笛卡尔树(知识总结+板子整理)
笛卡尔树
例题1:hdu-6305
RMQ Similar Sequence
【题意】:
题意:定义RMQ(A,l,r)为:序列A中,满足A[i] = max(A[l],A[l+1],...,A[r])的最小的i。如果对于任意(l,r)都满足RMQ(A,l,r)=RMQ(B,l,r)则为A和B是RMQ Similar。现在出A序列,B序列的每个数都是0~1之间的实数,问满足与A是RMQ Similar的所有B序列中所有数之和的期望。
题解:不难看出如果A和B是RMQ Similar,则A和B的笛卡尔树同构。考虑B中的每个数是0~1之间的实数,因此出现相同数字的概率为0,可以假设B是每个数都不相同排列。设A的笛卡尔树每个子树的大小为sz[u],则任一B排列与A同构的概率是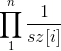 ,因为B中每个数满足均匀分布,因此期望值为1/2,和的期望为n/2,因此满足与A同构的B中所有数之和的期望为
,因为B中每个数满足均匀分布,因此期望值为1/2,和的期望为n/2,因此满足与A同构的B中所有数之和的期望为
所以求:sz[i] 指的是笛卡尔树每个子树的大小。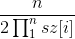
贴上代码:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<stack> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long ll; 6 const int N = 1e6 + 5 ; 7 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 8 const int mod = 1e9+7; 9 inline int read(){ 10 int x = 0 , f = 1 ; 11 char c = getchar(); 12 while ( c < '0' || c > '9' ) { 13 if( c=='-' ) f = -1 ; 14 c = getchar(); 15 } 16 while ( '0' <= c && c <= '9' ){ 17 x = x*10 + c-'0'; 18 c = getchar(); 19 } 20 return x * f ; 21 } 22 typedef struct Node{ 23 int val,fa,sz; 24 int L,R; 25 Node(){} 26 }Node; 27 Node t[N]; 28 stack<int>st; 29 void Init(int n){ 30 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ 31 t[i].sz = t[i].L = t[i].R = t[i].fa = 0; 32 } 33 t[0].val = INF; 34 while(!st.empty()) st.pop(); 35 st.push(0); 36 } 37 38 void build(int n){ 39 int k ; 40 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 41 while( !st.empty() && t[st.top()].val < t[i].val ) 42 st.pop(); 43 k = st.top(); 44 t[i].L = t[k].R; 45 t[k].R = i ; 46 t[i].fa = k; 47 t[t[i].L].fa = i ; 48 st.push(i); 49 } 50 } 51 void dfs(int u) { 52 if ( !u ) return ; 53 t[u].sz = 1 ; 54 dfs( t[u].L ); 55 dfs( t[u].R ); 56 t[u].sz += t[t[u].L].sz 57 + t[t[u].R].sz ; 58 } 59 ll inv[N]; 60 void Init() { 61 inv[1] = 1; 62 for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) 63 inv[i] = inv[mod % i] * (mod - mod / i) % mod; 64 } 65 int main() 66 { 67 int T,n; 68 Init(); 69 for ( scanf("%d",&T) ; T ; T-- ){ 70 71 n = read(); 72 Init(n); 73 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 74 t[i].val = read() ; 75 } 76 //puts("####"); 77 78 build(n); 79 dfs(t[0].R); 80 81 ll ans=n *inv[2]%mod; 82 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 83 ans=ans*inv[t[i].sz]%mod; 84 85 printf("%lld ",ans); 86 } 87 return 0; 88 } 89 /* 90 3 91 3 92 1 2 3 93 3 94 1 2 1 95 5 96 1 2 3 2 1 97 */
【例题2】poj-2201
Cartesian Tree
题目大意:裸的笛卡尔树,建树输出每个点的父节点和儿子节点编号,没有为0。
构造一颗笛卡尔树,然后输出这棵树即可。
首先进行排序,然后用一个栈维护最右的树的节点信息,插入的时候按照第二关键字去找,找到之后插入,下面的树成为它的左子树即可。
然后插入分三种情况讨论(最下面,中间,成为了新的树根)
题目分析:注意这题肯定要输出YES,因为给的每一对关键字都不相同,所以能建唯一的笛卡尔树,不存在NO的情况。还有排序后序号就乱了,注意一下就行了,其他的没什么了。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 const int N = 5e4+5; 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef struct Node{ 6 int id , L , R , val , key ,fa ; 7 bool operator < (const Node &rhs )const { 8 return key < rhs.key ; 9 } 10 }Node ; 11 Node t[N]; 12 int n,L[N],R[N],st[N],Fa[N]; 13 void build(){ 14 int top = 0 ; 15 st[top] = 1 ; 16 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ 17 while( top >= 0 && t[st[top]].val > t[i].val ) 18 top -- ; 19 if ( top > -1 ){ 20 t[i].L = t[st[top]].R; 21 t[st[top]].R = i ; 22 t[i].fa = st[top]; 23 t[t[i].L].fa = i ; 24 }else{ 25 t[st[0]].fa = i ; 26 t[i].L = st[0]; 27 } 28 st[++top] = i ; 29 } 30 } 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 while(~scanf("%d",&n)){ 35 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 36 scanf("%d%d",&t[i].key,&t[i].val); 37 t[i].id = i ; 38 t[i].L = t[i].R = t[i].fa = 0 ; 39 } 40 sort( t+1 , t+1+n ) ; 41 build(); 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 43 Fa[t[i].id] = t[t[i].fa].id; 44 L[t[i].id] = t[t[i].L].id ; 45 R[t[i].id] = t[t[i].R].id ; 46 } 47 puts("YES"); 48 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 49 printf("%d %d %d ",Fa[i],L[i],R[i]); 50 } 51 } 52 return 0; 53 } 54 /* 55 56 7 57 5 4 58 2 2 59 3 9 60 0 5 61 1 3 62 6 6 63 4 11 64 65 YES 66 2 3 6 67 0 5 1 68 1 0 7 69 5 0 0 70 2 4 0 71 1 0 0 72 3 0 0 73 */
