamic-component-demo" class="demo"> <button v-for="tab in tabs" v-bind:key="tab" v-bind:class="['tab-button', { active: currentTab === tab }]" v-on:click="currentTab = tab">{{ tab }}</button> <component v-bind:is="currentTabComponent" class="tab"></component> </div> <script> Vue.component('tab-home', { template: '<div>Home component</div>' }) Vue.component('tab-posts', { template: '<div>Posts component</div>' }) Vue.component('tab-archive', { template: '<div>Archive component</div>' }) new Vue({ el: '#dynamic-component-demo', data: { currentTab: 'Home', tabs: ['Home', 'Posts', 'Archive'] }, computed: { currentTabComponent: function() { return 'tab-' + this.currentTab.toLowerCase() } } }) </script> </body> </html>
或一个组件的选项对象:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script> <style> .tab-button { padding: 6px 10px; border-top-left-radius: 3px; border-top-right-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid #ccc; cursor: pointer; background: #f0f0f0; margin-bottom: -1px; margin-right: -1px; } .tab-button:hover { background: #e0e0e0; } .tab-button.active { background: #e0e0e0; } .tab { border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script> <div id="dynamic-component-demo" class="demo"> <button v-for="tab in tabs" v-bind:key="tab.name" v-bind:class="['tab-button', { active: currentTab.name === tab.name }]" v-on:click="currentTab = tab">{{ tab.name }}</button> <component v-bind:is="currentTab.component" class="tab"></component> </div> <script> var tabs = [{ name: 'Home', component: { template: '<div>Home component</div>' } }, { name: 'Posts', component: { template: '<div>Posts component</div>' } }, { name: 'Archive', component: { template: '<div>Archive component</div>', } } ] new Vue({ el: '#dynamic-component-demo', data: { tabs: tabs, currentTab: tabs[0] } }) </script> </body> </html>
通过vue-cli使用组件
准备
-
安装
npm install vue-cli -g
-
初始化项目目录
vue init webpack-simple [项目目录名]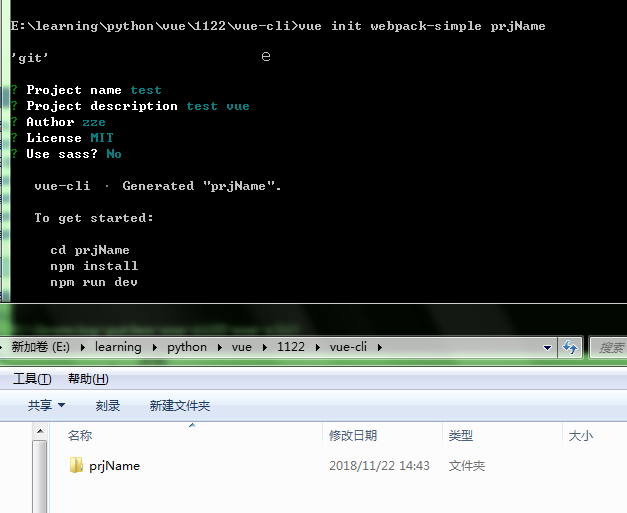
-
按提示依次执行
cd prjName npm install
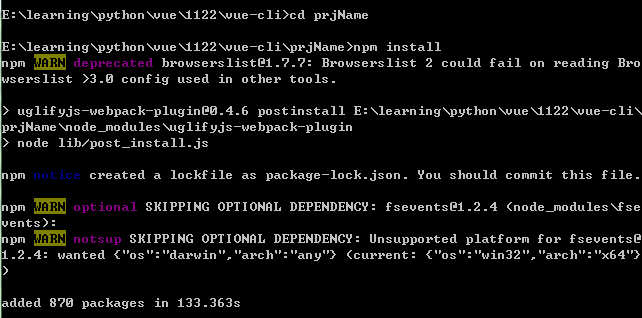
-
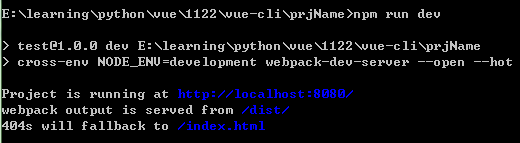
运行
npm run dev
使用
-
目录结构
完成上述准备后会生成如下目录结构:
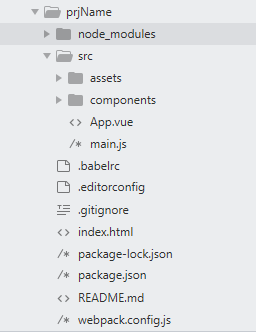
-
新建组件
在 components 目录下新建如下组件: /src/components/VHeader.vue
/src/components/VHeader.vue1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h3>{{msg}}</h3> 4 </div> 5 </template> 6 <script> 7 export default{ 8 name:'header', 9 data(){ 10 return { 11 msg:'这是头部分' 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 </script> 16 <style scoped> 17 h3{ 18 background-color: blue; 19 } 20 </style>
 /src/components/VContent.vue
/src/components/VContent.vue1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h3>{{msg}}</h3> 4 </div> 5 </template> 6 <script> 7 export default{ 8 name:'content', 9 data(){ 10 return { 11 msg:'这是内容部分' 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 </script> 16 <!-- scoped可使当前样式块只对当前组件生效 --> 17 <style scoped> 18 h3{ 19 background-color: red; 20 } 21 </style>
 /src/components/VFooter.vue
/src/components/VFooter.vue1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h3>{{msg}}</h3> 4 </div> 5 </template> 6 <script> 7 export default{ 8 name:'header', 9 data(){ 10 return { 11 msg:'这是尾部分' 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 </script> 16 <style scoped> 17 h3{ 18 background-color: yellow; 19 } 20 21 </style>
 /src/components/VPage.vue
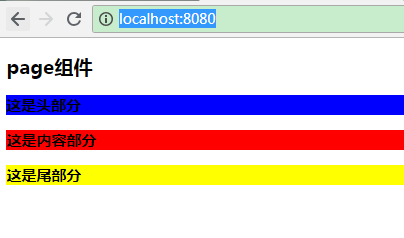
/src/components/VPage.vue1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h2>{{msg}}</h2> 4 <VHeader></VHeader> 5 <VContent></VContent> 6 <VFooter></VFooter> 7 </div> 8 </template> 9 <script> 10 // 引入子组件 11 import VHeader from './VHeader.vue' 12 import VContent from './VContent.vue' 13 import VFooter from './VFooter.vue' 14 15 export default{ 16 name:'page', 17 data(){ 18 return { 19 msg:'page组件' 20 } 21 }, 22 // 挂载子组件 23 components:{ 24 VHeader, 25 VContent, 26 VFooter 27 } 28 } 29 </script> 30 <style></style>
在上述文件中的 style 块中有一个 scoped 属性(例如在 VContent.vue 的 17 行),这个属性的作用是让当前样式块只对当前组件生效。
-
配置组件
 /src/main.js
/src/main.js1 import Vue from 'vue' 2 import VPage from './components/VPage.vue' 3 4 var page_vm = new Vue({ 5 el: "#page", //对应 /index.html 中div元素的id 6 render: h => h(VPage) // 将指定组件(这里是VPage)渲染到上面el属性对应位置 7 }) 8 9 10 console.info(page_vm.$children[0]); //VueComponent {_uid: 1, _isVue: true, $options: {…}, _renderProxy: Proxy, _self: VueComponent, …}
 /index.html
/index.html<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>test</title> </head> <body> <div id="page"></div> <script src="/dist/build.js"></script> </body> </html>
-
效果
访问运行时输出的地址,默认是 http://localhost:8080/ :