1.概述
注释:用文字描述程序的。给程序员看的
注解:说明程序的。给计算机看的
概念描述:
- JDK1.5之后的新特性
- 说明程序的
- 使用注解:@注解名称
作用分类:
- 编写文档:通过代码里标识的注解生成文档【生成文档doc文档】
- 代码分析:通过代码里标识的注解对代码进行分析【使用反射】
- 编译检查:通过代码里标识的注解让编译器能够实现基本的编译检查【Override】

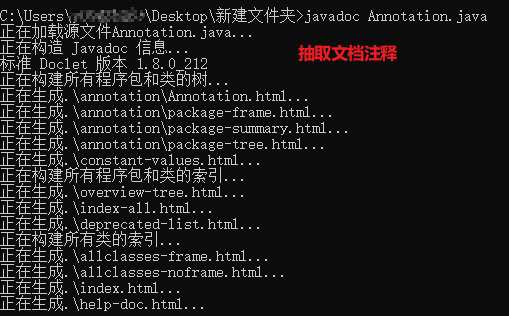
生成下列文件
打开index.html,可以看到下面的

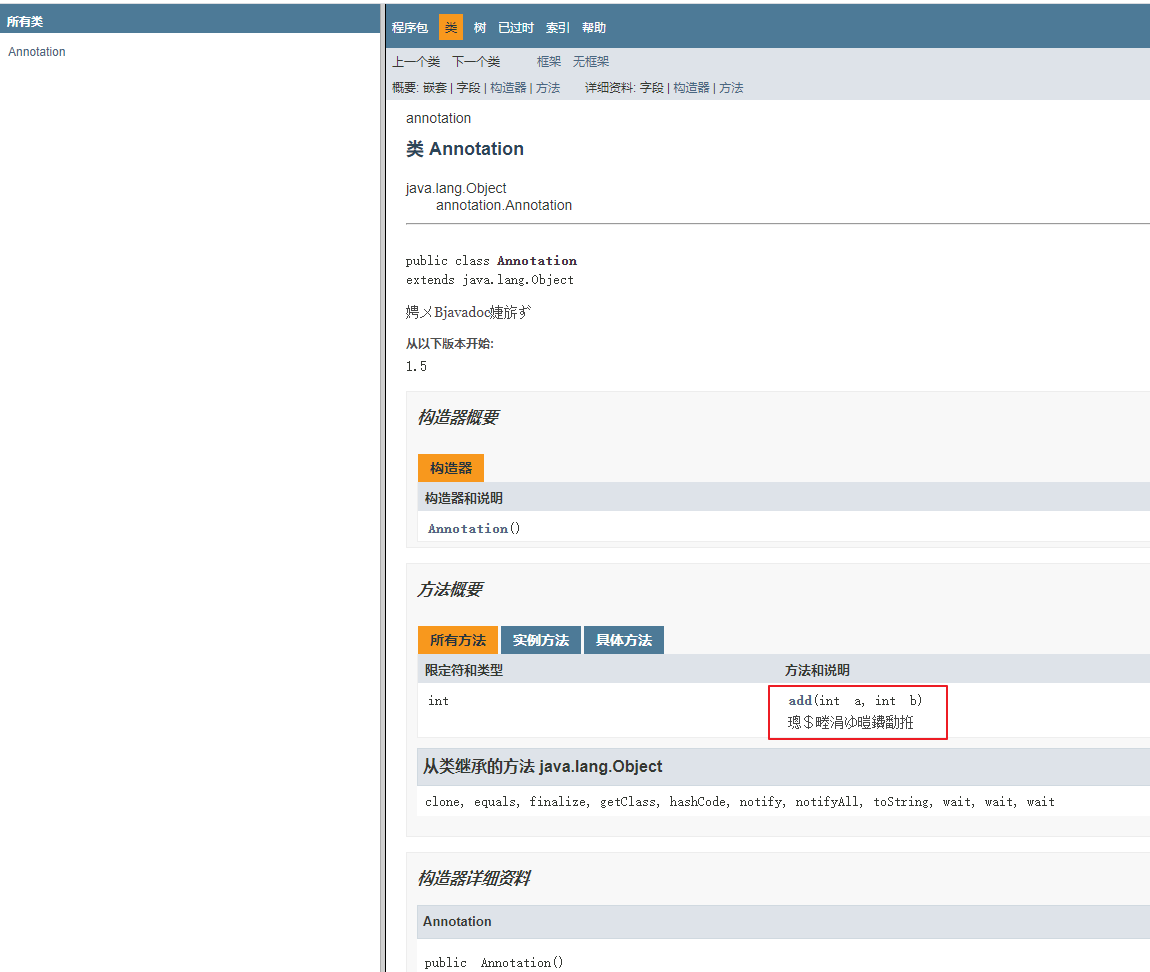
这样就生成了文档
2.JDK内置注解
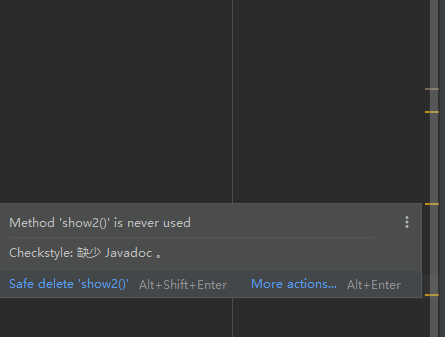
(1)@Override:检测被该注解标注的方法是否是继承自父类(接口)
(2)@Deprecated:将该注解标注的内容,表示已过时
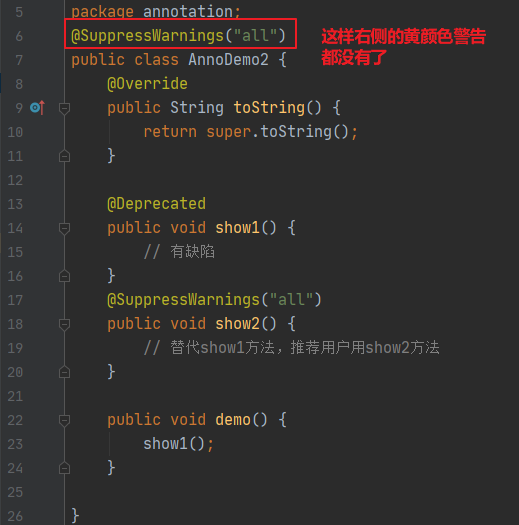
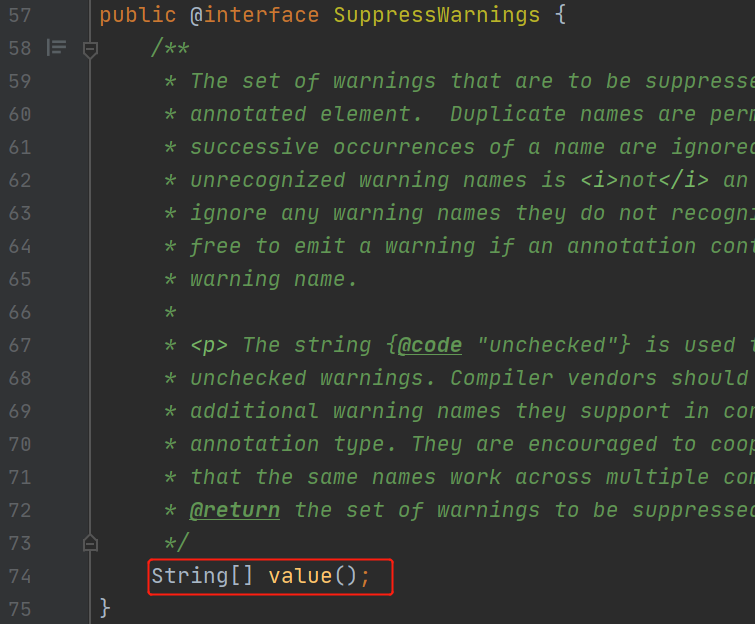
(3)@SuppressWarnings:压制警告
一般传递参数all @SuppressWarnings("all")
IDE编辑器右侧会出现一些黄颜色的警告信息
3.自定义注解
(1)格式
元注解
public @interface 注解名称{
属性列表;
}



(2)注解的本质
本质上就是一个接口,该接口默认继承Annotation 接口
public interface annotation.MyAnno extends java.lang.annotation.Annotation {
}
(3)属性(接口中的抽象方法)
就是接口中可以定义的内容(成员方法)

要求:
属性的返回值类型有下列取值
基本数据类型
String
枚举
注解
以上类型的数组
注意:没有void

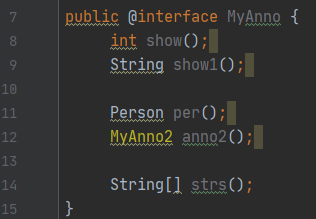
定义了属性,在使用时,需要给属性赋值


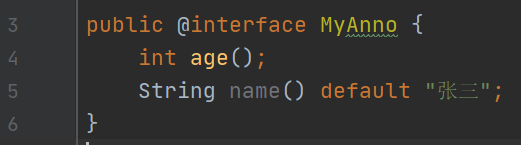
如果定义属性时,使用default关键字给默认属性初始化值,则使用注解时,可以不进行属性的赋值
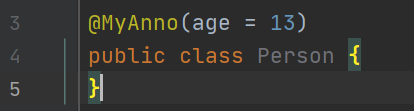
如果只有一个属性需要赋值,并且属性的名称是value,则value可以省略,直接定义值即可。
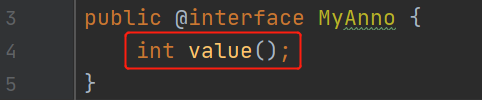

上面的@SuppressWarnings("all")中只有"all"也是因为注解中是String[] value();
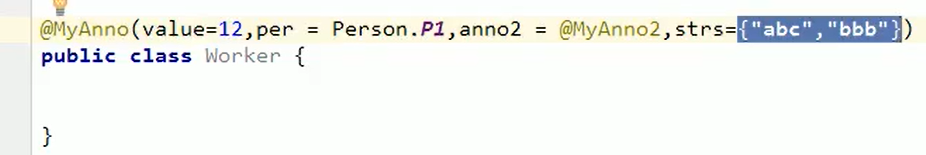
数组赋值时,值使用{}包裹,如果数组中只有一个值,则{}省略
(4)元注解
用于描述注解的注解
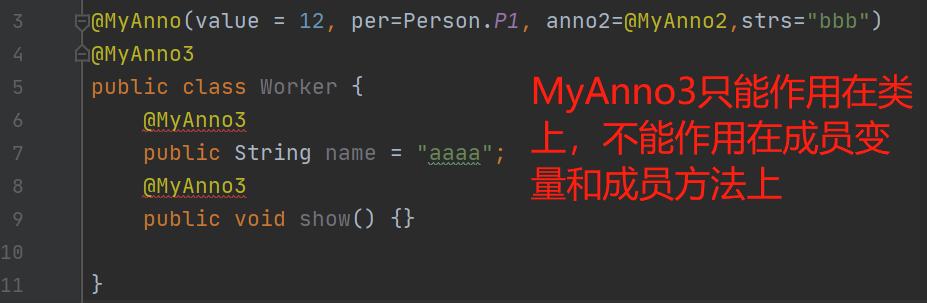
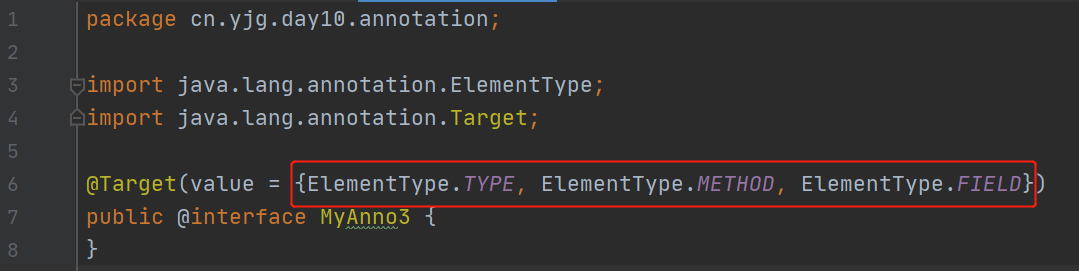
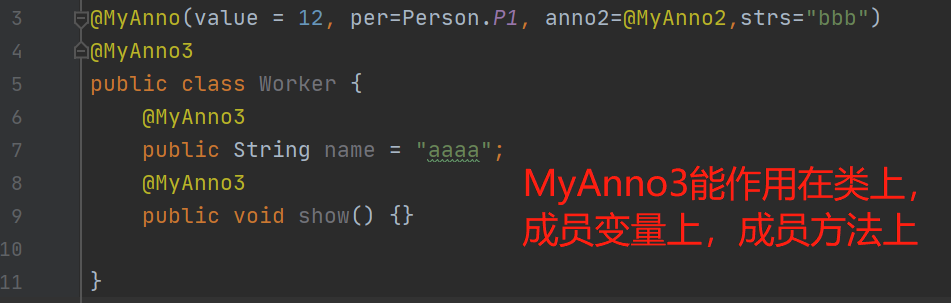
@Target:描述注解能够作用的位置
ElementType取值:
TYPE:可以作用在类上
METHOD:可以作用在方法上
FIELD:可以作用在成员变量上
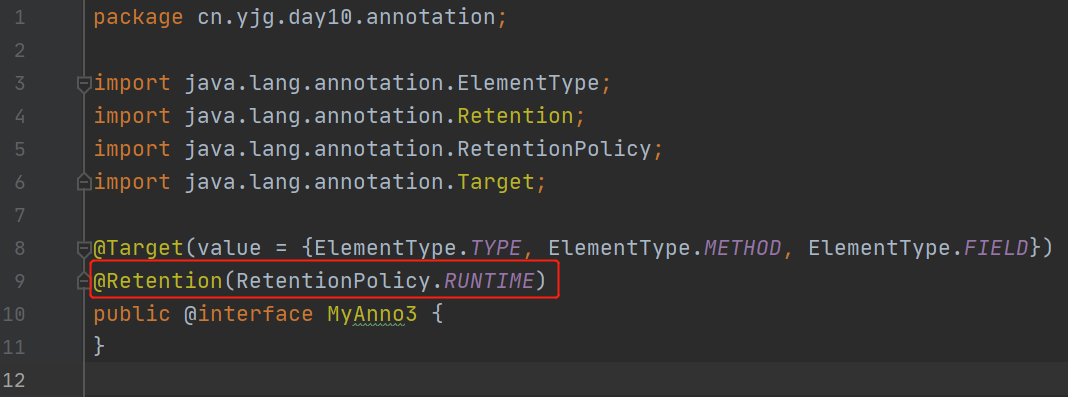
@Retention:描述注解被保留的阶段
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):当前被描述的注解,会保留到class字节码文件中,并被JVM读取到
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS):当前被描述的注解,会保留到class字节码文件中,但不会被JVM读取到
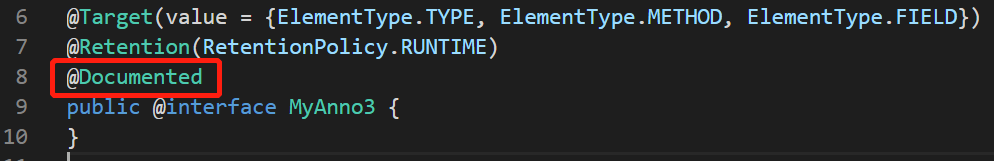
@Documented:描述注解是否被抽取到api文档中
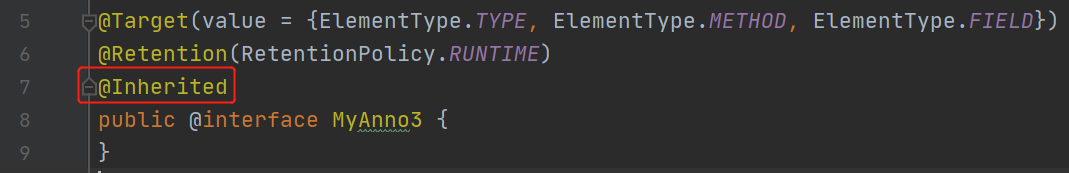
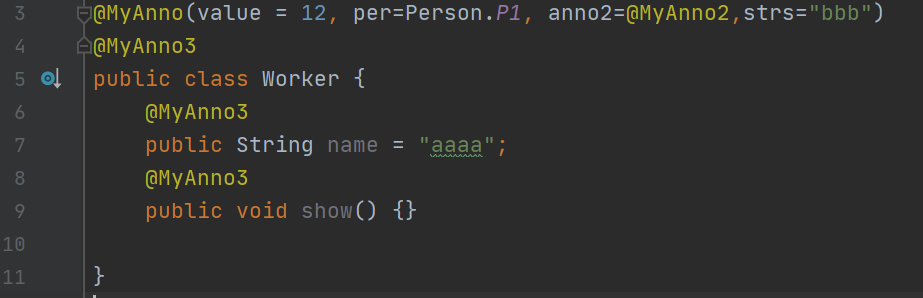
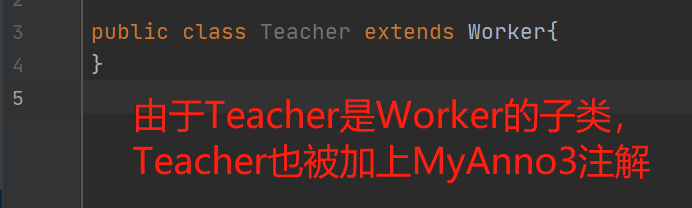
@Inherited:描述注解是否被子类继承
@Target

@Retention
@Doucmented
@Inherited

4.在程序中使用(解析)注解:获取注释中定义的属性值
(1)获取注解定义的位置的对象(Class, Method, Field)
(2)获取指定的注解
getAnnotation(Class)
其实就是在内存中生成了一个该注解接口的子类实现对象
public class ProImpl implements Pro{
public String className(){
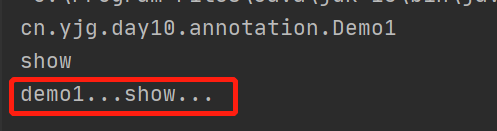
return "cn.yjg.day10.annotation.Demo1";
}
public String methodName() {
return "show";
}
}
(3)调用注解中的抽象方法获取配置的属性值
Pro
package cn.yjg.day10.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 描述需要执行的类名和方法名
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Pro {
String className();
String methodName();
}
ReflectTest
package cn.yjg.day10.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Pro(className = "cn.yjg.day10.annotation.Demo1", methodName = "show")
public class ReflectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 前提:不能改变该类的任何代码,可以创建任意类的对象,可以执行任意方法
*/
// 1.解析注解
// 1.1 获取该类的字节码文件对象
Class<ReflectTest> reflectTestClass = ReflectTest.class;
// 2.获取上边的注解对象
// 其实就是在内存中生成了一个该注解接口的子类实现对象
Pro annotation = reflectTestClass.getAnnotation(Pro.class);
// 3.调用注解对象中定义的抽象方法,获取返回值
String className = annotation.className();
String methodName = annotation.methodName();
System.out.println(className);
System.out.println(methodName);
// 4.加载该类进内存
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
// 5.创建对象
Object obj = aClass.newInstance();
// 6. 获取方法对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
// 7.执行方法
method.invoke(obj);
}
}
Demo1
package cn.yjg.day10.annotation;
public class Demo1 {
public void show(){
System.out.println("demo1...show...");
}
}
运行结果: