Vector Quantization
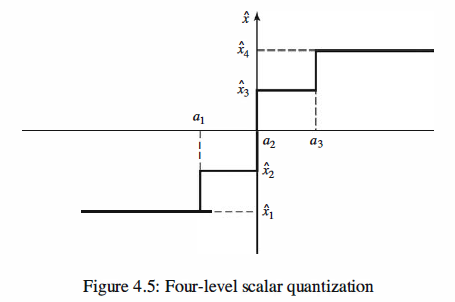
In scalar quantization each output of the discrete-time source is quantized separately
and then encoded. For example, if we are using a four-level scalar quantizer and encoding
each level into 2 bits, we are using 2 bits per each source output. This quantization
scheme is shown in Figure 4.5.
Now if we consider two samples of the source at each time and interpret these two
samples as a point in a plane, the scalar quantizer partitions the entire plane into 16
quantization regions, as shown in Figure 4.6.
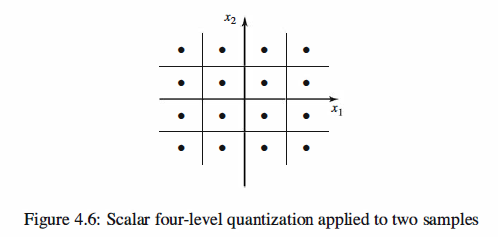
It is seen that the regions in the two-dimensional space are all of rectangular shape.
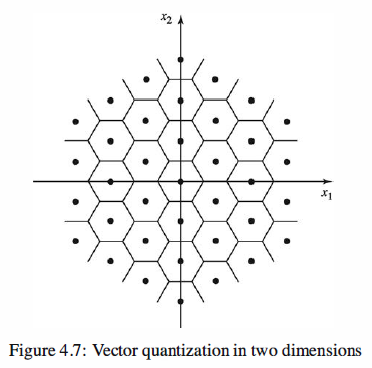
If we allow 16 regions of any shape in the two-dimensional space, we are capable of
obtaining better results. This means that we are quantizing two source outputs at a
time using 16 regions, which is equivalent to 4 bits per two source outputs or 2 bits
per each source output. Therefore, the number of bits per source output for quantizing
two samples at a time is equal to the number of bits per source output obtained in the
scalar case. Because we are relaxing the requirement of having rectangular regions, the
performance may be improved. Now if we take three samples at a time and quantize the
entire three-dimensional space into 64 regions, we may have even less distortion with
the same number of bits per source output.
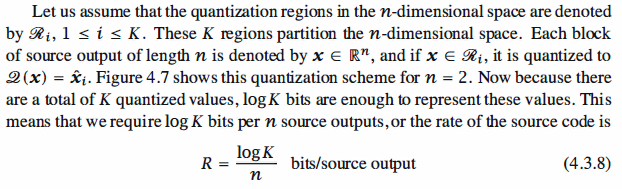
The idea of vector quantization is to take blocks of source outputs of length n and design
the quantizer in the n-dimensional Euclidean space rather than doing the quantization based
on single samples in onedimensional space.
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis