0 Java反射机制
反射(Reflection)是 Java 的高级特性之一,是框架实现的基础。
0.1 定义
Java 反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为 Java 语言的反射机制。
一般而言,当用户使用一个类的时候,应该获取这个类,而后通过这个类实例化对象,但是使用反射则可以相反的通过对象获取类中的信息。
通俗的讲反射就是可以在程序运行的时候动态装载类,查看类的信息,生成对象,或操作生成的对象。它允许运行中的 Java 程序获取自身的信息,自己能看到自己,就像照镜子一样。【源自gitChat】
1 Class类的使用
1.1 扫盲知识点
在Java的世界里,万事万物都是对象【PS: 类也是一个对象】。
坑01:java语言中,静态成员、普通数据类型不是对象
技巧01:普通的数据类型虽然不是对象,但是普通的数据类型都有对应的包装类来让其转化成一个对象
技巧02:静态的成员是属于类的而不是属于对象的,所以静态的成员不是对象
技巧03:所有的类都是java.lang.Class的实例对象【there is a class name Class:Class类的实例就是所有的实例对象所属的类】
1.2 Class类实例的创建
任何一个类都是Class类的实例对象,Class类的实例对象有三种表示方式;
类也是一个实例对象,是Class类的实例对象,这个对象我们称为该类的类类型;
例如:我们创建一个名为Foo的类,Foo类就是Class类的实例对象,假设Foo类对应的Class类的实例名为c1,那么我们就称c1是Foo类的类类型
总结:类类型就是Class类的一个实例,而且一个类只能有一个类类型,也就是所一个类只能和一个Class对应;虽然可以通过三种方式创建一个Class实例,但是针对一个类而言这三种方式创建得到的Class实例都是相等的,因为一个类的类类型只能和一个Class的实例对象。(即:一个类通过三种方式创建的类类型其实是一样的)
技巧01:不同的类对应的类类型都不一样,同理,不同的类对应的Class类实例都不一样
技巧02:同一个类只有一个类类型,同理,同一个类只和一个Class类实例对应;所以,同一个类通过不同方式创建的类类型都是一样的
1.2.1 利用class创建
任何一个类都默认拥有一个名为class的静态成员变量,该类可以利用class静态成员去创建该类的类实例。
例如:创建了一个名为Foo的类,执行 Foo.class 就会创建一个 Class 的实例,我们把得到的Class实例命名为c1,这个c1就是Foo类对应的类类型
1.2.2 利用实例对象创建
如果已经得到了某个类的实例,那么可以调用这个实例的成员方法getClass去创建该实例所属类的类类型
例如:创建了一个名为Foo的类,根据Foo创建了一个Foo的实例对象foo,我们可以利用foo去调用getClass来创建Class类的一个实例c2,这个c2就是foo所属类Foo的类类型
1.2.3 利用Class类创建
Class类有一个静态方法forName,Class类可以利用这个静态方法创建一个Class实例;forName方法的参数是一个类的全名
例如:创建了一个类Foo,该类的全名为 demo06_reflect.case01_class.Foo ,那么就可以利 Class.forName("demo06_reflect.case01_class.Foo")
去创建一个Class类的实例c3,这个c3就是Foo类的类类型

package demo06_reflect.case01_class; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-03 21:43 * @desc Class的使用 **/ public class Demo01_Class { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建Foo类的一个实例foo, Foo是foo的实例类型,foo是Foo的一个实例 Foo foo = new Foo(); // Class实例创建01:利用静态成员calss创建 Class c1 = Foo.class; // Class实例创建02:利用实例成员ngetClass创建 Class c2 = foo.getClass(); // 因为一个类只和一个Class实例对应,所以结果为true System.out.println(c1 == c2); // Class实例创建03:利用Class类的静态成员forName创建 try { Class c3 = Class.forName("demo06_reflect.case01_class.Foo"); System.out.println(c1 == c3); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Foo { public String name = "warrio"; public void pirnt() { System.out.println("foo"); } }
1.3 Class类实例的作用
可以利用Class类实例去创建对应类的实例
例如:c1是Foo类对应的Class实例(即:c1是Foo类的类类型),那么可以调用c1的实例方法newInstance去创建一个Foo实例foo,此时Foo类就称为foo实例的实例类型
技巧01:通过Class实例创建该实例对应类的实例是必须进行类型转换,因为Class实例创建出来的实例类型都是Object类型的;而且还必须进行异常处理
技巧02:Class实例对应的类必须拥有无参构造器【PS: 有参构造器会覆盖默认的无参构造器】

package demo06_reflect.case01_class; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-03 21:43 * @desc Class的使用 **/ public class Demo01_Class { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Foo foo = (Foo) Foo.class.newInstance(); foo.print(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Foo { public String name = "warrio"; public void print() { System.out.println("foo"); } public Foo() { } public Foo(String name) { this.name = name; } }
1.4 代码汇总

package demo06_reflect.case01_class; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-03 21:43 * @desc Class的使用 **/ public class Demo01_Class { public static void main(String[] args) { // Foo实例的表示 Foo f1 = new Foo(); // Foo也是一个实例对象【Foo类是Class类的实例对象】 /** * 任何一个类都是Class类的实例对象,Class类的实例对象有三种表示方式 */ // Class实例的表示01:任何一个类都有一个隐含的静态成员变量class Class c1 = Foo.class; // Class实例的表示02:任何一个实例对象通过getClass方法就可以创建出一个Class类的实例 Class c2 = f1.getClass(); /** * c1 c2 表示了Foo类的类类型(class type) * 类也是一个实例对象,是Class类的实例对象;这个对象我们成为该类的类类型 * 【类类型就是Class类的一个实例对象,而且一个类类型只能和一个Class的实例对应】 */ // c1 和 c2 都代表了Foo类的类类型,一个类只可能是Class类的一个实例对象 System.out.println(c1 == c2); // Class实例的表示03:直接利用 Class 类的 forName 静态方法实现 try { Class c3 = Class.forName("demo06_reflect.case01_class.Foo"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 04 可以利用该类的类类型创建该类的对象【通过c1/c2/c3创建Foo的实例】 // 前提:Foo类必须拥有无参数的构造方法 try { Foo f2 = (Foo) c2.newInstance(); f2.print(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Class c = Foo2.class; System.out.println(c1 == c); } } class Foo { void print(){ System.out.println("foo"); } } class Foo2 {}
2 动态加载类
2.1 扫盲知识点
Class.forName("类的全名") 不仅表示了类的类类型,还代表了动态加载类;
编译时刻加载类是静态加载类,运行时刻加载类是动态加载类 。
2.2 静态加载测试
2.2.1 需求
根据主函数中的参数创建对应的实例,并调用实例的方法
2.2.2 代码实现

public class Office { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello Boy"); if ("Word".equals(args[0])) { Word word = new Word(); word.start(); } if ("Excel".equals(args[0])) { Excel excel = new Excel(); excel.start(); } } }
2.2.3 编译
进入到存放源文件的文件夹,执行 javac "源文件名.java" 就可以对源文件进行编译
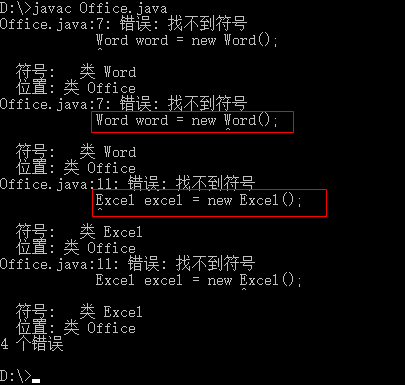
2.2.4 编译报错原因
在源代码中需要用到 Word 和 Excel 两个类,所以这两个类必须存在,而且必须经过编译
技巧01:因为源代码中是利用 new 关键字进行实例创建的,这种方式是静态加载类的方式,所以用到的类必须存在而且编译好的
技巧02:执行 javac Office.java 时会自动编译 Word.java、Excel.java 两个文件【PS: 前提是存在】

public class Word { public void start() { System.out.println("Word start..."); } }

public class Excel { public void start() { System.out.println("Excel start..."); } }
2.2.5 运行测试
运行 Office 时,传入 Word 或者 Excel ,查看效果:
例如: java Office Word

2.3 静态加载的缺点
需要进行静态加载的类必须存在,如果有一个不存在的话就会导致整个代码编译失败
例如:删掉Excel类,再次执行 javac Office.java

2.4 动态加载类的作用
技巧01根据类的全名去动态加载类是在运行期间进行的
2.4.1 需求
根据不同的类名称去动态加载不同的类,让后调用该类的实例【PS: 这里的不同类指的是实现了同一接口的不同实现类】
2.4.2 思路
》定义一个OfficeAble接口,让Word和Excel都实现这个接口
》通过Class.fromName来动态加载类得到的类类型
》通过类类型去创建实例,将的到的实例类型指定为OfficeAble类型
》利用多态的特性去调用实例的方法
2.4.3 代码改进
技巧01:动态加载用到的类需要提前编译好,不然运行时会找不到需要的文件
技巧02:动态加载类可以根据不同的参数动态加载不同的实现类

public interface OfficeAble { void start(); }

public class Word implements OfficeAble { public void start() { System.out.println("Word start..."); } }

public class Excel implements OfficeAble { public void start() { System.out.println("Excel start..."); } }

public class OfficeBetter { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class c = Class.forName(args[0]); OfficeAble officeAble = (OfficeAble)c.newInstance(); officeAble.start(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2.5 动态加载使用场景
业务功能更新,某个业务需要更新时,只需要一个重新实现了该业务接口的类,将其进行编译后,程序调用时修改调用的类名即可,这样就可以通过类的动态加载来实现局部业务的更新。
3 类类型说明
除了类拥有类类型外,基本的数据类型也拥有类类型。
技巧01:基本类型和基本类型对应的包装类型各自都有各自的类类型
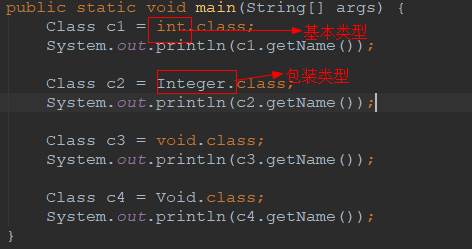

package demo06_reflect.case03_method; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-05 22:25 * @desc 基本类型和void都有类类型 **/ public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Class c1 = int.class; System.out.println(c1.getName()); Class c2 = Integer.class; System.out.println(c2.getName()); Class c3 = void.class; System.out.println(c3.getName()); Class c4 = Void.class; System.out.println(c4.getName()); } }
4 获取类的信息
通过一个类的类型可以获取到该类的所有信息,详情可以参见Class源码

/* * Copyright (c) 1994, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * */ package java.lang; import java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.lang.reflect.GenericArrayType; import java.lang.reflect.GenericDeclaration; import java.lang.reflect.Member; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Executable; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.lang.reflect.TypeVariable; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedType; import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.ObjectStreamField; import java.security.AccessController; import java.security.PrivilegedAction; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Objects; import sun.misc.Unsafe; import sun.reflect.CallerSensitive; import sun.reflect.ConstantPool; import sun.reflect.Reflection; import sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory; import sun.reflect.generics.factory.CoreReflectionFactory; import sun.reflect.generics.factory.GenericsFactory; import sun.reflect.generics.repository.ClassRepository; import sun.reflect.generics.repository.MethodRepository; import sun.reflect.generics.repository.ConstructorRepository; import sun.reflect.generics.scope.ClassScope; import sun.security.util.SecurityConstants; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import sun.reflect.annotation.*; import sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil; /** * Instances of the class {@code Class} represent classes and * interfaces in a running Java application. An enum is a kind of * class and an annotation is a kind of interface. Every array also * belongs to a class that is reflected as a {@code Class} object * that is shared by all arrays with the same element type and number * of dimensions. The primitive Java types ({@code boolean}, * {@code byte}, {@code char}, {@code short}, * {@code int}, {@code long}, {@code float}, and * {@code double}), and the keyword {@code void} are also * represented as {@code Class} objects. * * <p> {@code Class} has no public constructor. Instead {@code Class} * objects are constructed automatically by the Java Virtual Machine as classes * are loaded and by calls to the {@code defineClass} method in the class * loader. * * <p> The following example uses a {@code Class} object to print the * class name of an object: * * <blockquote><pre> * void printClassName(Object obj) { * System.out.println("The class of " + obj + * " is " + obj.getClass().getName()); * } * </pre></blockquote> * * <p> It is also possible to get the {@code Class} object for a named * type (or for void) using a class literal. See Section 15.8.2 of * <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>. * For example: * * <blockquote> * {@code System.out.println("The name of class Foo is: "+Foo.class.getName());} * </blockquote> * * @param <T> the type of the class modeled by this {@code Class} * object. For example, the type of {@code String.class} is {@code * Class<String>}. Use {@code Class<?>} if the class being modeled is * unknown. * * @author unascribed * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#defineClass(byte[], int, int) * @since JDK1.0 */ public final class Class<T> implements java.io.Serializable, GenericDeclaration, Type, AnnotatedElement { private static final int ANNOTATION= 0x00002000; private static final int ENUM = 0x00004000; private static final int SYNTHETIC = 0x00001000; private static native void registerNatives(); static { registerNatives(); } /* * Private constructor. Only the Java Virtual Machine creates Class objects. * This constructor is not used and prevents the default constructor being * generated. */ private Class(ClassLoader loader) { // Initialize final field for classLoader. The initialization value of non-null // prevents future JIT optimizations from assuming this final field is null. classLoader = loader; } /** * Converts the object to a string. The string representation is the * string "class" or "interface", followed by a space, and then by the * fully qualified name of the class in the format returned by * {@code getName}. If this {@code Class} object represents a * primitive type, this method returns the name of the primitive type. If * this {@code Class} object represents void this method returns * "void". * * @return a string representation of this class object. */ public String toString() { return (isInterface() ? "interface " : (isPrimitive() ? "" : "class ")) + getName(); } /** * Returns a string describing this {@code Class}, including * information about modifiers and type parameters. * * The string is formatted as a list of type modifiers, if any, * followed by the kind of type (empty string for primitive types * and {@code class}, {@code enum}, {@code interface}, or * <code>@</code>{@code interface}, as appropriate), followed * by the type's name, followed by an angle-bracketed * comma-separated list of the type's type parameters, if any. * * A space is used to separate modifiers from one another and to * separate any modifiers from the kind of type. The modifiers * occur in canonical order. If there are no type parameters, the * type parameter list is elided. * * <p>Note that since information about the runtime representation * of a type is being generated, modifiers not present on the * originating source code or illegal on the originating source * code may be present. * * @return a string describing this {@code Class}, including * information about modifiers and type parameters * * @since 1.8 */ public String toGenericString() { if (isPrimitive()) { return toString(); } else { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // Class modifiers are a superset of interface modifiers int modifiers = getModifiers() & Modifier.classModifiers(); if (modifiers != 0) { sb.append(Modifier.toString(modifiers)); sb.append(' '); } if (isAnnotation()) { sb.append('@'); } if (isInterface()) { // Note: all annotation types are interfaces sb.append("interface"); } else { if (isEnum()) sb.append("enum"); else sb.append("class"); } sb.append(' '); sb.append(getName()); TypeVariable<?>[] typeparms = getTypeParameters(); if (typeparms.length > 0) { boolean first = true; sb.append('<'); for(TypeVariable<?> typeparm: typeparms) { if (!first) sb.append(','); sb.append(typeparm.getTypeName()); first = false; } sb.append('>'); } return sb.toString(); } } /** * Returns the {@code Class} object associated with the class or * interface with the given string name. Invoking this method is * equivalent to: * * <blockquote> * {@code Class.forName(className, true, currentLoader)} * </blockquote> * * where {@code currentLoader} denotes the defining class loader of * the current class. * * <p> For example, the following code fragment returns the * runtime {@code Class} descriptor for the class named * {@code java.lang.Thread}: * * <blockquote> * {@code Class t = Class.forName("java.lang.Thread")} * </blockquote> * <p> * A call to {@code forName("X")} causes the class named * {@code X} to be initialized. * * @param className the fully qualified name of the desired class. * @return the {@code Class} object for the class with the * specified name. * @exception LinkageError if the linkage fails * @exception ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization provoked * by this method fails * @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class cannot be located */ @CallerSensitive public static Class<?> forName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller); } /** * Returns the {@code Class} object associated with the class or * interface with the given string name, using the given class loader. * Given the fully qualified name for a class or interface (in the same * format returned by {@code getName}) this method attempts to * locate, load, and link the class or interface. The specified class * loader is used to load the class or interface. If the parameter * {@code loader} is null, the class is loaded through the bootstrap * class loader. The class is initialized only if the * {@code initialize} parameter is {@code true} and if it has * not been initialized earlier. * * <p> If {@code name} denotes a primitive type or void, an attempt * will be made to locate a user-defined class in the unnamed package whose * name is {@code name}. Therefore, this method cannot be used to * obtain any of the {@code Class} objects representing primitive * types or void. * * <p> If {@code name} denotes an array class, the component type of * the array class is loaded but not initialized. * * <p> For example, in an instance method the expression: * * <blockquote> * {@code Class.forName("Foo")} * </blockquote> * * is equivalent to: * * <blockquote> * {@code Class.forName("Foo", true, this.getClass().getClassLoader())} * </blockquote> * * Note that this method throws errors related to loading, linking or * initializing as specified in Sections 12.2, 12.3 and 12.4 of <em>The * Java Language Specification</em>. * Note that this method does not check whether the requested class * is accessible to its caller. * * <p> If the {@code loader} is {@code null}, and a security * manager is present, and the caller's class loader is not null, then this * method calls the security manager's {@code checkPermission} method * with a {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission to * ensure it's ok to access the bootstrap class loader. * * @param name fully qualified name of the desired class * @param initialize if {@code true} the class will be initialized. * See Section 12.4 of <em>The Java Language Specification</em>. * @param loader class loader from which the class must be loaded * @return class object representing the desired class * * @exception LinkageError if the linkage fails * @exception ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization provoked * by this method fails * @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class cannot be located by * the specified class loader * * @see java.lang.Class#forName(String) * @see java.lang.ClassLoader * @since 1.2 */ @CallerSensitive public static Class<?> forName(String name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = null; SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { // Reflective call to get caller class is only needed if a security manager // is present. Avoid the overhead of making this call otherwise. caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); if (sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader)) { ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller); if (!sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) { sm.checkPermission( SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); } } } return forName0(name, initialize, loader, caller); } /** Called after security check for system loader access checks have been made. */ private static native Class<?> forName0(String name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader, Class<?> caller) throws ClassNotFoundException; /** * Creates a new instance of the class represented by this {@code Class} * object. The class is instantiated as if by a {@code new} * expression with an empty argument list. The class is initialized if it * has not already been initialized. * * <p>Note that this method propagates any exception thrown by the * nullary constructor, including a checked exception. Use of * this method effectively bypasses the compile-time exception * checking that would otherwise be performed by the compiler. * The {@link * java.lang.reflect.Constructor#newInstance(java.lang.Object...) * Constructor.newInstance} method avoids this problem by wrapping * any exception thrown by the constructor in a (checked) {@link * java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException}. * * @return a newly allocated instance of the class represented by this * object. * @throws IllegalAccessException if the class or its nullary * constructor is not accessible. * @throws InstantiationException * if this {@code Class} represents an abstract class, * an interface, an array class, a primitive type, or void; * or if the class has no nullary constructor; * or if the instantiation fails for some other reason. * @throws ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization * provoked by this method fails. * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. */ @CallerSensitive public T newInstance() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false); } // NOTE: the following code may not be strictly correct under // the current Java memory model. // Constructor lookup if (cachedConstructor == null) { if (this == Class.class) { throw new IllegalAccessException( "Can not call newInstance() on the Class for java.lang.Class" ); } try { Class<?>[] empty = {}; final Constructor<T> c = getConstructor0(empty, Member.DECLARED); // Disable accessibility checks on the constructor // since we have to do the security check here anyway // (the stack depth is wrong for the Constructor's // security check to work) java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged( new java.security.PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { c.setAccessible(true); return null; } }); cachedConstructor = c; } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw (InstantiationException) new InstantiationException(getName()).initCause(e); } } Constructor<T> tmpConstructor = cachedConstructor; // Security check (same as in java.lang.reflect.Constructor) int modifiers = tmpConstructor.getModifiers(); if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(this, modifiers)) { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); if (newInstanceCallerCache != caller) { Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, this, null, modifiers); newInstanceCallerCache = caller; } } // Run constructor try { return tmpConstructor.newInstance((Object[])null); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { Unsafe.getUnsafe().throwException(e.getTargetException()); // Not reached return null; } } private volatile transient Constructor<T> cachedConstructor; private volatile transient Class<?> newInstanceCallerCache; /** * Determines if the specified {@code Object} is assignment-compatible * with the object represented by this {@code Class}. This method is * the dynamic equivalent of the Java language {@code instanceof} * operator. The method returns {@code true} if the specified * {@code Object} argument is non-null and can be cast to the * reference type represented by this {@code Class} object without * raising a {@code ClassCastException.} It returns {@code false} * otherwise. * * <p> Specifically, if this {@code Class} object represents a * declared class, this method returns {@code true} if the specified * {@code Object} argument is an instance of the represented class (or * of any of its subclasses); it returns {@code false} otherwise. If * this {@code Class} object represents an array class, this method * returns {@code true} if the specified {@code Object} argument * can be converted to an object of the array class by an identity * conversion or by a widening reference conversion; it returns * {@code false} otherwise. If this {@code Class} object * represents an interface, this method returns {@code true} if the * class or any superclass of the specified {@code Object} argument * implements this interface; it returns {@code false} otherwise. If * this {@code Class} object represents a primitive type, this method * returns {@code false}. * * @param obj the object to check * @return true if {@code obj} is an instance of this class * * @since JDK1.1 */ public native boolean isInstance(Object obj); /** * Determines if the class or interface represented by this * {@code Class} object is either the same as, or is a superclass or * superinterface of, the class or interface represented by the specified * {@code Class} parameter. It returns {@code true} if so; * otherwise it returns {@code false}. If this {@code Class} * object represents a primitive type, this method returns * {@code true} if the specified {@code Class} parameter is * exactly this {@code Class} object; otherwise it returns * {@code false}. * * <p> Specifically, this method tests whether the type represented by the * specified {@code Class} parameter can be converted to the type * represented by this {@code Class} object via an identity conversion * or via a widening reference conversion. See <em>The Java Language * Specification</em>, sections 5.1.1 and 5.1.4 , for details. * * @param cls the {@code Class} object to be checked * @return the {@code boolean} value indicating whether objects of the * type {@code cls} can be assigned to objects of this class * @exception NullPointerException if the specified Class parameter is * null. * @since JDK1.1 */ public native boolean isAssignableFrom(Class<?> cls); /** * Determines if the specified {@code Class} object represents an * interface type. * * @return {@code true} if this object represents an interface; * {@code false} otherwise. */ public native boolean isInterface(); /** * Determines if this {@code Class} object represents an array class. * * @return {@code true} if this object represents an array class; * {@code false} otherwise. * @since JDK1.1 */ public native boolean isArray(); /** * Determines if the specified {@code Class} object represents a * primitive type. * * <p> There are nine predefined {@code Class} objects to represent * the eight primitive types and void. These are created by the Java * Virtual Machine, and have the same names as the primitive types that * they represent, namely {@code boolean}, {@code byte}, * {@code char}, {@code short}, {@code int}, * {@code long}, {@code float}, and {@code double}. * * <p> These objects may only be accessed via the following public static * final variables, and are the only {@code Class} objects for which * this method returns {@code true}. * * @return true if and only if this class represents a primitive type * * @see java.lang.Boolean#TYPE * @see java.lang.Character#TYPE * @see java.lang.Byte#TYPE * @see java.lang.Short#TYPE * @see java.lang.Integer#TYPE * @see java.lang.Long#TYPE * @see java.lang.Float#TYPE * @see java.lang.Double#TYPE * @see java.lang.Void#TYPE * @since JDK1.1 */ public native boolean isPrimitive(); /** * Returns true if this {@code Class} object represents an annotation * type. Note that if this method returns true, {@link #isInterface()} * would also return true, as all annotation types are also interfaces. * * @return {@code true} if this class object represents an annotation * type; {@code false} otherwise * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isAnnotation() { return (getModifiers() & ANNOTATION) != 0; } /** * Returns {@code true} if this class is a synthetic class; * returns {@code false} otherwise. * @return {@code true} if and only if this class is a synthetic class as * defined by the Java Language Specification. * @jls 13.1 The Form of a Binary * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isSynthetic() { return (getModifiers() & SYNTHETIC) != 0; } /** * Returns the name of the entity (class, interface, array class, * primitive type, or void) represented by this {@code Class} object, * as a {@code String}. * * <p> If this class object represents a reference type that is not an * array type then the binary name of the class is returned, as specified * by * <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>. * * <p> If this class object represents a primitive type or void, then the * name returned is a {@code String} equal to the Java language * keyword corresponding to the primitive type or void. * * <p> If this class object represents a class of arrays, then the internal * form of the name consists of the name of the element type preceded by * one or more '{@code [}' characters representing the depth of the array * nesting. The encoding of element type names is as follows: * * <blockquote><table summary="Element types and encodings"> * <tr><th> Element Type <th> <th> Encoding * <tr><td> boolean <td> <td align=center> Z * <tr><td> byte <td> <td align=center> B * <tr><td> char <td> <td align=center> C * <tr><td> class or interface * <td> <td align=center> L<i>classname</i>; * <tr><td> double <td> <td align=center> D * <tr><td> float <td> <td align=center> F * <tr><td> int <td> <td align=center> I * <tr><td> long <td> <td align=center> J * <tr><td> short <td> <td align=center> S * </table></blockquote> * * <p> The class or interface name <i>classname</i> is the binary name of * the class specified above. * * <p> Examples: * <blockquote><pre> * String.class.getName() * returns "java.lang.String" * byte.class.getName() * returns "byte" * (new Object[3]).getClass().getName() * returns "[Ljava.lang.Object;" * (new int[3][4][5][6][7][8][9]).getClass().getName() * returns "[[[[[[[I" * </pre></blockquote> * * @return the name of the class or interface * represented by this object. */ public String getName() { String name = this.name; if (name == null) this.name = name = getName0(); return name; } // cache the name to reduce the number of calls into the VM private transient String name; private native String getName0(); /** * Returns the class loader for the class. Some implementations may use * null to represent the bootstrap class loader. This method will return * null in such implementations if this class was loaded by the bootstrap * class loader. * * <p> If a security manager is present, and the caller's class loader is * not null and the caller's class loader is not the same as or an ancestor of * the class loader for the class whose class loader is requested, then * this method calls the security manager's {@code checkPermission} * method with a {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} * permission to ensure it's ok to access the class loader for the class. * * <p>If this object * represents a primitive type or void, null is returned. * * @return the class loader that loaded the class or interface * represented by this object. * @throws SecurityException * if a security manager exists and its * {@code checkPermission} method denies * access to the class loader for the class. * @see java.lang.ClassLoader * @see SecurityManager#checkPermission * @see java.lang.RuntimePermission */ @CallerSensitive public ClassLoader getClassLoader() { ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (cl == null) return null; SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { ClassLoader.checkClassLoaderPermission(cl, Reflection.getCallerClass()); } return cl; } // Package-private to allow ClassLoader access ClassLoader getClassLoader0() { return classLoader; } // Initialized in JVM not by private constructor // This field is filtered from reflection access, i.e. getDeclaredField // will throw NoSuchFieldException private final ClassLoader classLoader; /** * Returns an array of {@code TypeVariable} objects that represent the * type variables declared by the generic declaration represented by this * {@code GenericDeclaration} object, in declaration order. Returns an * array of length 0 if the underlying generic declaration declares no type * variables. * * @return an array of {@code TypeVariable} objects that represent * the type variables declared by this generic declaration * @throws java.lang.reflect.GenericSignatureFormatError if the generic * signature of this generic declaration does not conform to * the format specified in * <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite> * @since 1.5 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public TypeVariable<Class<T>>[] getTypeParameters() { ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo(); if (info != null) return (TypeVariable<Class<T>>[])info.getTypeParameters(); else return (TypeVariable<Class<T>>[])new TypeVariable<?>[0]; } /** * Returns the {@code Class} representing the superclass of the entity * (class, interface, primitive type or void) represented by this * {@code Class}. If this {@code Class} represents either the * {@code Object} class, an interface, a primitive type, or void, then * null is returned. If this object represents an array class then the * {@code Class} object representing the {@code Object} class is * returned. * * @return the superclass of the class represented by this object. */ public native Class<? super T> getSuperclass(); /** * Returns the {@code Type} representing the direct superclass of * the entity (class, interface, primitive type or void) represented by * this {@code Class}. * * <p>If the superclass is a parameterized type, the {@code Type} * object returned must accurately reflect the actual type * parameters used in the source code. The parameterized type * representing the superclass is created if it had not been * created before. See the declaration of {@link * java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType ParameterizedType} for the * semantics of the creation process for parameterized types. If * this {@code Class} represents either the {@code Object} * class, an interface, a primitive type, or void, then null is * returned. If this object represents an array class then the * {@code Class} object representing the {@code Object} class is * returned. * * @throws java.lang.reflect.GenericSignatureFormatError if the generic * class signature does not conform to the format specified in * <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite> * @throws TypeNotPresentException if the generic superclass * refers to a non-existent type declaration * @throws java.lang.reflect.MalformedParameterizedTypeException if the * generic superclass refers to a parameterized type that cannot be * instantiated for any reason * @return the superclass of the class represented by this object * @since 1.5 */ public Type getGenericSuperclass() { ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo(); if (info == null) { return getSuperclass(); } // Historical irregularity: // Generic signature marks interfaces with superclass = Object // but this API returns null for interfaces if (isInterface()) { return null; } return info.getSuperclass(); } /** * Gets the package for this class. The class loader of this class is used * to find the package. If the class was loaded by the bootstrap class * loader the set of packages loaded from CLASSPATH is searched to find the * package of the class. Null is returned if no package object was created * by the class loader of this class. * * <p> Packages have attributes for versions and specifications only if the * information was defined in the manifests that accompany the classes, and * if the class loader created the package instance with the attributes * from the manifest. * * @return the package of the class, or null if no package * information is available from the archive or codebase. */ public Package getPackage() { return Package.getPackage(this); } /** * Determines the interfaces implemented by the class or interface * represented by this object. * * <p> If this object represents a class, the return value is an array * containing objects representing all interfaces implemented by the * class. The order of the interface objects in the array corresponds to * the order of the interface names in the {@code implements} clause * of the declaration of the class represented by this object. For * example, given the declaration: * <blockquote> * {@code class Shimmer implements FloorWax, DessertTopping { ... }} * </blockquote> * suppose the value of {@code s} is an instance of * {@code Shimmer}; the value of the expression: * <blockquote> * {@code s.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]} * </blockquote> * is the {@code Class} object that represents interface * {@code FloorWax}; and the value of: * <blockquote> * {@code s.getClass().getInterfaces()[1]} * </blockquote> * is the {@code Class} object that represents interface * {@code DessertTopping}. * * <p> If this object represents an interface, the array contains objects * representing all interfaces extended by the interface. The order of the * interface objects in the array corresponds to the order of the interface * names in the {@code extends} clause of the declaration of the * interface represented by this object. * * <p> If this object represents a class or interface that implements no * interfaces, the method returns an array of length 0. * * <p> If this object represents a primitive type or void, the method * returns an array of length 0. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, the * interfaces {@code Cloneable} and {@code java.io.Serializable} are * returned in that order. * * @return an array of interfaces implemented by this class. */ public Class<?>[] getInterfaces() { ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd == null) { // no cloning required return getInterfaces0(); } else { Class<?>[] interfaces = rd.interfaces; if (interfaces == null) { interfaces = getInterfaces0(); rd.interfaces = interfaces; } // defensively copy before handing over to user code return interfaces.clone(); } } private native Class<?>[] getInterfaces0(); /** * Returns the {@code Type}s representing the interfaces * directly implemented by the class or interface represented by * this object. * * <p>If a superinterface is a parameterized type, the * {@code Type} object returned for it must accurately reflect * the actual type parameters used in the source code. The * parameterized type representing each superinterface is created * if it had not been created before. See the declaration of * {@link java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType ParameterizedType} * for the semantics of the creation process for parameterized * types. * * <p> If this object represents a class, the return value is an * array containing objects representing all interfaces * implemented by the class. The order of the interface objects in * the array corresponds to the order of the interface names in * the {@code implements} clause of the declaration of the class * represented by this object. In the case of an array class, the * interfaces {@code Cloneable} and {@code Serializable} are * returned in that order. * * <p>If this object represents an interface, the array contains * objects representing all interfaces directly extended by the * interface. The order of the interface objects in the array * corresponds to the order of the interface names in the * {@code extends} clause of the declaration of the interface * represented by this object. * * <p>If this object represents a class or interface that * implements no interfaces, the method returns an array of length * 0. * * <p>If this object represents a primitive type or void, the * method returns an array of length 0. * * @throws java.lang.reflect.GenericSignatureFormatError * if the generic class signature does not conform to the format * specified in * <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite> * @throws TypeNotPresentException if any of the generic * superinterfaces refers to a non-existent type declaration * @throws java.lang.reflect.MalformedParameterizedTypeException * if any of the generic superinterfaces refer to a parameterized * type that cannot be instantiated for any reason * @return an array of interfaces implemented by this class * @since 1.5 */ public Type[] getGenericInterfaces() { ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo(); return (info == null) ? getInterfaces() : info.getSuperInterfaces(); } /** * Returns the {@code Class} representing the component type of an * array. If this class does not represent an array class this method * returns null. * * @return the {@code Class} representing the component type of this * class if this class is an array * @see java.lang.reflect.Array * @since JDK1.1 */ public native Class<?> getComponentType(); /** * Returns the Java language modifiers for this class or interface, encoded * in an integer. The modifiers consist of the Java Virtual Machine's * constants for {@code public}, {@code protected}, * {@code private}, {@code final}, {@code static}, * {@code abstract} and {@code interface}; they should be decoded * using the methods of class {@code Modifier}. * * <p> If the underlying class is an array class, then its * {@code public}, {@code private} and {@code protected} * modifiers are the same as those of its component type. If this * {@code Class} represents a primitive type or void, its * {@code public} modifier is always {@code true}, and its * {@code protected} and {@code private} modifiers are always * {@code false}. If this object represents an array class, a * primitive type or void, then its {@code final} modifier is always * {@code true} and its interface modifier is always * {@code false}. The values of its other modifiers are not determined * by this specification. * * <p> The modifier encodings are defined in <em>The Java Virtual Machine * Specification</em>, table 4.1. * * @return the {@code int} representing the modifiers for this class * @see java.lang.reflect.Modifier * @since JDK1.1 */ public native int getModifiers(); /** * Gets the signers of this class. * * @return the signers of this class, or null if there are no signers. In * particular, this method returns null if this object represents * a primitive type or void. * @since JDK1.1 */ public native Object[] getSigners(); /** * Set the signers of this class. */ native void setSigners(Object[] signers); /** * If this {@code Class} object represents a local or anonymous * class within a method, returns a {@link * java.lang.reflect.Method Method} object representing the * immediately enclosing method of the underlying class. Returns * {@code null} otherwise. * * In particular, this method returns {@code null} if the underlying * class is a local or anonymous class immediately enclosed by a type * declaration, instance initializer or static initializer. * * @return the immediately enclosing method of the underlying class, if * that class is a local or anonymous class; otherwise {@code null}. * * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of the enclosing class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the methods within the enclosing class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the enclosing class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of the enclosing class * * </ul> * @since 1.5 */ @CallerSensitive public Method getEnclosingMethod() throws SecurityException { EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo(); if (enclosingInfo == null) return null; else { if (!enclosingInfo.isMethod()) return null; MethodRepository typeInfo = MethodRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(), getFactory()); Class<?> returnType = toClass(typeInfo.getReturnType()); Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes(); Class<?>[] parameterClasses = new Class<?>[parameterTypes.length]; // Convert Types to Classes; returned types *should* // be class objects since the methodDescriptor's used // don't have generics information for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++) parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]); // Perform access check Class<?> enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass(); enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); /* * Loop over all declared methods; match method name, * number of and type of parameters, *and* return * type. Matching return type is also necessary * because of covariant returns, etc. */ for(Method m: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredMethods()) { if (m.getName().equals(enclosingInfo.getName()) ) { Class<?>[] candidateParamClasses = m.getParameterTypes(); if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) { boolean matches = true; for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) { if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) { matches = false; break; } } if (matches) { // finally, check return type if (m.getReturnType().equals(returnType) ) return m; } } } } throw new InternalError("Enclosing method not found"); } } private native Object[] getEnclosingMethod0(); private EnclosingMethodInfo getEnclosingMethodInfo() { Object[] enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethod0(); if (enclosingInfo == null) return null; else { return new EnclosingMethodInfo(enclosingInfo); } } private final static class EnclosingMethodInfo { private Class<?> enclosingClass; private String name; private String descriptor; private EnclosingMethodInfo(Object[] enclosingInfo) { if (enclosingInfo.length != 3) throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information"); try { // The array is expected to have three elements: // the immediately enclosing class enclosingClass = (Class<?>) enclosingInfo[0]; assert(enclosingClass != null); // the immediately enclosing method or constructor's // name (can be null). name = (String) enclosingInfo[1]; // the immediately enclosing method or constructor's // descriptor (null iff name is). descriptor = (String) enclosingInfo[2]; assert((name != null && descriptor != null) || name == descriptor); } catch (ClassCastException cce) { throw new InternalError("Invalid type in enclosing method information", cce); } } boolean isPartial() { return enclosingClass == null || name == null || descriptor == null; } boolean isConstructor() { return !isPartial() && "<init>".equals(name); } boolean isMethod() { return !isPartial() && !isConstructor() && !"<clinit>".equals(name); } Class<?> getEnclosingClass() { return enclosingClass; } String getName() { return name; } String getDescriptor() { return descriptor; } } private static Class<?> toClass(Type o) { if (o instanceof GenericArrayType) return Array.newInstance(toClass(((GenericArrayType)o).getGenericComponentType()), 0) .getClass(); return (Class<?>)o; } /** * If this {@code Class} object represents a local or anonymous * class within a constructor, returns a {@link * java.lang.reflect.Constructor Constructor} object representing * the immediately enclosing constructor of the underlying * class. Returns {@code null} otherwise. In particular, this * method returns {@code null} if the underlying class is a local * or anonymous class immediately enclosed by a type declaration, * instance initializer or static initializer. * * @return the immediately enclosing constructor of the underlying class, if * that class is a local or anonymous class; otherwise {@code null}. * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of the enclosing class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the constructors within the enclosing class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the enclosing class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of the enclosing class * * </ul> * @since 1.5 */ @CallerSensitive public Constructor<?> getEnclosingConstructor() throws SecurityException { EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo(); if (enclosingInfo == null) return null; else { if (!enclosingInfo.isConstructor()) return null; ConstructorRepository typeInfo = ConstructorRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(), getFactory()); Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes(); Class<?>[] parameterClasses = new Class<?>[parameterTypes.length]; // Convert Types to Classes; returned types *should* // be class objects since the methodDescriptor's used // don't have generics information for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++) parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]); // Perform access check Class<?> enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass(); enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); /* * Loop over all declared constructors; match number * of and type of parameters. */ for(Constructor<?> c: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredConstructors()) { Class<?>[] candidateParamClasses = c.getParameterTypes(); if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) { boolean matches = true; for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) { if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) { matches = false; break; } } if (matches) return c; } } throw new InternalError("Enclosing constructor not found"); } } /** * If the class or interface represented by this {@code Class} object * is a member of another class, returns the {@code Class} object * representing the class in which it was declared. This method returns * null if this class or interface is not a member of any other class. If * this {@code Class} object represents an array class, a primitive * type, or void,then this method returns null. * * @return the declaring class for this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and the caller's * class loader is not the same as or an ancestor of the class * loader for the declaring class and invocation of {@link * SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess s.checkPackageAccess()} * denies access to the package of the declaring class * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Class<?> getDeclaringClass() throws SecurityException { final Class<?> candidate = getDeclaringClass0(); if (candidate != null) candidate.checkPackageAccess( ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true); return candidate; } private native Class<?> getDeclaringClass0(); /** * Returns the immediately enclosing class of the underlying * class. If the underlying class is a top level class this * method returns {@code null}. * @return the immediately enclosing class of the underlying class * @exception SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and the caller's * class loader is not the same as or an ancestor of the class * loader for the enclosing class and invocation of {@link * SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess s.checkPackageAccess()} * denies access to the package of the enclosing class * @since 1.5 */ @CallerSensitive public Class<?> getEnclosingClass() throws SecurityException { // There are five kinds of classes (or interfaces): // a) Top level classes // b) Nested classes (static member classes) // c) Inner classes (non-static member classes) // d) Local classes (named classes declared within a method) // e) Anonymous classes // JVM Spec 4.8.6: A class must have an EnclosingMethod // attribute if and only if it is a local class or an // anonymous class. EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo(); Class<?> enclosingCandidate; if (enclosingInfo == null) { // This is a top level or a nested class or an inner class (a, b, or c) enclosingCandidate = getDeclaringClass(); } else { Class<?> enclosingClass = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass(); // This is a local class or an anonymous class (d or e) if (enclosingClass == this || enclosingClass == null) throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information"); else enclosingCandidate = enclosingClass; } if (enclosingCandidate != null) enclosingCandidate.checkPackageAccess( ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true); return enclosingCandidate; } /** * Returns the simple name of the underlying class as given in the * source code. Returns an empty string if the underlying class is * anonymous. * * <p>The simple name of an array is the simple name of the * component type with "[]" appended. In particular the simple * name of an array whose component type is anonymous is "[]". * * @return the simple name of the underlying class * @since 1.5 */ public String getSimpleName() { if (isArray()) return getComponentType().getSimpleName()+"[]"; String simpleName = getSimpleBinaryName(); if (simpleName == null) { // top level class simpleName = getName(); return simpleName.substring(simpleName.lastIndexOf(".")+1); // strip the package name } // According to JLS3 "Binary Compatibility" (13.1) the binary // name of non-package classes (not top level) is the binary // name of the immediately enclosing class followed by a '$' followed by: // (for nested and inner classes): the simple name. // (for local classes): 1 or more digits followed by the simple name. // (for anonymous classes): 1 or more digits. // Since getSimpleBinaryName() will strip the binary name of // the immediatly enclosing class, we are now looking at a // string that matches the regular expression "$[0-9]*" // followed by a simple name (considering the simple of an // anonymous class to be the empty string). // Remove leading "$[0-9]*" from the name int length = simpleName.length(); if (length < 1 || simpleName.charAt(0) != '$') throw new InternalError("Malformed class name"); int index = 1; while (index < length && isAsciiDigit(simpleName.charAt(index))) index++; // Eventually, this is the empty string iff this is an anonymous class return simpleName.substring(index); } /** * Return an informative string for the name of this type. * * @return an informative string for the name of this type * @since 1.8 */ public String getTypeName() { if (isArray()) { try { Class<?> cl = this; int dimensions = 0; while (cl.isArray()) { dimensions++; cl = cl.getComponentType(); } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(cl.getName()); for (int i = 0; i < dimensions; i++) { sb.append("[]"); } return sb.toString(); } catch (Throwable e) { /*FALLTHRU*/ } } return getName(); } /** * Character.isDigit answers {@code true} to some non-ascii * digits. This one does not. */ private static boolean isAsciiDigit(char c) { return '0' <= c && c <= '9'; } /** * Returns the canonical name of the underlying class as * defined by the Java Language Specification. Returns null if * the underlying class does not have a canonical name (i.e., if * it is a local or anonymous class or an array whose component * type does not have a canonical name). * @return the canonical name of the underlying class if it exists, and * {@code null} otherwise. * @since 1.5 */ public String getCanonicalName() { if (isArray()) { String canonicalName = getComponentType().getCanonicalName(); if (canonicalName != null) return canonicalName + "[]"; else return null; } if (isLocalOrAnonymousClass()) return null; Class<?> enclosingClass = getEnclosingClass(); if (enclosingClass == null) { // top level class return getName(); } else { String enclosingName = enclosingClass.getCanonicalName(); if (enclosingName == null) return null; return enclosingName + "." + getSimpleName(); } } /** * Returns {@code true} if and only if the underlying class * is an anonymous class. * * @return {@code true} if and only if this class is an anonymous class. * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isAnonymousClass() { return "".equals(getSimpleName()); } /** * Returns {@code true} if and only if the underlying class * is a local class. * * @return {@code true} if and only if this class is a local class. * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isLocalClass() { return isLocalOrAnonymousClass() && !isAnonymousClass(); } /** * Returns {@code true} if and only if the underlying class * is a member class. * * @return {@code true} if and only if this class is a member class. * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isMemberClass() { return getSimpleBinaryName() != null && !isLocalOrAnonymousClass(); } /** * Returns the "simple binary name" of the underlying class, i.e., * the binary name without the leading enclosing class name. * Returns {@code null} if the underlying class is a top level * class. */ private String getSimpleBinaryName() { Class<?> enclosingClass = getEnclosingClass(); if (enclosingClass == null) // top level class return null; // Otherwise, strip the enclosing class' name try { return getName().substring(enclosingClass.getName().length()); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new InternalError("Malformed class name", ex); } } /** * Returns {@code true} if this is a local class or an anonymous * class. Returns {@code false} otherwise. */ private boolean isLocalOrAnonymousClass() { // JVM Spec 4.8.6: A class must have an EnclosingMethod // attribute if and only if it is a local class or an // anonymous class. return getEnclosingMethodInfo() != null; } /** * Returns an array containing {@code Class} objects representing all * the public classes and interfaces that are members of the class * represented by this {@code Class} object. This includes public * class and interface members inherited from superclasses and public class * and interface members declared by the class. This method returns an * array of length 0 if this {@code Class} object has no public member * classes or interfaces. This method also returns an array of length 0 if * this {@code Class} object represents a primitive type, an array * class, or void. * * @return the array of {@code Class} objects representing the public * members of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Class<?>[] getClasses() { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false); // Privileged so this implementation can look at DECLARED classes, // something the caller might not have privilege to do. The code here // is allowed to look at DECLARED classes because (1) it does not hand // out anything other than public members and (2) public member access // has already been ok'd by the SecurityManager. return java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged( new java.security.PrivilegedAction<Class<?>[]>() { public Class<?>[] run() { List<Class<?>> list = new ArrayList<>(); Class<?> currentClass = Class.this; while (currentClass != null) { Class<?>[] members = currentClass.getDeclaredClasses(); for (int i = 0; i < members.length; i++) { if (Modifier.isPublic(members[i].getModifiers())) { list.add(members[i]); } } currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass(); } return list.toArray(new Class<?>[0]); } }); } /** * Returns an array containing {@code Field} objects reflecting all * the accessible public fields of the class or interface represented by * this {@code Class} object. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class or interface with no * no accessible public fields, then this method returns an array of length * 0. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class, then this method * returns the public fields of the class and of all its superclasses. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an interface, then this * method returns the fields of the interface and of all its * superinterfaces. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, a primitive * type, or void, then this method returns an array of length 0. * * <p> The elements in the returned array are not sorted and are not in any * particular order. * * @return the array of {@code Field} objects representing the * public fields * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @since JDK1.1 * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.3 Field Declarations */ @CallerSensitive public Field[] getFields() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyFields(privateGetPublicFields(null)); } /** * Returns an array containing {@code Method} objects reflecting all the * public methods of the class or interface represented by this {@code * Class} object, including those declared by the class or interface and * those inherited from superclasses and superinterfaces. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a type that has multiple * public methods with the same name and parameter types, but different * return types, then the returned array has a {@code Method} object for * each such method. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a type with a class * initialization method {@code <clinit>}, then the returned array does * <em>not</em> have a corresponding {@code Method} object. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, then the * returned array has a {@code Method} object for each of the public * methods inherited by the array type from {@code Object}. It does not * contain a {@code Method} object for {@code clone()}. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an interface then the * returned array does not contain any implicitly declared methods from * {@code Object}. Therefore, if no methods are explicitly declared in * this interface or any of its superinterfaces then the returned array * has length 0. (Note that a {@code Class} object which represents a class * always has public methods, inherited from {@code Object}.) * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a primitive type or void, * then the returned array has length 0. * * <p> Static methods declared in superinterfaces of the class or interface * represented by this {@code Class} object are not considered members of * the class or interface. * * <p> The elements in the returned array are not sorted and are not in any * particular order. * * @return the array of {@code Method} objects representing the * public methods of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.4 Method Declarations * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Method[] getMethods() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyMethods(privateGetPublicMethods()); } /** * Returns an array containing {@code Constructor} objects reflecting * all the public constructors of the class represented by this * {@code Class} object. An array of length 0 is returned if the * class has no public constructors, or if the class is an array class, or * if the class reflects a primitive type or void. * * Note that while this method returns an array of {@code * Constructor<T>} objects (that is an array of constructors from * this class), the return type of this method is {@code * Constructor<?>[]} and <em>not</em> {@code Constructor<T>[]} as * might be expected. This less informative return type is * necessary since after being returned from this method, the * array could be modified to hold {@code Constructor} objects for * different classes, which would violate the type guarantees of * {@code Constructor<T>[]}. * * @return the array of {@code Constructor} objects representing the * public constructors of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyConstructors(privateGetDeclaredConstructors(true)); } /** * Returns a {@code Field} object that reflects the specified public member * field of the class or interface represented by this {@code Class} * object. The {@code name} parameter is a {@code String} specifying the * simple name of the desired field. * * <p> The field to be reflected is determined by the algorithm that * follows. Let C be the class or interface represented by this object: * * <OL> * <LI> If C declares a public field with the name specified, that is the * field to be reflected.</LI> * <LI> If no field was found in step 1 above, this algorithm is applied * recursively to each direct superinterface of C. The direct * superinterfaces are searched in the order they were declared.</LI> * <LI> If no field was found in steps 1 and 2 above, and C has a * superclass S, then this algorithm is invoked recursively upon S. * If C has no superclass, then a {@code NoSuchFieldException} * is thrown.</LI> * </OL> * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, then this * method does not find the {@code length} field of the array type. * * @param name the field name * @return the {@code Field} object of this class specified by * {@code name} * @throws NoSuchFieldException if a field with the specified name is * not found. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code name} is {@code null} * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @since JDK1.1 * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.3 Field Declarations */ @CallerSensitive public Field getField(String name) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); Field field = getField0(name); if (field == null) { throw new NoSuchFieldException(name); } return field; } /** * Returns a {@code Method} object that reflects the specified public * member method of the class or interface represented by this * {@code Class} object. The {@code name} parameter is a * {@code String} specifying the simple name of the desired method. The * {@code parameterTypes} parameter is an array of {@code Class} * objects that identify the method's formal parameter types, in declared * order. If {@code parameterTypes} is {@code null}, it is * treated as if it were an empty array. * * <p> If the {@code name} is "{@code <init>}" or "{@code <clinit>}" a * {@code NoSuchMethodException} is raised. Otherwise, the method to * be reflected is determined by the algorithm that follows. Let C be the * class or interface represented by this object: * <OL> * <LI> C is searched for a <I>matching method</I>, as defined below. If a * matching method is found, it is reflected.</LI> * <LI> If no matching method is found by step 1 then: * <OL TYPE="a"> * <LI> If C is a class other than {@code Object}, then this algorithm is * invoked recursively on the superclass of C.</LI> * <LI> If C is the class {@code Object}, or if C is an interface, then * the superinterfaces of C (if any) are searched for a matching * method. If any such method is found, it is reflected.</LI> * </OL></LI> * </OL> * * <p> To find a matching method in a class or interface C: If C * declares exactly one public method with the specified name and exactly * the same formal parameter types, that is the method reflected. If more * than one such method is found in C, and one of these methods has a * return type that is more specific than any of the others, that method is * reflected; otherwise one of the methods is chosen arbitrarily. * * <p>Note that there may be more than one matching method in a * class because while the Java language forbids a class to * declare multiple methods with the same signature but different * return types, the Java virtual machine does not. This * increased flexibility in the virtual machine can be used to * implement various language features. For example, covariant * returns can be implemented with {@linkplain * java.lang.reflect.Method#isBridge bridge methods}; the bridge * method and the method being overridden would have the same * signature but different return types. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, then this * method does not find the {@code clone()} method. * * <p> Static methods declared in superinterfaces of the class or interface * represented by this {@code Class} object are not considered members of * the class or interface. * * @param name the name of the method * @param parameterTypes the list of parameters * @return the {@code Method} object that matches the specified * {@code name} and {@code parameterTypes} * @throws NoSuchMethodException if a matching method is not found * or if the name is "<init>"or "<clinit>". * @throws NullPointerException if {@code name} is {@code null} * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.4 Method Declarations * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes, true); if (method == null) { throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes)); } return method; } /** * Returns a {@code Constructor} object that reflects the specified * public constructor of the class represented by this {@code Class} * object. The {@code parameterTypes} parameter is an array of * {@code Class} objects that identify the constructor's formal * parameter types, in declared order. * * If this {@code Class} object represents an inner class * declared in a non-static context, the formal parameter types * include the explicit enclosing instance as the first parameter. * * <p> The constructor to reflect is the public constructor of the class * represented by this {@code Class} object whose formal parameter * types match those specified by {@code parameterTypes}. * * @param parameterTypes the parameter array * @return the {@code Constructor} object of the public constructor that * matches the specified {@code parameterTypes} * @throws NoSuchMethodException if a matching method is not found. * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class. * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return getConstructor0(parameterTypes, Member.PUBLIC); } /** * Returns an array of {@code Class} objects reflecting all the * classes and interfaces declared as members of the class represented by * this {@code Class} object. This includes public, protected, default * (package) access, and private classes and interfaces declared by the * class, but excludes inherited classes and interfaces. This method * returns an array of length 0 if the class declares no classes or * interfaces as members, or if this {@code Class} object represents a * primitive type, an array class, or void. * * @return the array of {@code Class} objects representing all the * declared members of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared classes within this class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Class<?>[] getDeclaredClasses() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false); return getDeclaredClasses0(); } /** * Returns an array of {@code Field} objects reflecting all the fields * declared by the class or interface represented by this * {@code Class} object. This includes public, protected, default * (package) access, and private fields, but excludes inherited fields. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class or interface with no * declared fields, then this method returns an array of length 0. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, a primitive * type, or void, then this method returns an array of length 0. * * <p> The elements in the returned array are not sorted and are not in any * particular order. * * @return the array of {@code Field} objects representing all the * declared fields of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared fields within this class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @since JDK1.1 * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.3 Field Declarations */ @CallerSensitive public Field[] getDeclaredFields() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyFields(privateGetDeclaredFields(false)); } /** * * Returns an array containing {@code Method} objects reflecting all the * declared methods of the class or interface represented by this {@code * Class} object, including public, protected, default (package) * access, and private methods, but excluding inherited methods. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a type that has multiple * declared methods with the same name and parameter types, but different * return types, then the returned array has a {@code Method} object for * each such method. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a type that has a class * initialization method {@code <clinit>}, then the returned array does * <em>not</em> have a corresponding {@code Method} object. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class or interface with no * declared methods, then the returned array has length 0. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, a primitive * type, or void, then the returned array has length 0. * * <p> The elements in the returned array are not sorted and are not in any * particular order. * * @return the array of {@code Method} objects representing all the * declared methods of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared methods within this class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.4 Method Declarations * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Method[] getDeclaredMethods() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false)); } /** * Returns an array of {@code Constructor} objects reflecting all the * constructors declared by the class represented by this * {@code Class} object. These are public, protected, default * (package) access, and private constructors. The elements in the array * returned are not sorted and are not in any particular order. If the * class has a default constructor, it is included in the returned array. * This method returns an array of length 0 if this {@code Class} * object represents an interface, a primitive type, an array class, or * void. * * <p> See <em>The Java Language Specification</em>, section 8.2. * * @return the array of {@code Constructor} objects representing all the * declared constructors of this class * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared constructors within this class * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() throws SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return copyConstructors(privateGetDeclaredConstructors(false)); } /** * Returns a {@code Field} object that reflects the specified declared * field of the class or interface represented by this {@code Class} * object. The {@code name} parameter is a {@code String} that specifies * the simple name of the desired field. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, then this * method does not find the {@code length} field of the array type. * * @param name the name of the field * @return the {@code Field} object for the specified field in this * class * @throws NoSuchFieldException if a field with the specified name is * not found. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code name} is {@code null} * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared field * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @since JDK1.1 * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.3 Field Declarations */ @CallerSensitive public Field getDeclaredField(String name) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); Field field = searchFields(privateGetDeclaredFields(false), name); if (field == null) { throw new NoSuchFieldException(name); } return field; } /** * Returns a {@code Method} object that reflects the specified * declared method of the class or interface represented by this * {@code Class} object. The {@code name} parameter is a * {@code String} that specifies the simple name of the desired * method, and the {@code parameterTypes} parameter is an array of * {@code Class} objects that identify the method's formal parameter * types, in declared order. If more than one method with the same * parameter types is declared in a class, and one of these methods has a * return type that is more specific than any of the others, that method is * returned; otherwise one of the methods is chosen arbitrarily. If the * name is "<init>"or "<clinit>" a {@code NoSuchMethodException} * is raised. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an array type, then this * method does not find the {@code clone()} method. * * @param name the name of the method * @param parameterTypes the parameter array * @return the {@code Method} object for the method of this class * matching the specified name and parameters * @throws NoSuchMethodException if a matching method is not found. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code name} is {@code null} * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared method * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @jls 8.2 Class Members * @jls 8.4 Method Declarations * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes); if (method == null) { throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes)); } return method; } /** * Returns a {@code Constructor} object that reflects the specified * constructor of the class or interface represented by this * {@code Class} object. The {@code parameterTypes} parameter is * an array of {@code Class} objects that identify the constructor's * formal parameter types, in declared order. * * If this {@code Class} object represents an inner class * declared in a non-static context, the formal parameter types * include the explicit enclosing instance as the first parameter. * * @param parameterTypes the parameter array * @return The {@code Constructor} object for the constructor with the * specified parameter list * @throws NoSuchMethodException if a matching method is not found. * @throws SecurityException * If a security manager, <i>s</i>, is present and any of the * following conditions is met: * * <ul> * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as the * class loader of this class and invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} method with * {@code RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers")} * denies access to the declared constructor * * <li> the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the current class and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package * of this class * * </ul> * * @since JDK1.1 */ @CallerSensitive public Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true); return getConstructor0(parameterTypes, Member.DECLARED); } /** * Finds a resource with a given name. The rules for searching resources * associated with a given class are implemented by the defining * {@linkplain ClassLoader class loader} of the class. This method * delegates to this object's class loader. If this object was loaded by * the bootstrap class loader, the method delegates to {@link * ClassLoader#getSystemResourceAsStream}. * * <p> Before delegation, an absolute resource name is constructed from the * given resource name using this algorithm: * * <ul> * * <li> If the {@code name} begins with a {@code '/'} * (<tt>'\u002f'</tt>), then the absolute name of the resource is the * portion of the {@code name} following the {@code '/'}. * * <li> Otherwise, the absolute name is of the following form: * * <blockquote> * {@code modified_package_name/name} * </blockquote> * * <p> Where the {@code modified_package_name} is the package name of this * object with {@code '/'} substituted for {@code '.'} * (<tt>'\u002e'</tt>). * * </ul> * * @param name name of the desired resource * @return A {@link java.io.InputStream} object or {@code null} if * no resource with this name is found * @throws NullPointerException If {@code name} is {@code null} * @since JDK1.1 */ public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) { name = resolveName(name); ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (cl==null) { // A system class. return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name); } return cl.getResourceAsStream(name); } /** * Finds a resource with a given name. The rules for searching resources * associated with a given class are implemented by the defining * {@linkplain ClassLoader class loader} of the class. This method * delegates to this object's class loader. If this object was loaded by * the bootstrap class loader, the method delegates to {@link * ClassLoader#getSystemResource}. * * <p> Before delegation, an absolute resource name is constructed from the * given resource name using this algorithm: * * <ul> * * <li> If the {@code name} begins with a {@code '/'} * (<tt>'\u002f'</tt>), then the absolute name of the resource is the * portion of the {@code name} following the {@code '/'}. * * <li> Otherwise, the absolute name is of the following form: * * <blockquote> * {@code modified_package_name/name} * </blockquote> * * <p> Where the {@code modified_package_name} is the package name of this * object with {@code '/'} substituted for {@code '.'} * (<tt>'\u002e'</tt>). * * </ul> * * @param name name of the desired resource * @return A {@link java.net.URL} object or {@code null} if no * resource with this name is found * @since JDK1.1 */ public java.net.URL getResource(String name) { name = resolveName(name); ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (cl==null) { // A system class. return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name); } return cl.getResource(name); } /** protection domain returned when the internal domain is null */ private static java.security.ProtectionDomain allPermDomain; /** * Returns the {@code ProtectionDomain} of this class. If there is a * security manager installed, this method first calls the security * manager's {@code checkPermission} method with a * {@code RuntimePermission("getProtectionDomain")} permission to * ensure it's ok to get the * {@code ProtectionDomain}. * * @return the ProtectionDomain of this class * * @throws SecurityException * if a security manager exists and its * {@code checkPermission} method doesn't allow * getting the ProtectionDomain. * * @see java.security.ProtectionDomain * @see SecurityManager#checkPermission * @see java.lang.RuntimePermission * @since 1.2 */ public java.security.ProtectionDomain getProtectionDomain() { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_PD_PERMISSION); } java.security.ProtectionDomain pd = getProtectionDomain0(); if (pd == null) { if (allPermDomain == null) { java.security.Permissions perms = new java.security.Permissions(); perms.add(SecurityConstants.ALL_PERMISSION); allPermDomain = new java.security.ProtectionDomain(null, perms); } pd = allPermDomain; } return pd; } /** * Returns the ProtectionDomain of this class. */ private native java.security.ProtectionDomain getProtectionDomain0(); /* * Return the Virtual Machine's Class object for the named * primitive type. */ static native Class<?> getPrimitiveClass(String name); /* * Check if client is allowed to access members. If access is denied, * throw a SecurityException. * * This method also enforces package access. * * <p> Default policy: allow all clients access with normal Java access * control. */ private void checkMemberAccess(int which, Class<?> caller, boolean checkProxyInterfaces) { final SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager(); if (s != null) { /* Default policy allows access to all {@link Member#PUBLIC} members, * as well as access to classes that have the same class loader as the caller. * In all other cases, it requires RuntimePermission("accessDeclaredMembers") * permission. */ final ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller); final ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (which != Member.PUBLIC) { if (ccl != cl) { s.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.CHECK_MEMBER_ACCESS_PERMISSION); } } this.checkPackageAccess(ccl, checkProxyInterfaces); } } /* * Checks if a client loaded in ClassLoader ccl is allowed to access this * class under the current package access policy. If access is denied, * throw a SecurityException. */ private void checkPackageAccess(final ClassLoader ccl, boolean checkProxyInterfaces) { final SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager(); if (s != null) { final ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (ReflectUtil.needsPackageAccessCheck(ccl, cl)) { String name = this.getName(); int i = name.lastIndexOf('.'); if (i != -1) { // skip the package access check on a proxy class in default proxy package String pkg = name.substring(0, i); if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(this) || ReflectUtil.isNonPublicProxyClass(this)) { s.checkPackageAccess(pkg); } } } // check package access on the proxy interfaces if (checkProxyInterfaces && Proxy.isProxyClass(this)) { ReflectUtil.checkProxyPackageAccess(ccl, this.getInterfaces()); } } } /** * Add a package name prefix if the name is not absolute Remove leading "/" * if name is absolute */ private String resolveName(String name) { if (name == null) { return name; } if (!name.startsWith("/")) { Class<?> c = this; while (c.isArray()) { c = c.getComponentType(); } String baseName = c.getName(); int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.'); if (index != -1) { name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/') +"/"+name; } } else { name = name.substring(1); } return name; } /** * Atomic operations support. */ private static class Atomic { // initialize Unsafe machinery here, since we need to call Class.class instance method // and have to avoid calling it in the static initializer of the Class class... private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe(); // offset of Class.reflectionData instance field private static final long reflectionDataOffset; // offset of Class.annotationType instance field private static final long annotationTypeOffset; // offset of Class.annotationData instance field private static final long annotationDataOffset; static { Field[] fields = Class.class.getDeclaredFields0(false); // bypass caches reflectionDataOffset = objectFieldOffset(fields, "reflectionData"); annotationTypeOffset = objectFieldOffset(fields, "annotationType"); annotationDataOffset = objectFieldOffset(fields, "annotationData"); } private static long objectFieldOffset(Field[] fields, String fieldName) { Field field = searchFields(fields, fieldName); if (field == null) { throw new Error("No " + fieldName + " field found in java.lang.Class"); } return unsafe.objectFieldOffset(field); } static <T> boolean casReflectionData(Class<?> clazz, SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> oldData, SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> newData) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(clazz, reflectionDataOffset, oldData, newData); } static <T> boolean casAnnotationType(Class<?> clazz, AnnotationType oldType, AnnotationType newType) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(clazz, annotationTypeOffset, oldType, newType); } static <T> boolean casAnnotationData(Class<?> clazz, AnnotationData oldData, AnnotationData newData) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(clazz, annotationDataOffset, oldData, newData); } } /** * Reflection support. */ // Caches for certain reflective results private static boolean useCaches = true; // reflection data that might get invalidated when JVM TI RedefineClasses() is called private static class ReflectionData<T> { volatile Field[] declaredFields; volatile Field[] publicFields; volatile Method[] declaredMethods; volatile Method[] publicMethods; volatile Constructor<T>[] declaredConstructors; volatile Constructor<T>[] publicConstructors; // Intermediate results for getFields and getMethods volatile Field[] declaredPublicFields; volatile Method[] declaredPublicMethods; volatile Class<?>[] interfaces; // Value of classRedefinedCount when we created this ReflectionData instance final int redefinedCount; ReflectionData(int redefinedCount) { this.redefinedCount = redefinedCount; } } private volatile transient SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> reflectionData; // Incremented by the VM on each call to JVM TI RedefineClasses() // that redefines this class or a superclass. private volatile transient int classRedefinedCount = 0; // Lazily create and cache ReflectionData private ReflectionData<T> reflectionData() { SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> reflectionData = this.reflectionData; int classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount; ReflectionData<T> rd; if (useCaches && reflectionData != null && (rd = reflectionData.get()) != null && rd.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) { return rd; } // else no SoftReference or cleared SoftReference or stale ReflectionData // -> create and replace new instance return newReflectionData(reflectionData, classRedefinedCount); } private ReflectionData<T> newReflectionData(SoftReference<ReflectionData<T>> oldReflectionData, int classRedefinedCount) { if (!useCaches) return null; while (true) { ReflectionData<T> rd = new ReflectionData<>(classRedefinedCount); // try to CAS it... if (Atomic.casReflectionData(this, oldReflectionData, new SoftReference<>(rd))) { return rd; } // else retry oldReflectionData = this.reflectionData; classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount; if (oldReflectionData != null && (rd = oldReflectionData.get()) != null && rd.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) { return rd; } } } // Generic signature handling private native String getGenericSignature0(); // Generic info repository; lazily initialized private volatile transient ClassRepository genericInfo; // accessor for factory private GenericsFactory getFactory() { // create scope and factory return CoreReflectionFactory.make(this, ClassScope.make(this)); } // accessor for generic info repository; // generic info is lazily initialized private ClassRepository getGenericInfo() { ClassRepository genericInfo = this.genericInfo; if (genericInfo == null) { String signature = getGenericSignature0(); if (signature == null) { genericInfo = ClassRepository.NONE; } else { genericInfo = ClassRepository.make(signature, getFactory()); } this.genericInfo = genericInfo; } return (genericInfo != ClassRepository.NONE) ? genericInfo : null; } // Annotations handling native byte[] getRawAnnotations(); // Since 1.8 native byte[] getRawTypeAnnotations(); static byte[] getExecutableTypeAnnotationBytes(Executable ex) { return getReflectionFactory().getExecutableTypeAnnotationBytes(ex); } native ConstantPool getConstantPool(); // // // java.lang.reflect.Field handling // // // Returns an array of "root" fields. These Field objects must NOT // be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied // via ReflectionFactory.copyField. private Field[] privateGetDeclaredFields(boolean publicOnly) { checkInitted(); Field[] res; ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd != null) { res = publicOnly ? rd.declaredPublicFields : rd.declaredFields; if (res != null) return res; } // No cached value available; request value from VM res = Reflection.filterFields(this, getDeclaredFields0(publicOnly)); if (rd != null) { if (publicOnly) { rd.declaredPublicFields = res; } else { rd.declaredFields = res; } } return res; } // Returns an array of "root" fields. These Field objects must NOT // be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied // via ReflectionFactory.copyField. private Field[] privateGetPublicFields(Set<Class<?>> traversedInterfaces) { checkInitted(); Field[] res; ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd != null) { res = rd.publicFields; if (res != null) return res; } // No cached value available; compute value recursively. // Traverse in correct order for getField(). List<Field> fields = new ArrayList<>(); if (traversedInterfaces == null) { traversedInterfaces = new HashSet<>(); } // Local fields Field[] tmp = privateGetDeclaredFields(true); addAll(fields, tmp); // Direct superinterfaces, recursively for (Class<?> c : getInterfaces()) { if (!traversedInterfaces.contains(c)) { traversedInterfaces.add(c); addAll(fields, c.privateGetPublicFields(traversedInterfaces)); } } // Direct superclass, recursively if (!isInterface()) { Class<?> c = getSuperclass(); if (c != null) { addAll(fields, c.privateGetPublicFields(traversedInterfaces)); } } res = new Field[fields.size()]; fields.toArray(res); if (rd != null) { rd.publicFields = res; } return res; } private static void addAll(Collection<Field> c, Field[] o) { for (int i = 0; i < o.length; i++) { c.add(o[i]); } } // // // java.lang.reflect.Constructor handling // // // Returns an array of "root" constructors. These Constructor // objects must NOT be propagated to the outside world, but must // instead be copied via ReflectionFactory.copyConstructor. private Constructor<T>[] privateGetDeclaredConstructors(boolean publicOnly) { checkInitted(); Constructor<T>[] res; ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd != null) { res = publicOnly ? rd.publicConstructors : rd.declaredConstructors; if (res != null) return res; } // No cached value available; request value from VM if (isInterface()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Constructor<T>[] temporaryRes = (Constructor<T>[]) new Constructor<?>[0]; res = temporaryRes; } else { res = getDeclaredConstructors0(publicOnly); } if (rd != null) { if (publicOnly) { rd.publicConstructors = res; } else { rd.declaredConstructors = res; } } return res; } // // // java.lang.reflect.Method handling // // // Returns an array of "root" methods. These Method objects must NOT // be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied // via ReflectionFactory.copyMethod. private Method[] privateGetDeclaredMethods(boolean publicOnly) { checkInitted(); Method[] res; ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd != null) { res = publicOnly ? rd.declaredPublicMethods : rd.declaredMethods; if (res != null) return res; } // No cached value available; request value from VM res = Reflection.filterMethods(this, getDeclaredMethods0(publicOnly)); if (rd != null) { if (publicOnly) { rd.declaredPublicMethods = res; } else { rd.declaredMethods = res; } } return res; } static class MethodArray { // Don't add or remove methods except by add() or remove() calls. private Method[] methods; private int length; private int defaults; MethodArray() { this(20); } MethodArray(int initialSize) { if (initialSize < 2) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size should be 2 or more"); methods = new Method[initialSize]; length = 0; defaults = 0; } boolean hasDefaults() { return defaults != 0; } void add(Method m) { if (length == methods.length) { methods = Arrays.copyOf(methods, 2 * methods.length); } methods[length++] = m; if (m != null && m.isDefault()) defaults++; } void addAll(Method[] ma) { for (int i = 0; i < ma.length; i++) { add(ma[i]); } } void addAll(MethodArray ma) { for (int i = 0; i < ma.length(); i++) { add(ma.get(i)); } } void addIfNotPresent(Method newMethod) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Method m = methods[i]; if (m == newMethod || (m != null && m.equals(newMethod))) { return; } } add(newMethod); } void addAllIfNotPresent(MethodArray newMethods) { for (int i = 0; i < newMethods.length(); i++) { Method m = newMethods.get(i); if (m != null) { addIfNotPresent(m); } } } /* Add Methods declared in an interface to this MethodArray. * Static methods declared in interfaces are not inherited. */ void addInterfaceMethods(Method[] methods) { for (Method candidate : methods) { if (!Modifier.isStatic(candidate.getModifiers())) { add(candidate); } } } int length() { return length; } Method get(int i) { return methods[i]; } Method getFirst() { for (Method m : methods) if (m != null) return m; return null; } void removeByNameAndDescriptor(Method toRemove) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Method m = methods[i]; if (m != null && matchesNameAndDescriptor(m, toRemove)) { remove(i); } } } private void remove(int i) { if (methods[i] != null && methods[i].isDefault()) defaults--; methods[i] = null; } private boolean matchesNameAndDescriptor(Method m1, Method m2) { return m1.getReturnType() == m2.getReturnType() && m1.getName() == m2.getName() && // name is guaranteed to be interned arrayContentsEq(m1.getParameterTypes(), m2.getParameterTypes()); } void compactAndTrim() { int newPos = 0; // Get rid of null slots for (int pos = 0; pos < length; pos++) { Method m = methods[pos]; if (m != null) { if (pos != newPos) { methods[newPos] = m; } newPos++; } } if (newPos != methods.length) { methods = Arrays.copyOf(methods, newPos); } } /* Removes all Methods from this MethodArray that have a more specific * default Method in this MethodArray. * * Users of MethodArray are responsible for pruning Methods that have * a more specific <em>concrete</em> Method. */ void removeLessSpecifics() { if (!hasDefaults()) return; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Method m = get(i); if (m == null || !m.isDefault()) continue; for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) { if (i == j) continue; Method candidate = get(j); if (candidate == null) continue; if (!matchesNameAndDescriptor(m, candidate)) continue; if (hasMoreSpecificClass(m, candidate)) remove(j); } } } Method[] getArray() { return methods; } // Returns true if m1 is more specific than m2 static boolean hasMoreSpecificClass(Method m1, Method m2) { Class<?> m1Class = m1.getDeclaringClass(); Class<?> m2Class = m2.getDeclaringClass(); return m1Class != m2Class && m2Class.isAssignableFrom(m1Class); } } // Returns an array of "root" methods. These Method objects must NOT // be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied // via ReflectionFactory.copyMethod. private Method[] privateGetPublicMethods() { checkInitted(); Method[] res; ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData(); if (rd != null) { res = rd.publicMethods; if (res != null) return res; } // No cached value available; compute value recursively. // Start by fetching public declared methods MethodArray methods = new MethodArray(); { Method[] tmp = privateGetDeclaredMethods(true); methods.addAll(tmp); } // Now recur over superclass and direct superinterfaces. // Go over superinterfaces first so we can more easily filter // out concrete implementations inherited from superclasses at // the end. MethodArray inheritedMethods = new MethodArray(); for (Class<?> i : getInterfaces()) { inheritedMethods.addInterfaceMethods(i.privateGetPublicMethods()); } if (!isInterface()) { Class<?> c = getSuperclass(); if (c != null) { MethodArray supers = new MethodArray(); supers.addAll(c.privateGetPublicMethods()); // Filter out concrete implementations of any // interface methods for (int i = 0; i < supers.length(); i++) { Method m = supers.get(i); if (m != null && !Modifier.isAbstract(m.getModifiers()) && !m.isDefault()) { inheritedMethods.removeByNameAndDescriptor(m); } } // Insert superclass's inherited methods before // superinterfaces' to satisfy getMethod's search // order supers.addAll(inheritedMethods); inheritedMethods = supers; } } // Filter out all local methods from inherited ones for (int i = 0; i < methods.length(); i++) { Method m = methods.get(i); inheritedMethods.removeByNameAndDescriptor(m); } methods.addAllIfNotPresent(inheritedMethods); methods.removeLessSpecifics(); methods.compactAndTrim(); res = methods.getArray(); if (rd != null) { rd.publicMethods = res; } return res; } // // Helpers for fetchers of one field, method, or constructor // private static Field searchFields(Field[] fields, String name) { String internedName = name.intern(); for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { if (fields[i].getName() == internedName) { return getReflectionFactory().copyField(fields[i]); } } return null; } private Field getField0(String name) throws NoSuchFieldException { // Note: the intent is that the search algorithm this routine // uses be equivalent to the ordering imposed by // privateGetPublicFields(). It fetches only the declared // public fields for each class, however, to reduce the number // of Field objects which have to be created for the common // case where the field being requested is declared in the // class which is being queried. Field res; // Search declared public fields if ((res = searchFields(privateGetDeclaredFields(true), name)) != null) { return res; } // Direct superinterfaces, recursively Class<?>[] interfaces = getInterfaces(); for (int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; i++) { Class<?> c = interfaces[i]; if ((res = c.getField0(name)) != null) { return res; } } // Direct superclass, recursively if (!isInterface()) { Class<?> c = getSuperclass(); if (c != null) { if ((res = c.getField0(name)) != null) { return res; } } } return null; } private static Method searchMethods(Method[] methods, String name, Class<?>[] parameterTypes) { Method res = null; String internedName = name.intern(); for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) { Method m = methods[i]; if (m.getName() == internedName && arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes, m.getParameterTypes()) && (res == null || res.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType()))) res = m; } return (res == null ? res : getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(res)); } private Method getMethod0(String name, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, boolean includeStaticMethods) { MethodArray interfaceCandidates = new MethodArray(2); Method res = privateGetMethodRecursive(name, parameterTypes, includeStaticMethods, interfaceCandidates); if (res != null) return res; // Not found on class or superclass directly interfaceCandidates.removeLessSpecifics(); return interfaceCandidates.getFirst(); // may be null } private Method privateGetMethodRecursive(String name, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, boolean includeStaticMethods, MethodArray allInterfaceCandidates) { // Note: the intent is that the search algorithm this routine // uses be equivalent to the ordering imposed by // privateGetPublicMethods(). It fetches only the declared // public methods for each class, however, to reduce the // number of Method objects which have to be created for the // common case where the method being requested is declared in // the class which is being queried. // // Due to default methods, unless a method is found on a superclass, // methods declared in any superinterface needs to be considered. // Collect all candidates declared in superinterfaces in {@code // allInterfaceCandidates} and select the most specific if no match on // a superclass is found. // Must _not_ return root methods Method res; // Search declared public methods if ((res = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(true), name, parameterTypes)) != null) { if (includeStaticMethods || !Modifier.isStatic(res.getModifiers())) return res; } // Search superclass's methods if (!isInterface()) { Class<? super T> c = getSuperclass(); if (c != null) { if ((res = c.getMethod0(name, parameterTypes, true)) != null) { return res; } } } // Search superinterfaces' methods Class<?>[] interfaces = getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> c : interfaces) if ((res = c.getMethod0(name, parameterTypes, false)) != null) allInterfaceCandidates.add(res); // Not found return null; } private Constructor<T> getConstructor0(Class<?>[] parameterTypes, int which) throws NoSuchMethodException { Constructor<T>[] constructors = privateGetDeclaredConstructors((which == Member.PUBLIC)); for (Constructor<T> constructor : constructors) { if (arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes, constructor.getParameterTypes())) { return getReflectionFactory().copyConstructor(constructor); } } throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + ".<init>" + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes)); } // // Other helpers and base implementation // private static boolean arrayContentsEq(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) { if (a1 == null) { return a2 == null || a2.length == 0; } if (a2 == null) { return a1.length == 0; } if (a1.length != a2.length) { return false; } for (int i = 0; i < a1.length; i++) { if (a1[i] != a2[i]) { return false; } } return true; } private static Field[] copyFields(Field[] arg) { Field[] out = new Field[arg.length]; ReflectionFactory fact = getReflectionFactory(); for (int i = 0; i < arg.length; i++) { out[i] = fact.copyField(arg[i]); } return out; } private static Method[] copyMethods(Method[] arg) { Method[] out = new Method[arg.length]; ReflectionFactory fact = getReflectionFactory(); for (int i = 0; i < arg.length; i++) { out[i] = fact.copyMethod(arg[i]); } return out; } private static <U> Constructor<U>[] copyConstructors(Constructor<U>[] arg) { Constructor<U>[] out = arg.clone(); ReflectionFactory fact = getReflectionFactory(); for (int i = 0; i < out.length; i++) { out[i] = fact.copyConstructor(out[i]); } return out; } private native Field[] getDeclaredFields0(boolean publicOnly); private native Method[] getDeclaredMethods0(boolean publicOnly); private native Constructor<T>[] getDeclaredConstructors0(boolean publicOnly); private native Class<?>[] getDeclaredClasses0(); private static String argumentTypesToString(Class<?>[] argTypes) { StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); buf.append("("); if (argTypes != null) { for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) { if (i > 0) { buf.append(", "); } Class<?> c = argTypes[i]; buf.append((c == null) ? "null" : c.getName()); } } buf.append(")"); return buf.toString(); } /** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.1 for interoperability */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 3206093459760846163L; /** * Class Class is special cased within the Serialization Stream Protocol. * * A Class instance is written initially into an ObjectOutputStream in the * following format: * <pre> * {@code TC_CLASS} ClassDescriptor * A ClassDescriptor is a special cased serialization of * a {@code java.io.ObjectStreamClass} instance. * </pre> * A new handle is generated for the initial time the class descriptor * is written into the stream. Future references to the class descriptor * are written as references to the initial class descriptor instance. * * @see java.io.ObjectStreamClass */ private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields = new ObjectStreamField[0]; /** * Returns the assertion status that would be assigned to this * class if it were to be initialized at the time this method is invoked. * If this class has had its assertion status set, the most recent * setting will be returned; otherwise, if any package default assertion * status pertains to this class, the most recent setting for the most * specific pertinent package default assertion status is returned; * otherwise, if this class is not a system class (i.e., it has a * class loader) its class loader's default assertion status is returned; * otherwise, the system class default assertion status is returned. * <p> * Few programmers will have any need for this method; it is provided * for the benefit of the JRE itself. (It allows a class to determine at * the time that it is initialized whether assertions should be enabled.) * Note that this method is not guaranteed to return the actual * assertion status that was (or will be) associated with the specified * class when it was (or will be) initialized. * * @return the desired assertion status of the specified class. * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#setClassAssertionStatus * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#setPackageAssertionStatus * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#setDefaultAssertionStatus * @since 1.4 */ public boolean desiredAssertionStatus() { ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader(); // If the loader is null this is a system class, so ask the VM if (loader == null) return desiredAssertionStatus0(this); // If the classloader has been initialized with the assertion // directives, ask it. Otherwise, ask the VM. synchronized(loader.assertionLock) { if (loader.classAssertionStatus != null) { return loader.desiredAssertionStatus(getName()); } } return desiredAssertionStatus0(this); } // Retrieves the desired assertion status of this class from the VM private static native boolean desiredAssertionStatus0(Class<?> clazz); /** * Returns true if and only if this class was declared as an enum in the * source code. * * @return true if and only if this class was declared as an enum in the * source code * @since 1.5 */ public boolean isEnum() { // An enum must both directly extend java.lang.Enum and have // the ENUM bit set; classes for specialized enum constants // don't do the former. return (this.getModifiers() & ENUM) != 0 && this.getSuperclass() == java.lang.Enum.class; } // Fetches the factory for reflective objects private static ReflectionFactory getReflectionFactory() { if (reflectionFactory == null) { reflectionFactory = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged (new sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory.GetReflectionFactoryAction()); } return reflectionFactory; } private static ReflectionFactory reflectionFactory; // To be able to query system properties as soon as they're available private static boolean initted = false; private static void checkInitted() { if (initted) return; AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { // Tests to ensure the system properties table is fully // initialized. This is needed because reflection code is // called very early in the initialization process (before // command-line arguments have been parsed and therefore // these user-settable properties installed.) We assume that // if System.out is non-null then the System class has been // fully initialized and that the bulk of the startup code // has been run. if (System.out == null) { // java.lang.System not yet fully initialized return null; } // Doesn't use Boolean.getBoolean to avoid class init. String val = System.getProperty("sun.reflect.noCaches"); if (val != null && val.equals("true")) { useCaches = false; } initted = true; return null; } }); } /** * Returns the elements of this enum class or null if this * Class object does not represent an enum type. * * @return an array containing the values comprising the enum class * represented by this Class object in the order they're * declared, or null if this Class object does not * represent an enum type * @since 1.5 */ public T[] getEnumConstants() { T[] values = getEnumConstantsShared(); return (values != null) ? values.clone() : null; } /** * Returns the elements of this enum class or null if this * Class object does not represent an enum type; * identical to getEnumConstants except that the result is * uncloned, cached, and shared by all callers. */ T[] getEnumConstantsShared() { if (enumConstants == null) { if (!isEnum()) return null; try { final Method values = getMethod("values"); java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged( new java.security.PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { values.setAccessible(true); return null; } }); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T[] temporaryConstants = (T[])values.invoke(null); enumConstants = temporaryConstants; } // These can happen when users concoct enum-like classes // that don't comply with the enum spec. catch (InvocationTargetException | NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException ex) { return null; } } return enumConstants; } private volatile transient T[] enumConstants = null; /** * Returns a map from simple name to enum constant. This package-private * method is used internally by Enum to implement * {@code public static <T extends Enum<T>> T valueOf(Class<T>, String)} * efficiently. Note that the map is returned by this method is * created lazily on first use. Typically it won't ever get created. */ Map<String, T> enumConstantDirectory() { if (enumConstantDirectory == null) { T[] universe = getEnumConstantsShared(); if (universe == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException( getName() + " is not an enum type"); Map<String, T> m = new HashMap<>(2 * universe.length); for (T constant : universe) m.put(((Enum<?>)constant).name(), constant); enumConstantDirectory = m; } return enumConstantDirectory; } private volatile transient Map<String, T> enumConstantDirectory = null; /** * Casts an object to the class or interface represented * by this {@code Class} object. * * @param obj the object to be cast * @return the object after casting, or null if obj is null * * @throws ClassCastException if the object is not * null and is not assignable to the type T. * * @since 1.5 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public T cast(Object obj) { if (obj != null && !isInstance(obj)) throw new ClassCastException(cannotCastMsg(obj)); return (T) obj; } private String cannotCastMsg(Object obj) { return "Cannot cast " + obj.getClass().getName() + " to " + getName(); } /** * Casts this {@code Class} object to represent a subclass of the class * represented by the specified class object. Checks that the cast * is valid, and throws a {@code ClassCastException} if it is not. If * this method succeeds, it always returns a reference to this class object. * * <p>This method is useful when a client needs to "narrow" the type of * a {@code Class} object to pass it to an API that restricts the * {@code Class} objects that it is willing to accept. A cast would * generate a compile-time warning, as the correctness of the cast * could not be checked at runtime (because generic types are implemented * by erasure). * * @param <U> the type to cast this class object to * @param clazz the class of the type to cast this class object to * @return this {@code Class} object, cast to represent a subclass of * the specified class object. * @throws ClassCastException if this {@code Class} object does not * represent a subclass of the specified class (here "subclass" includes * the class itself). * @since 1.5 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <U> Class<? extends U> asSubclass(Class<U> clazz) { if (clazz.isAssignableFrom(this)) return (Class<? extends U>) this; else throw new ClassCastException(this.toString()); } /** * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.5 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) { Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass); return (A) annotationData().annotations.get(annotationClass); } /** * {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.5 */ @Override public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) { return GenericDeclaration.super.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass); } /** * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.8 */ @Override public <A extends Annotation> A[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<A> annotationClass) { Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass); AnnotationData annotationData = annotationData(); return AnnotationSupport.getAssociatedAnnotations(annotationData.declaredAnnotations, this, annotationClass); } /** * @since 1.5 */ public Annotation[] getAnnotations() { return AnnotationParser.toArray(annotationData().annotations); } /** * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.8 */ @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <A extends Annotation> A getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) { Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass); return (A) annotationData().declaredAnnotations.get(annotationClass); } /** * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.8 */ @Override public <A extends Annotation> A[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<A> annotationClass) { Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass); return AnnotationSupport.getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(annotationData().declaredAnnotations, annotationClass); } /** * @since 1.5 */ public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() { return AnnotationParser.toArray(annotationData().declaredAnnotations); } // annotation data that might get invalidated when JVM TI RedefineClasses() is called private static class AnnotationData { final Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> annotations; final Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations; // Value of classRedefinedCount when we created this AnnotationData instance final int redefinedCount; AnnotationData(Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> annotations, Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations, int redefinedCount) { this.annotations = annotations; this.declaredAnnotations = declaredAnnotations; this.redefinedCount = redefinedCount; } } // Annotations cache @SuppressWarnings("UnusedDeclaration") private volatile transient AnnotationData annotationData; private AnnotationData annotationData() { while (true) { // retry loop AnnotationData annotationData = this.annotationData; int classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount; if (annotationData != null && annotationData.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) { return annotationData; } // null or stale annotationData -> optimistically create new instance AnnotationData newAnnotationData = createAnnotationData(classRedefinedCount); // try to install it if (Atomic.casAnnotationData(this, annotationData, newAnnotationData)) { // successfully installed new AnnotationData return newAnnotationData; } } } private AnnotationData createAnnotationData(int classRedefinedCount) { Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations = AnnotationParser.parseAnnotations(getRawAnnotations(), getConstantPool(), this); Class<?> superClass = getSuperclass(); Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> annotations = null; if (superClass != null) { Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> superAnnotations = superClass.annotationData().annotations; for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> e : superAnnotations.entrySet()) { Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass = e.getKey(); if (AnnotationType.getInstance(annotationClass).isInherited()) { if (annotations == null) { // lazy construction annotations = new LinkedHashMap<>((Math.max( declaredAnnotations.size(), Math.min(12, declaredAnnotations.size() + superAnnotations.size()) ) * 4 + 2) / 3 ); } annotations.put(annotationClass, e.getValue()); } } } if (annotations == null) { // no inherited annotations -> share the Map with declaredAnnotations annotations = declaredAnnotations; } else { // at least one inherited annotation -> declared may override inherited annotations.putAll(declaredAnnotations); } return new AnnotationData(annotations, declaredAnnotations, classRedefinedCount); } // Annotation types cache their internal (AnnotationType) form @SuppressWarnings("UnusedDeclaration") private volatile transient AnnotationType annotationType; boolean casAnnotationType(AnnotationType oldType, AnnotationType newType) { return Atomic.casAnnotationType(this, oldType, newType); } AnnotationType getAnnotationType() { return annotationType; } Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> getDeclaredAnnotationMap() { return annotationData().declaredAnnotations; } /* Backing store of user-defined values pertaining to this class. * Maintained by the ClassValue class. */ transient ClassValue.ClassValueMap classValueMap; /** * Returns an {@code AnnotatedType} object that represents the use of a * type to specify the superclass of the entity represented by this {@code * Class} object. (The <em>use</em> of type Foo to specify the superclass * in '... extends Foo' is distinct from the <em>declaration</em> of type * Foo.) * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a type whose declaration * does not explicitly indicate an annotated superclass, then the return * value is an {@code AnnotatedType} object representing an element with no * annotations. * * <p> If this {@code Class} represents either the {@code Object} class, an * interface type, an array type, a primitive type, or void, the return * value is {@code null}. * * @return an object representing the superclass * @since 1.8 */ public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedSuperclass() { if (this == Object.class || isInterface() || isArray() || isPrimitive() || this == Void.TYPE) { return null; } return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedSuperclass(getRawTypeAnnotations(), getConstantPool(), this); } /** * Returns an array of {@code AnnotatedType} objects that represent the use * of types to specify superinterfaces of the entity represented by this * {@code Class} object. (The <em>use</em> of type Foo to specify a * superinterface in '... implements Foo' is distinct from the * <em>declaration</em> of type Foo.) * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class, the return value is * an array containing objects representing the uses of interface types to * specify interfaces implemented by the class. The order of the objects in * the array corresponds to the order of the interface types used in the * 'implements' clause of the declaration of this {@code Class} object. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents an interface, the return * value is an array containing objects representing the uses of interface * types to specify interfaces directly extended by the interface. The * order of the objects in the array corresponds to the order of the * interface types used in the 'extends' clause of the declaration of this * {@code Class} object. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents a class or interface whose * declaration does not explicitly indicate any annotated superinterfaces, * the return value is an array of length 0. * * <p> If this {@code Class} object represents either the {@code Object} * class, an array type, a primitive type, or void, the return value is an * array of length 0. * * @return an array representing the superinterfaces * @since 1.8 */ public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedInterfaces() { return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedInterfaces(getRawTypeAnnotations(), getConstantPool(), this); } }
4.1 获取类名信息
Class类的成员方法 getSimpleName、getName 可以获取到类名相关的信息
技巧01:虽然参数类型是Object类型,但是实际上传递过来的实参是哪个类的对象,c就是哪个类的类类型
例如:传入的 String 的一个实例,那么 c 就是 String 的类类型
public static void printClassInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); // 02 调用Class实例的相关方法获取类名信息 System.out.println("类的名称为:" + c.getSimpleName()); System.out.println("类的全名为:" + c.getName()); }
4.2 获取方法信息
技巧01:所有的方法都是Method的实例
技巧02:Class类的getMethods获取的是本类以及父类中public修饰的方法;Class类的getDeclaredMethods()获取到的是本类中所有的方法【不包括父类的】
技巧03:Method类的相关成员方法
getReturnType -> 获取方法返回类型 -> 返回值是一个Class实例
getName -> 获取方法名 -> 返回值是一个String实例
getParameterTypes -> 获取方法的参数类型列表 -> 返回值是一个 Class实例 组成的数组

public static void printMethodsInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); // 技巧01:虽然参数类型是Object类型,但是实际上传递过来的实参是哪个类的对象,c就是哪个类的类类型 // 例如:传入的 String 的一个实例,那么 c 就是 String 的类类型 // 02 获取所有的方法组成的数组 // 技巧02:所有的方法都是Method的实例 // 技巧03:getMethods获取的是本类以及父类中public修饰的方法;getDeclaredMethods()获取到的是本类中所有的方法【不包括父类的】 Method[] methods = c.getMethods(); for (Integer i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) { // 0201 获取方法返回值类型 Class returnType = methods[i].getReturnType(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的返回值类型为:" + returnType.getName()); // 0202 获取方法名称 String methodName = methods[i].getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的方法名为:" + methodName); // 0203 获取方法参数 Class[] paramTypes = methods[i].getParameterTypes(); for (Integer j = 0; j < paramTypes.length; j++) { System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的第" + j + "个参数类型为:" + paramTypes[j].getName()); } } }
4.3 获取属性信息
技巧01:所有属性都是Filed的实例
技巧02:Class类的getFields获取public修饰的成员变量,Class类的getDeclaredFields获取本类声明的所有成员
技巧03:Field类的相关方法
getType -> 获取属性类型 -> 返回值是一个Class实例
getName -> 获取属性名称 -> 返回值是一个String实例

public static void printFieldInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); Field[] fields = c.getFields(); for (Integer i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { String fieldName = fields[i].getName(); String fieldType = fields[i].getType().getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个成员变量的信息为:字段类型 -> " + fieldType + " 字段名称 -> " + fieldName); } }
4.4 获取构造器信息
技巧01:所有的构造器都是Constructor的实例
技巧02:Class类的 getConstructors 获取本类和父类中有pulbic修饰的构造器,Class类的 getDeclaredConstructors 获取本类中声明的构造器
技巧03:Constructor类的相关方法
getName -> 获取构造器名称 -> 返回的是一个String实例
getParameterTypes -> 获取构造器参数类型列表 -> 返回的是一个Class实例组成的数组

public static void printConstructorInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); Constructor[] constructors = c.getConstructors(); for (Integer i = 0; i < constructors.length; i++) { String constructorName = constructors[i].getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个构造函数逇名称为:" + constructorName); Class[] paramTypes = constructors[i].getParameterTypes(); for (Integer j = 0; j < paramTypes.length; j++) { System.out.println("第" + i + "个构造函数的" + "第" + j + "个参数类型为:" + paramTypes[j].getName() ); } } }
4.5 代码汇总

package demo_test02; import org.omg.CORBA.OBJECT_NOT_EXIST; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-06 10:34 * @desc **/ public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = 3; ClassUtil.printClassInfo(i); System.out.println("============"); ClassUtil.printMethodsInfo(i); System.out.println("============"); ClassUtil.printFieldInfo(i); System.out.println("============"); ClassUtil.printConstructorInfo(i); } } class ClassUtil { public static void printClassInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); // 02 调用Class实例的相关方法获取类名信息 System.out.println("类的名称为:" + c.getSimpleName()); System.out.println("类的全名为:" + c.getName()); } public static void printMethodsInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); // 技巧01:虽然参数类型是Object类型,但是实际上传递过来的实参是哪个类的对象,c就是哪个类的类类型 // 例如:传入的 String 的一个实例,那么 c 就是 String 的类类型 // 02 获取所有的方法组成的数组 // 技巧02:所有的方法都是Method的实例 // 技巧03:getMethods获取的是本类以及父类中public修饰的方法;getDeclaredMethods()获取到的是本类中所有的方法【不包括父类的】 Method[] methods = c.getMethods(); for (Integer i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) { // 0201 获取方法返回值类型 Class returnType = methods[i].getReturnType(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的返回值类型为:" + returnType.getName()); // 0202 获取方法名称 String methodName = methods[i].getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的方法名为:" + methodName); // 0203 获取方法参数 Class[] paramTypes = methods[i].getParameterTypes(); for (Integer j = 0; j < paramTypes.length; j++) { System.out.println("第" + i + "个方法的第" + j + "个参数类型为:" + paramTypes[j].getName()); } } } public static void printFieldInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); Field[] fields = c.getFields(); for (Integer i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { String fieldName = fields[i].getName(); String fieldType = fields[i].getType().getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个成员变量的信息为:字段类型 -> " + fieldType + " 字段名称 -> " + fieldName); } } public static void printConstructorInfo(Object object) { // 01 获取类类型 Class c = object.getClass(); Constructor[] constructors = c.getConstructors(); for (Integer i = 0; i < constructors.length; i++) { String constructorName = constructors[i].getName(); System.out.println("第" + i + "个构造函数逇名称为:" + constructorName); Class[] paramTypes = constructors[i].getParameterTypes(); for (Integer j = 0; j < paramTypes.length; j++) { System.out.println("第" + i + "个构造函数的" + "第" + j + "个参数类型为:" + paramTypes[j].getName() ); } } } }
5 方法反射
Method类的invoke方法可以执行一个实例的方法;
一个Class实例可以通过getMethod方法获取到单个的Method实例。
5.1 准备类

class Foo { public void print() { System.out.println("渝足"); } public void print(Integer a, Integer b) { System.out.println(a + b); } public void print(String a, String b) { System.out.println(a.toUpperCase() + " , " + b.toLowerCase()); } }
5.2 获取Method实例并用其调用Foo实例的方法
》创建一个Foo实例
》Method实例
// 根据方法名和方法类型列表获取方法对象 Method method0 = c.getMethod("print", new Class[]{String.class, String.class});
》利用Method实例调用Foo实例的方法
// 执行方法对象 method0.invoke(foo, new String[]{"hello", "Fury"});
5.3 代码汇总

package demo06_reflect.case04_method; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-06 9:21 * @desc 方法反射 **/ public class Method_Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Foo foo = new Foo(); // foo.print(1, 2); // foo.print("hello", "word"); Class c = foo.getClass(); try { // 根据方法名和方法类型列表获取方法对象 Method method0 = c.getMethod("print", new Class[]{String.class, String.class}); // 执行方法对象 method0.invoke(foo, new String[]{"hello", "Fury"}); // Method method = c.getMethod("print", String.class, String.class); // method.invoke(foo, "good", "boy"); System.out.println("===================="); Method method1 = c.getMethod("print", Integer.class, Integer.class); method1.invoke(foo, 3, 4); Method method2 = c.getMethod("print", new Class[]{Integer.class, Integer.class}); method2.invoke(foo, new Integer[]{4, 4}); System.out.println("===================="); // Method method3 = c.getMethod("print"); // method3.invoke(foo); Method method4 = c.getMethod("print", new Class[]{}); method4.invoke(foo, new Object[]{}); System.out.println("===================="); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Foo { public void print() { System.out.println("渝足"); } public void print(Integer a, Integer b) { System.out.println(a + b); } public void print(String a, String b) { System.out.println(a.toUpperCase() + " , " + b.toLowerCase()); } }
5.4 方法反射的应用
列表的泛型其实是在编译阶段起作用的;所以在运行阶段可以利用方法反射去掉用List的add方法,从而绕过泛型的限制

package demo06_reflect.case04_method; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-08-06 9:33 * @desc 方法反射的应用 **/ public class Method_Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { List list01 = new ArrayList(); list01.add(333); list01.add("warrior"); System.out.println(list01); List<String> list02 = new ArrayList<>(); list02.add("warrior"); // list02.add(333); System.out.println(list02); System.out.println("==============================="); Class c01 = list01.getClass(); // 运行阶段执行 Class c02 = list02.getClass(); System.out.println(c01 == c02); // 说明列表的泛型只是作用于编译阶段 System.out.println("==============================="); Class c = list02.getClass(); try { // 获取Method实例 Method method = c.getMethod("add", Object.class); // 利用Method实例调用List的add方法 method.invoke(list02, 333); System.out.println(list02); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("==============================="); } }
·下面是我的公众号二维码,欢迎关注·
尋渝記

微信号:xyj_fury
