进程与程序
- 程序是包含可执行代码以及执行代码需要的数据等信息的文件,存放在磁盘等介质上。
- 当程序被操作系统装载到内存并分配给它一定资源后,此时可称为进程。
- 程序是静态概念,进程是动态概念
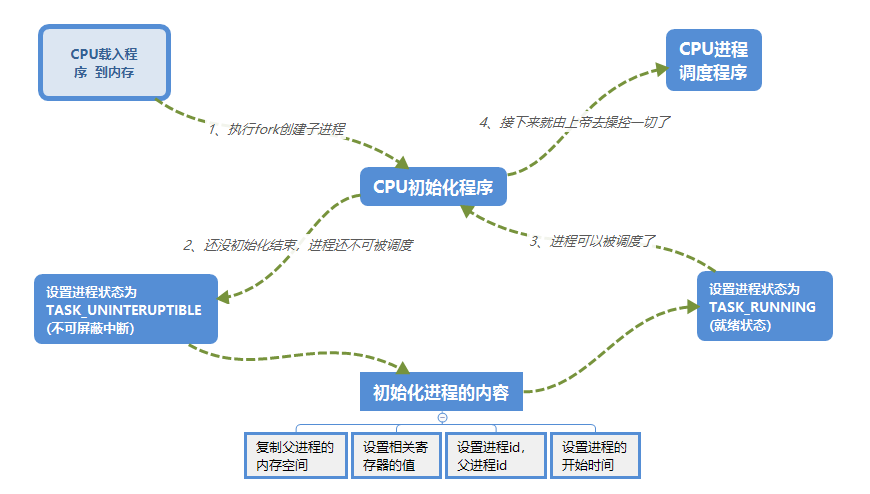
进程在内核中的组织形式:进程控制块(PCB)

Linux 进程控制块: task_struct 结构
pid_t pid; uid_t uid,euid; gid_t gid,egid; volatile long state; int exit_state; unsigned int rt_priority; unsigned int policy; struct list_head tasks; struct task_struct *real_parent; struct task_struct *parent; struct list_head children,sibling; struct fs_struct *fs; struct files_struct *files; struct mm_struct *mm; struct signal_struct *signal; struct sighand_struct *sighand; cputime_t utime, stime; struct timespec start_time; struct timespec real_start_time;
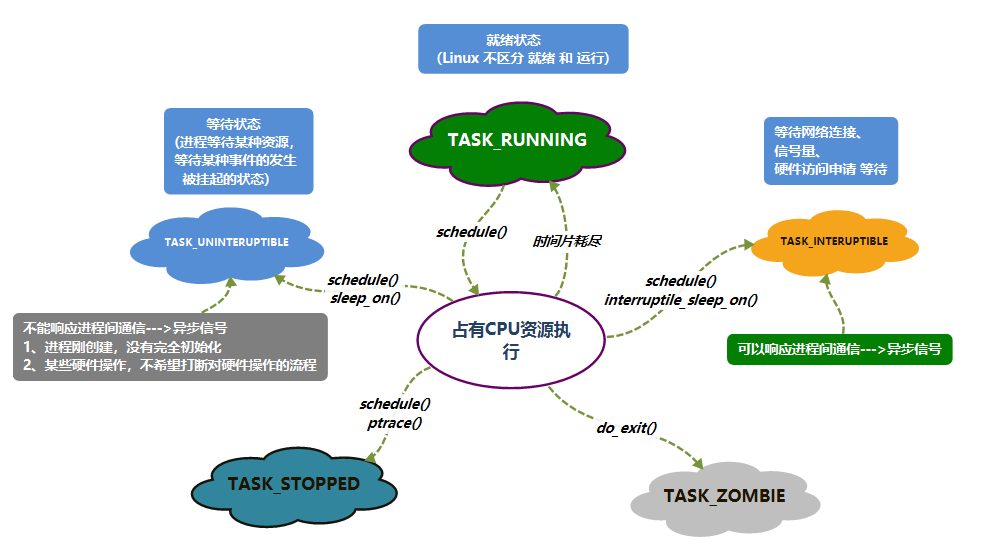
- 进程状态:
volatile long state;
- state 成员的可能取值如下:
- #define TASK_RUNNING 0
- #define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 1
- #define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 2
- #define TASK_ZOMBIE 4
- #define TASK_STOPPED 8
进程状态切换