题目描述
给一棵二叉树的层序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,求这棵二叉树的先序遍历序列和后序遍历序列。
输入
每个输入文件中一组数据。
第一行一个正整数N(1<=N<=30),代表二叉树的结点个数(结点编号为1~N)。接下来两行,每行N个正整数,分别代表二叉树的层序遍历序列和中序遍历序列。数据保证序列中1~N的每个数出现且只出现一次。
输出
输出一行,包含N个正整数,代表二叉树的先序遍历序列。每行末尾不输出额外的空格。
样例输入
7
3 5 4 2 6 7 1
2 5 3 6 4 7 1
样例输出
3 5 2 4 6 7 1
思路:层序的第一个节点是根节点,那么接下来就是找其左子树和右子树了,然后递归建树就行了。
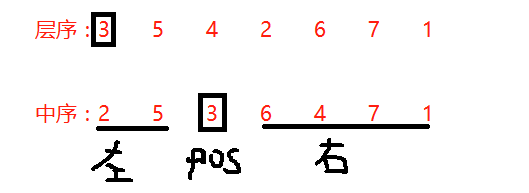
思路和中序+其他建树一样,递归建立即可,同样首先要找到每次递归需要的参数,左子树、右子树的层序遍历和中序遍历的左右端点。
1、层序第一个节点为根节点,按值找到中序中的根结点记录位置为pos。
2、从层序的第二个结点开始遍历序列,每次去中序中找该结点的值,如果找到位置小于pos,则说明在左子树,插入左子树的层序序列;如果找到位置大于pos,则说明在右子树,插入右子树的层序序列。比如层序第二个是5,在中序中找5,其位置在pos左边,说明在左子树中,插入左子树,接着找4, 4在右边插入右子树,依次插入即可。
(因为拆分成左右子树的时候,左子树和右子树的层序遍历和整棵树的层序遍历保持一致。直到遍历完成,此时LayerLeft和LayerRight也建立好了,递归即可。)
/**
* Copyright(c)
* All rights reserved.
* Author : Mered1th
* Date : 2019-02-21-19.51.25
* Description : build
*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10000;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* lchild;
Node* rchild;
Node(int _data){
data=_data;
lchild=NULL;
rchild=NULL;
}
};
vector<int> layer,in;
int n;
Node* buildBiTree(vector<int> layer,vector<int> in,int inL,int inR)
{
if(layer.size()==0 || inL>inR) return nullptr;
int rootVal=layer[0];
Node* root=new Node(rootVal);
int pos=inL;
while(in[pos]!=rootVal) pos++;
vector<int> layerLeft,layerRight;//存放左、右子树的层序序列
for(int i=1;i<layer.size();i++){
int j;
for(j=inL;j<pos;j++){
if(layer[i]==in[j]){
layerLeft.push_back(layer[i]); //如果在pos前找到,插入左子树
break;
}
}
if(j==pos) layerRight.push_back(layer[i]); //超过pos,插入右子树(层序遍历保持左右子树层序遍历顺序的一致性)
}
root->lchild=buildBiTree(layerLeft,in,inL,pos-1);
root->rchild=buildBiTree(layerRight,in,pos+1,inR);
return root;
}
vector<int> ans;
void pre(Node * root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
ans.push_back(root->data);
pre(root->lchild);
pre(root->rchild);
}
}
int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
int temp;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>temp;
layer.push_back(temp);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
cin>>temp;
in.push_back(temp);
}
Node* root=NULL;
root=buildBiTree(layer,in,0,n-1);
pre(root);
int len=ans.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
printf("%d",ans[i]);
if(i!=len-1) printf(" "); //控制格式输出
}
return 0;
}