步骤1:增加
步骤2:判断是否存在
步骤3:获取指定位置的对象
步骤4:获取对象所处的位置
步骤5:删除
步骤6:替换
步骤7:获取大小
步骤8:转换为数组
步骤9:把另一个容器所有对象都加进来
步骤10:清空
步骤11:练习-判断是否相同
步骤12:答案-判断是否相同
步骤13:练习-MyStringBuffer
步骤14:答案-MyStringBuffer
步骤 1 : 增加
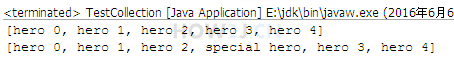
add 有两种用法
第一种是直接add对象,把对象加在最后面
|
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
|
第二种是在指定位置加对象
|
heros.add(3, specialHero);
|
|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 把5个对象加入到ArrayList中
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
System.out.println(heros);
// 在指定位置增加对象
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(3, specialHero);
System.out.println(heros.toString());
}
}
|
|
package charactor;
public class Hero {
public String name;
public float hp;
public int damage;
public Hero() {
}
// 增加一个初始化name的构造方法
public Hero(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 重写toString方法
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
|
步骤 2 : 判断是否存在
通过方法contains 判断一个对象是否在容器中
判断标准: 是否是同一个对象,而不是name是否相同

|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
// 判断一个对象是否在容器中
// 判断标准: 是否是同一个对象,而不是name是否相同
System.out.print("虽然一个新的对象名字也叫 hero 1,但是contains的返回是:");
System.out.println(heros.contains(new Hero("hero 1")));
System.out.print("而对specialHero的判断,contains的返回是:");
System.out.println(heros.contains(specialHero));
}
}
|
步骤 3 : 获取指定位置的对象
通过get获取指定位置的对象,如果输入的下标越界,一样会报错
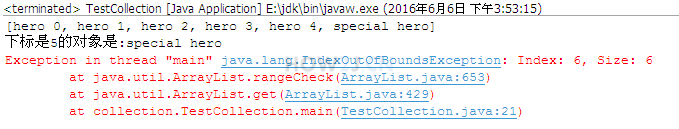
|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
//获取指定位置的对象
System.out.println(heros.get(5));
//如果超出了范围,依然会报错
System.out.println(heros.get(6));
}
}
|
步骤 4 : 获取对象所处的位置
indexOf用于判断一个对象在ArrayList中所处的位置
与contains一样,判断标准是对象是否相同,而非对象的name值是否相等

|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
System.out.println("specialHero所处的位置:"+heros.indexOf(specialHero));
System.out.println("新的英雄,但是名字是"hero 1"所处的位置:"+heros.indexOf(newHero("hero 1")));
}
}
|
步骤 5 : 删除
remove用于把对象从ArrayList中删除
remove可以根据下标删除ArrayList的元素
也可以根据对象删除
|
heros.remove(specialHero);
|

|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
heros.remove(2);
System.out.println("删除下标是2的对象");
System.out.println(heros);
System.out.println("删除special hero");
heros.remove(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
}
}
|
步骤 6 : 替换
set用于替换指定位置的元素

|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
System.out.println("把下标是5的元素,替换为"hero 5"");
heros.set(5, new Hero("hero 5"));
System.out.println(heros);
}
}
|
步骤 7 : 获取大小
size 用于获取ArrayList的大小
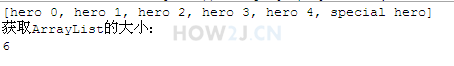
|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
System.out.println("获取ArrayList的大小:");
System.out.println(heros.size());
}
}
|
步骤 8 : 转换为数组
toArray可以把一个ArrayList对象转换为数组。
需要注意的是,如果要转换为一个Hero数组,那么需要传递一个Hero数组类型的对象给toArray(),这样toArray方法才知道,你希望转换为哪种类型的数组,否则只能转换为Object数组

|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero");
heros.add(specialHero);
System.out.println(heros);
Hero hs[] = (Hero[])heros.toArray(new Hero[]{});
System.out.println("数组:" +hs);
}
}
|
步骤 9 : 把另一个容器所有对象都加进来
addAll 把另一个容器所有对象都加进来
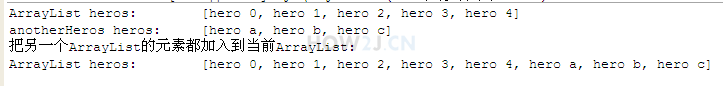
|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
System.out.println("ArrayList heros: " + heros);
//把另一个容器里所有的元素,都加入到该容器里来
ArrayList anotherHeros = new ArrayList();
anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero a"));
anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero b"));
anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero c"));
System.out.println("anotherHeros heros: " + anotherHeros);
heros.addAll(anotherHeros);
System.out.println("把另一个ArrayList的元素都加入到当前ArrayList:");
System.out.println("ArrayList heros: " + heros);
}
}
|
步骤 10 : 清空
clear 清空一个ArrayList
|
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList heros = new ArrayList();
// 初始化5个对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i));
}
System.out.println("ArrayList heros: " + heros);
System.out.println("使用clear清空");
heros.clear();
System.out.println("ArrayList heros: " + heros);
}
}
|
更多内容,点击了解: https://how2j.cn/k/collection/collection-arraylist-method/685.html