20145224-陈颢文 《Java程序设计》第三周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
一、定义类:
·类定义时使用class关键字,要对类中变量(值域成员/对象数据成员)行类型声明。
class Clothes1 {
String color;
char size;
}
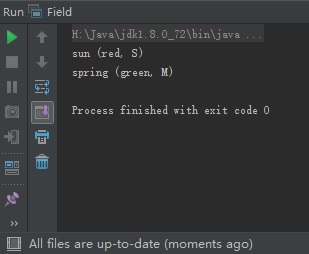
public class Field {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clothes1 sun = new Clothes1 ();
Clothes1 spring = new Clothes1();
sun.color = "red";
sun.size = 'S';
spring.color = "green";
spring.size = 'M';
System.out.printf("sun (%s, %c)%n", sun.color, sun.size);
System.out.printf("spring (%s, %c)%n", spring.color, spring.size);
}
}
·如果要将“c1”绑定到新建的对象上,可以使用“=”制定,称为“c1”名称参考至新建对象。
·一个原始码中可以有多个类定义,但只能有一个是公开类,且文档中的主文档名必须与公开类名称相同。
class Clothes2 {
String color;
char size;
Clothes2(String color, char size) {
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
}
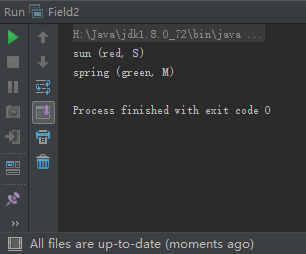
public class Field2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clothes2 sun = new Clothes2("red",'S');
Clothes2 spring = new Clothes2("green",'M');
System.out.printf("sun (%s, %c)%n",sun.color, sun.size);
System.out.printf("spring (%s, %c)%n", spring.color, spring.size);
}
}
二、使用标准类:
·java.util.Scanner
“System.in.read()"也可以用来读取用户的输入数据,但是其返回值为int型。
为了免去每次输入时都要写java.util.Scanner,可以一开始就是用import,在建立Scanner实例时必须传入java.io.InputStream的实例。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Guess {
public static void main(String[] ars) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
int guess;
do{
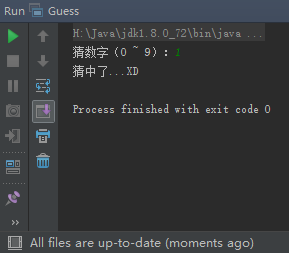
System.out.print("猜数字(0 ~ 9):");
guess = scanner.nextInt();
} while (guess != number);
System.out.println("猜中了...XD");
}
}
·java.math.BigDeciaml
由于java遵守IEEE754浮点数运算规范,使用分数与指数来表示浮点数,有的小数无法用分数精确表示,这回造成小数运算出错。
创建BigDecimal,他会剖析传入字符串,以默认精度进行接下来的运算,避免出现上述问题。提供plus()、substract()、multiply()、divide()等进行加减乘除的运算。
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class DecimalDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal op1 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal op2 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal op3 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal result = new BigDecimal("0.3");
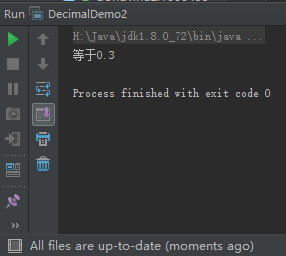
if (op1.add(op2).add(op3).equals(result)) {
System.out.println("等于0.3");
}
else {
System.out.println("不等于0.3");
}
}
}
三、对象制定与相等性
·= 是用在参考名称参考某个对象,而==是用在比较两个参考名称是都参考同一对象。
四、基本类型打包器
·要使基本类型如同对象一样操作,可以使用Long、Integer、Double、Float、Boolean、Byte等类型打包。
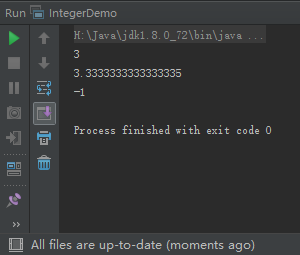
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int data1 = 10;
int data2 = 20;
Integer wrapper1 = new Integer(data1);
Integer wrapper2 = new Integer(data2);
System.out.println(data1 / 3);
System.out.println(wrapper1.doubleValue() / 3);
System.out.println(wrapper1.compareTo(wrapper2));
}
}
五、数组对象:
·在java中数组是对象,数组的长度属性可回去的数组长度,可以用for循环一次取出数组中的每个值
语法:
for(int score:scores){
System.out.printf(“分数:%d ”,score);
}
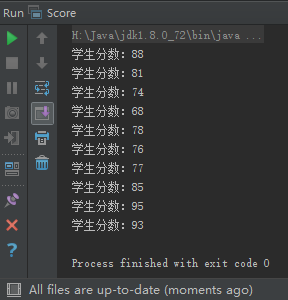
public class Score {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] score = {88, 81, 74, 68, 78, 76, 77, 85, 95, 93};
for (int i = 0;i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("学生分数:%d %n",score[i]);
}
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
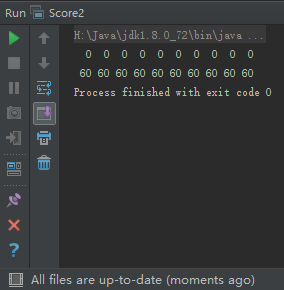
public class Score2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores = new int[10];
for (int score : scores) {
System.out.printf("%3d", score);
}
System.out.println();
Arrays.fill(scores,60);
for (int score : scores) {
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
}
}
·二维数组要在类型关键字旁加上 [] [] 确定行列。
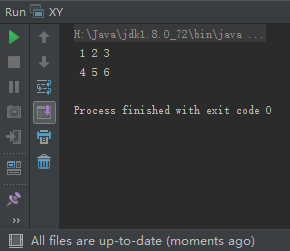
public class XY {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] [] cords = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
};
for (int x = 0;x < cords.length; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < cords[x].length; y++) {
System.out.printf("%2d",cords[x] [y]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
六、数组复制:
·建立长度为x1相同的新数组,再逐一访问其中的每一个索引元素,并指定给x2对应的索引位置。
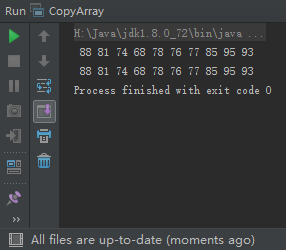
·简单方法,使用原生方式复制每个索引元素System,arraycopy()以及Arrays.CopyOf()。注:这两个方法都是浅层复制,如果要连同对象一起复制,需要自行操作。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] scores1 = {88, 81, 74, 68, 78, 76, 77, 85, 95, 93};
int [] scores2 = Arrays.copyOf(scores1, scores1.length);
for (int score : scores2) {
System.out.printf("%3d", score);
}
System.out.println();
scores2[0] = 99;
for (int score : scores1) {
System.out.printf("%3d", score);
}
}
}
七、字符串对象:
·length()长度
·charAt()字符
·toUpperCase()将原本小写的字符串转为大写的内容
·可以用+来连接字符串
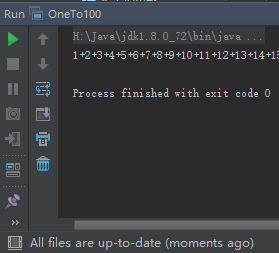
·字符串对象一旦建立,就无法更改对象中的任何内容,使用+会产生新的String实例。
/**
* Created by Kevin Chen on 2016/3/20.
*/
public class OneTo100 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
builder.append(i).append('+');
}
System.out.println(builder.append(100).toString());
}
}
·使用javac指令没有指定-encoding选项是,会使用操作系统默认编码。
八、对象封装:
·封装的目的是指隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,命名规范中以get开头,之后接上首字母大写的单词。
·只有在公开类程序中(public)才能够在类程序代码中存取类或对象成员。
·private关键字:是一个权限修饰符; 用于修饰成员(成员变量和成员函数);被私有化的成员只在本类中有效。
·this关键:在构造函数参数与对象数据成员同名时加以区分时用的。
·static关键字:用于修饰成员(成员变量和成员函数),静态方法只能访问静态成员;静态方法中不可以写this,super关键字;主函数是静态的。
/**
* Created by Kevin Chen on 2016/3/20.
*/
class CashCard2 {
String number;
int balance;
int bonus;
CashCard2(String number, int balance, int bonus) {
this.number = number;
this.balance = balance;
this.bonus = bonus;
}
void store(int money) {
if (money > 0) {
this.balance += money;
if(money >= 1000) {
this.bonus++;
}
}
else {
System.out.println("储存值为负!");
}
}
void charge(int money) {
if (money > 0) {
if(money <= this.balance) {
this.balance -= money;
}
else {
System.out.println("余额不足!");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("储存值为负!");
}
}
int exchange(int bonus) {
if(bonus > 0) {
this.bonus -= bonus;
}
return this.bonus;
}
}
/**
* Created by Kevin Chen on 2016/3/20.
*/
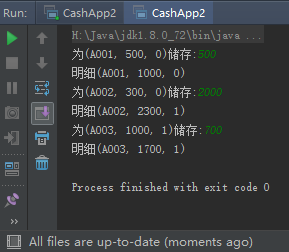
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CashApp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CashCard2[] card2s = {
new CashCard2("A001", 500, 0),
new CashCard2("A002", 300, 0),
new CashCard2("A003", 1000, 1),
};
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (CashCard2 card2 : card2s) {
System.out.printf("为(%s, %d, %d)储存:",card2.number, card2.balance, card2.bonus);
card2.store(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.printf("明细(%s, %d, %d)%n",card2.number, card2.balance, card2.bonus);
}
}
}
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
本周的学习量还真不少,不少语法在看课本时不能真正理解它的作用或是分不清它和另一个语法的区别,通过自己真正的去把它们都码出来运行才会真正的体会到没个语法的真正作用。
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
一开始我就是直接按书上代码敲上去,后来就编译出错了,说定义类重复,并在“Run”当前代码时将有重复定义类的那个文件也弹出来了,于是我就给类名称后都加上了序号问题就解决了。还有在src的文件中只要有编译不通过的文件,无论它是不是你当前正在“Run“的代码,系统都会给你把那个有错误的文件找出来的。
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 4500行 | 30篇 | 350小时 | |
| 第一周 | 150/150 | 1/1 | 15/15 | 初步了解了java |
| 第二周 | 200/200 | 1/2 | 20/35 | 掌握java基本语句 |
| 第三周 | 300/500 | 1/3 | 25/60 |