算法背景
人工蜂群算法 (Artificial Bee Colony, ABC) 是由 Karaboga 于 2005 年提出的一种新颖的基于集群智能的全局优化算法,其直观背景来源于蜂群的采蜜行为。它的主要特点是不需要了解问题的特殊信息,只需要对问题进行优劣的比较,通过各人工蜂个体的局部寻优行为,最终在群体中使全局最优值突现出来,有着较快的收敛速度。
蜜蜂是一种群居昆虫,虽然单个昆虫的行为极其简单,但是由单个简单的个体所组成的群体却表现出极其复杂的行为。真实的蜜蜂种群能够在任何环境下,以极高的效率从食物源(花朵)中采集花蜜;同时,它们能适应环境的改变。
搜索流程
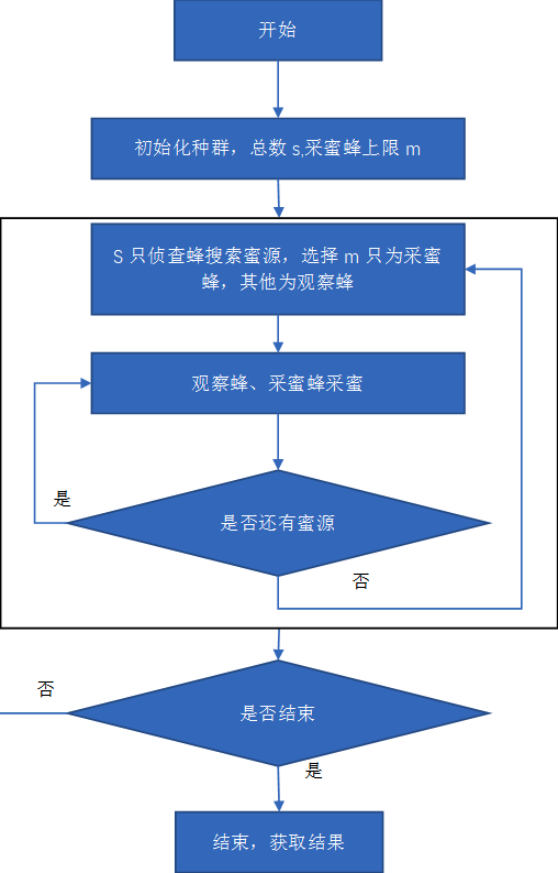
算法的调用过程如下:
初始化所有蜜源
记录最优蜜源
while:
雇佣蜂对所有蜜源进行邻域搜索(避免饥饿效应)
计算轮盘度,判断蜜源质量
观察蜂对优质蜜源进行邻域搜索(加速算法收敛)
记录最优蜜源
侦查蜂放弃枯竭蜜源进行全局搜索(跳出局部最优)
记录最优蜜源
end
其中雇佣蜂和观察蜂有着相似的逻辑,特别在对指定蜜源进行邻域搜索时,两者的逻辑是完全的一样的:
- 基于原有蜜源进行邻域突变
- 保证邻域突变的有效性
- 若为优质突变,则进行蜜源替换
- 若为劣质突变,则进行蜜源开采
但是算法的设计者们却特意区分出两种不同的逻辑,其原因可以从实现代码中看出。在进行领域搜索时,对指定蜜源的选择和限定是关键所在,它暗示了雇佣蜂和观察蜂的区别以及承担的不同角色。
首先对于雇佣蜂的角色,其指定蜜源的方式简单粗暴,对每一个蜜源进行遍历指定。通过这种方式进行邻域搜索,是建立整个算法的基础核心。
而对于观察蜂角色,它是根据轮盘赌策略进行蜜源的指定,也就是说,蜜源越是优质,其被指定的、被进行领域搜索的概率就越高。通过这种正向反馈的过程,加速了整个算法的收敛性,可以帮助我们在多个局部中快速找到最优解。
如此看来观察蜂似乎是雇佣蜂的进化版,观察蜂似乎可以完全替代雇佣蜂?其实不然。观察蜂角色在进行快速收敛、对优质蜜源进行了较多照顾的同时,劣质的蜜源可能会被忽略,从而产生饥饿效应。而雇佣蜂的角色让所有的蜜源,不论优劣,都有能够持续搜索的机会,雇佣蜂和观察蜂相互配合,使得算法能够均衡高效的执行。
最后的角色是侦查蜂。当持续的搜索使得蜜源枯竭的时候,侦查蜂对枯竭的蜜源进行放弃,跳出原有的局部空间,在全局空间中随机探索新的蜜源,之后转变为雇佣蜂重复上述过程。
Java 实现
主函数
public class test {
// 建立蜂群
static beeColony bee = new beeColony();
public static void main(String[] args) {
int iter = 0;
int run = 0;
int j = 0;
double mean = 0;
//srand(time(NULL));
// 重复计算,获得平均情况下的全局最优解
for (run = 0; run < bee.runtime; run++) {
// 初始化蜜源
bee.initial();
bee.MemorizeBestSource();
for (iter = 0; iter < bee.maxCycle; iter++) {
// 雇佣蜂的逻辑: 更新所有蜜源(确保能跳出局部蜜源)
bee.SendEmployedBees();
bee.CalculateProbabilities();
// 观察蜂的逻辑: 好蜜源正向反馈(加速收敛的作用)
bee.SendOnlookerBees();
bee.MemorizeBestSource();
// 仅仅重制枯竭的蜜源 (局部优质蜜源枯竭的快)
bee.SendScoutBees();
}
// 打印最优的坐标,以及最终的函数值
for (j = 0; j < bee.D; j++) {
//System.out.println("GlobalParam[%d]: %f
",j+1,GlobalParams[j]);
System.out.println("GlobalParam[" + (j + 1) + "]:" + bee.GlobalParams[j]);
}
//System.out.println("%d. run: %e
",run+1,GlobalMin);
System.out.println((run + 1) + ".run:" + bee.GlobalMin);
bee.GlobalMins[run] = bee.GlobalMin;
mean = mean + bee.GlobalMin;
}
mean = mean / bee.runtime;
//System.out.println("Means of %d runs: %e
",runtime,mean);
System.out.println("Means of " + bee.runtime + "runs: " + mean);
}
}
算法函数
import java.lang.Math;
public class beeColony {
/* Control Parameters of ABC algorithm*/
int NP = 20; /* The number of colony size (employed bees+onlooker bees)*/
int FoodNumber = NP / 2; /*The number of food sources equals the half of the colony size*/
int limit = 100; /*A food source which could not be improved through "limit" trials is abandoned by its employed bee*/
int maxCycle = 2500; /*The number of cycles for foraging {a stopping criteria}*/
/* Problem specific variables*/
int D = 100; /*The number of parameters of the problem to be optimized*/
double lb = -5.12; /*lower bound of the parameters. */
double ub = 5.12; /*upper bound of the parameters. lb and ub can be defined as arrays for the problems of which parameters have different bounds*/
int runtime = 30; /*Algorithm can be run many times in order to see its robustness*/
int dizi1[] = new int[10];
double Foods[][] = new double[FoodNumber][D]; /*Foods is the population of food sources. Each row of Foods matrix is a vector holding D parameters to be optimized. The number of rows of Foods matrix equals to the FoodNumber*/
double f[] = new double[FoodNumber]; /*f is a vector holding objective function values associated with food sources */
double fitness[] = new double[FoodNumber]; /*fitness is a vector holding fitness (quality) values associated with food sources*/
double trial[] = new double[FoodNumber]; /*trial is a vector holding trial numbers through which solutions can not be improved*/
double prob[] = new double[FoodNumber]; /*prob is a vector holding probabilities of food sources (solutions) to be chosen*/
double solution[] = new double[D]; /*New solution (neighbour) produced by v_{ij}=x_{ij}+phi_{ij}*(x_{kj}-x_{ij}) j is a randomly chosen parameter and k is a randomlu chosen solution different from i*/
double ObjValSol; /*Objective function value of new solution*/
double FitnessSol; /*Fitness value of new solution*/
int neighbour, param2change; /*param2change corrresponds to j, neighbour corresponds to k in equation v_{ij}=x_{ij}+phi_{ij}*(x_{kj}-x_{ij})*/
double GlobalMin; /*Optimum solution obtained by ABC algorithm*/
double GlobalParams[] = new double[D]; /*Parameters of the optimum solution*/
double GlobalMins[] = new double[runtime];
/*GlobalMins holds the GlobalMin of each run in multiple runs*/
double r; /*a random number in the range [0,1)*/
/*a function pointer returning double and taking a D-dimensional array as argument */
/*If your function takes additional arguments then change function pointer definition and lines calling "...=function(solution);" in the code*/
// typedef double (*FunctionCallback)(double sol[D]);
/*benchmark functions */
// double sphere(double sol[D]);
// double Rosenbrock(double sol[D]);
// double Griewank(double sol[D]);
// double Rastrigin(double sol[D]);
/*Write your own objective function name instead of sphere*/
// FunctionCallback function = &sphere;
/*Fitness function*/
double CalculateFitness(double fun) {
double result = 0;
if (fun >= 0) {
result = 1 / (fun + 1);
} else {
result = 1 + Math.abs(fun);
}
return result;
}
/*The best food source is memorized*/
void MemorizeBestSource() {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
if (f[i] < GlobalMin) {
GlobalMin = f[i];
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
GlobalParams[j] = Foods[i][j];
}
}
}
/*Variables are initialized in the range [lb,ub]. If each parameter has different range, use arrays lb[j], ub[j] instead of lb and ub */
/* Counters of food sources are also initialized in this function*/
void init(int index) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++) {
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) 32767 + (double) (1)));
Foods[index][j] = r * (ub - lb) + lb;
solution[j] = Foods[index][j];
}
f[index] = calculateFunction(solution);
fitness[index] = CalculateFitness(f[index]);
trial[index] = 0;
}
/*All food sources are initialized */
void initial() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
init(i);
}
GlobalMin = f[0];
for (i = 0; i < D; i++)
GlobalParams[i] = Foods[0][i];
}
void SendEmployedBees() {
int i, j;
/*Employed Bee Phase*/
for (i = 0; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
/*The parameter to be changed is determined randomly*/
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
param2change = (int) (r * D);
/*A randomly chosen solution is used in producing a mutant solution of the solution i*/
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
neighbour = (int) (r * FoodNumber);
/*Randomly selected solution must be different from the solution i*/
// while(neighbour==i)
// {
// r = ( (double)Math.random()*32767 / ((double)(32767)+(double)(1)) );
// neighbour=(int)(r*FoodNumber);
// }
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
solution[j] = Foods[i][j];
/*v_{ij}=x_{ij}+phi_{ij}*(x_{kj}-x_{ij}) */
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
solution[param2change] = Foods[i][param2change] + (Foods[i][param2change] - Foods[neighbour][param2change]) * (r - 0.5) * 2;
/*if generated parameter value is out of boundaries, it is shifted onto the boundaries*/
if (solution[param2change] < lb)
solution[param2change] = lb;
if (solution[param2change] > ub)
solution[param2change] = ub;
ObjValSol = calculateFunction(solution);
FitnessSol = CalculateFitness(ObjValSol);
/*a greedy selection is applied between the current solution i and its mutant*/
if (FitnessSol > fitness[i]) {
/*If the mutant solution is better than the current solution i, replace the solution with the mutant and reset the trial counter of solution i*/
trial[i] = 0;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
Foods[i][j] = solution[j];
f[i] = ObjValSol;
fitness[i] = FitnessSol;
} else { /*if the solution i can not be improved, increase its trial counter*/
trial[i] = trial[i] + 1;
}
}
/*end of employed bee phase*/
}
/* A food source is chosen with the probability which is proportioal to its quality*/
/*Different schemes can be used to calculate the probability values*/
/*For example prob(i)=fitness(i)/sum(fitness)*/
/*or in a way used in the metot below prob(i)=a*fitness(i)/max(fitness)+b*/
/*probability values are calculated by using fitness values and normalized by dividing maximum fitness value*/
void CalculateProbabilities() {
int i;
double maxfit;
maxfit = fitness[0];
for (i = 1; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
if (fitness[i] > maxfit)
maxfit = fitness[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
prob[i] = (0.9 * (fitness[i] / maxfit)) + 0.1;
}
}
// just add choose tactic, the center logic is as same as sendEmployedBees
void SendOnlookerBees() {
int i, j, t;
i = 0;
t = 0;
/*onlooker Bee Phase*/
while (t < FoodNumber) {
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
if (r < prob[i]) /*choose a food source depending on its probability to be chosen*/ {
t++;
/*The parameter to be changed is determined randomly*/
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
param2change = (int) (r * D);
/*A randomly chosen solution is used in producing a mutant solution of the solution i*/
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
neighbour = (int) (r * FoodNumber);
/*Randomly selected solution must be different from the solution i*/
while (neighbour == i) {
//System.out.println(Math.random()*32767+" "+32767);
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
neighbour = (int) (r * FoodNumber);
}
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
solution[j] = Foods[i][j];
/*v_{ij}=x_{ij}+phi_{ij}*(x_{kj}-x_{ij}) */
r = ((double) Math.random() * 32767 / ((double) (32767) + (double) (1)));
solution[param2change] = Foods[i][param2change] + (Foods[i][param2change] - Foods[neighbour][param2change]) * (r - 0.5) * 2;
/*if generated parameter value is out of boundaries, it is shifted onto the boundaries*/
if (solution[param2change] < lb)
solution[param2change] = lb;
if (solution[param2change] > ub)
solution[param2change] = ub;
ObjValSol = calculateFunction(solution);
FitnessSol = CalculateFitness(ObjValSol);
/*a greedy selection is applied between the current solution i and its mutant*/
if (FitnessSol > fitness[i]) {
/*If the mutant solution is better than the current solution i, replace the solution with the mutant and reset the trial counter of solution i*/
trial[i] = 0;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
Foods[i][j] = solution[j];
f[i] = ObjValSol;
fitness[i] = FitnessSol;
} else { /*if the solution i can not be improved, increase its trial counter*/
trial[i] = trial[i] + 1;
}
} /*if */
i++;
if (i == FoodNumber)
i = 0;
}/*while*/
/*end of onlooker bee phase */
}
/*determine the food sources whose trial counter exceeds the "limit" value. In Basic ABC, only one scout is allowed to occur in each cycle*/
void SendScoutBees() {
int maxtrialindex, i;
maxtrialindex = 0;
// 遍历当前所有食物源,寻找最大的trail
for (i = 1; i < FoodNumber; i++) {
if (trial[i] > trial[maxtrialindex])
maxtrialindex = i;
}
if (trial[maxtrialindex] >= limit) {
init(maxtrialindex);
}
}
// target function for calculate
double calculateFunction(double sol[]) {
return Rastrigin(sol);
}
double sphere(double sol[]) {
int j;
double top = 0;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++) {
top = top + sol[j] * sol[j];
}
return top;
}
double Rosenbrock(double sol[]) {
int j;
double top = 0;
for (j = 0; j < D - 1; j++) {
top = top + 100 * Math.pow((sol[j + 1] - Math.pow((sol[j]), (double) 2)), (double) 2) + Math.pow((sol[j] - 1), (double) 2);
}
return top;
}
double Griewank(double sol[]) {
int j;
double top1, top2, top;
top = 0;
top1 = 0;
top2 = 1;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++) {
top1 = top1 + Math.pow((sol[j]), (double) 2);
top2 = top2 * Math.cos((((sol[j]) / Math.sqrt((double) (j + 1))) * Math.PI) / 180);
}
top = (1 / (double) 4000) * top1 - top2 + 1;
return top;
}
double Rastrigin(double sol[]) {
int j;
double top = 0;
for (j = 0; j < D; j++) {
top = top + (Math.pow(sol[j], (double) 2) - 10 * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * sol[j]) + 10);
}
return top;
}
}
参考链接
[1] https://abc.erciyes.edu.tr/
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_functions_for_optimization
[3] https://www.pianshen.com/article/729179041/
[4] https://www.jianshu.com/p/ebd436d27cf8