指针(四)
- 字符数组与字符串
- 常量区
- 常见字符串操作
- 指针函数
一、字符数组与字符串
1、字符数组的定义与初始化
字符数组的初始化,最容易理解的方式就是逐个字符赋给数组中各元素。
char str[10]={ 'I',' ','a','m',' ',‘h','a','p','p','y'};
即把10个字符分别赋给str[0]到str[9]10个元素
如果花括号中提供的字符个数大于数组长度,则按语法错误处理;若小于数组长度,则只将这些字符数组中前面那些元素,其余的元素自动定为空字符(即 '�' )。
2、字符数组与字符串
在c语言中,将字符串作为字符数组来处理。(c++中不是)
在实际应用中人们关心的是有效字符串的长度而不是字符数组的长度,例如,定义一个字符数组长度为100,而实际有效字符只有40个,为了测定字符串的实际长度,C语言规定了一个“字符串结束标志”,以字符'�'代表。如果有一个字符串,其中第10个字符为'�',则此字符串的有效字符为9个。也就是说,在遇到第一个字符'�'时,表示字符串结束,由它前面的字符组成字符串。系统对字符串常量也自动加一个'�'作为结束符。例如"C Program”共有9个字符,但在内存中占10个字节,最后一个字节'�'是系统自动加上的。(通过sizeof()函数可验证)有了结束标志'�'后,字符数组的长度就显得不那么重要了,在程序中往往依靠检测'�'的位置来判定字符串是否结束,而不是根据数组的长度来决定字符串长度。当然,在定义字符数组时应估计实际字符串长度,保证数组长度始终大于字符串实际长度。(在实际字符串定义中,常常并不指定数组长度,如char str[ ])
说明:'
'代表ASCII码为0的字符,从ASCII码表中可以查到ASCII码为0的字符不是一个可以显示的字符,而是一个“空操作符”,即它什么也不干。用它来作为字符串结束标志不会产生附加的操作或增加有效字符,只起一个供辨别的标志。
对C语言处理字符串的方法由以上的了解后,再对字符数组初始化的方法补充一种方法——即可以用字符串常量来初始化字符数组:
1 char str[ ]={"I am happy"}; //可以省略花括号,如下所示
2 char str[ ]="I am happy";
注意:上述这种字符数组的整体赋值只能在字符数组初始化时使用,不能用于字符数组的赋值,字符数组的赋值只能对其元素一一赋值,下面的赋值方法是错误的
1 char str[ ];
2 str="I am happy";
不是用单个字符作为初值,而是用一个字符串(注意:字符串的两端是用双引号“”而不是单引号‘'括起来的)作为初值。显然,这种方法更直观方便。(注意:数组str的长度不是10,而是11,这点请务必记住,因为字符串常量"I am happy"的最后由系统自动加上一个'�'),因此,上面的初始化与下面的初始化等价
char str[ ]={'I',' ','a','m',' ','h','a','p','p','y','�'};
而不与下面的等价
1 char str[ ]={'I',' ','a','m',' ','h','a','p','p','y'};
前者的长度是11,后者的长度是10.
说明:字符数组并不要求它的最后一个字符为'�',甚至可以不包含'�',向下面这样写是完全合法的。
1 char str[5]={'C','h','i','n','a'};
可见,用两种不同方法初始化字符数组后得到的数组长度是不同的。
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 void main(void)
4 {
5 char c1[]={'I',' ','a','m',' ','h','a','p','p','y'};
6 char c2[]="I am happy";
7 int i1=sizeof(c1);
8 int i2=sizeof(c2);
9 printf("%d
",i1);
10 printf("%d
",i2);
11 }
结果:10 11
3、字符串的表示形式
在C语言中,可以用两种方法表示和存放字符串:
(1)用字符数组存放一个字符串
char str[ ]="I love China";
(2)用字符指针指向一个字符串
char* str="I love China";
对于第二种表示方法,有人认为str是一个字符串变量,以为定义时把字符串常量"I love China"直接赋给该字符串变量,这是不对的。
C语言对字符串常量是按字符数组处理的,在内存中开辟了一个字符数组用来存放字符串常量,程序在定义字符串指针变量str时只是把字符串首地址(即存放字符串的字符数组的首地址)赋给str。
两种表示方式的字符串输出都用 printf("%s
",str);%s表示输出一个字符串,给出字符指针变量名str(对于第一种表示方法,字符数组名即是字符数组的首地址,与第二种中的指针意义是一致的),则系统先输出它所指向的一个字符数据,然后自动使str自动加1,使之指向下一个字符...,如此,直到遇到字符串结束标识符 " � "。
二、常量区
1、哪个可以修改?哪个不能改?
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 char* x = "china";
4 char y[] = "china";
5
6 void Function()
7 {
8 //*(x + 1) = 'A'; //不能修改
9 y[1] = 'A';
10
11 printf("%s
%s
", x, y);
12 }
13
14 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
15 {
16 Function();
17 return 0;
18 }
2、哪个可以修改?哪个不能改?
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 void Function()
4 {
5 char* x = "china";
6 char y[] = "china";
7
8 //*(x + 1) = 'A';
9 y[1] = 'A';
10
11 printf("%s
%s
", x, y);
12 }
13
14 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
15 {
16 Function();
17 return 0;
18 }
我们通过反汇编看看,看看这下面两行代码有什么区别
1 char* x = "china";
2 char y[] = "china";
1 8: char* x = "china";
2 0040D798 mov dword ptr [ebp-4],offset string "china" (00422f74)
char* x,x是一个局部变量ebp-4,将0x00422f74处的“china”复制给ebp-4所代表的地址

我们可以紧接着看看0x422F74里头的内容
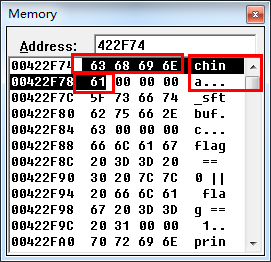
再看看
char y[] = "china";
0040D79F mov eax,[string "china" (00422f74)]
0040D7A4 mov dword ptr [ebp-0Ch],eax
0040D7A7 mov cx,word ptr [string "%s
%s
"+4 (00422f78)]
0040D7AE mov word ptr [ebp-8],cx
同样是0x00422f74,这里做的是拷贝操作,而上面指针操作则是直接让指针x指向0x422f74,使用了2个寄存器跟2块内存来做的拷贝
三、常见字符串操作
以下常见的字符串操作,Linux操作系统详情请看man手册,windows请查看MSDN
返回值是字符串s的长度。不包括结束符'/0'。
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 int strlen(char* s)
4 {
5 int length = 0;
6 while (*s != '�')
7 {
8 s ++;
9 length ++;
10 }
11 return length;
12 }
13
14 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
15 {
16 char str[] = "I love China!";
17 int len = strlen(str);
18
19 printf("%d
", len);
20
21 return 0;
22 }
2、char* strcpy(char* strDestination, char* strSource)
复制字符串strSource到strDestination中。返回指针为strDestination的值。
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 char* strcpy(char* strDestination, char* strSource)
4 {
5 char* ptrDest = strDestination; //保存strDestination的地址
6 while(*strSource != '�')
7 {
8 *strDestination = *strSource;
9 strDestination ++;
10 strSource ++;
11 }
12 *strDestination = '�'; //当*strSource等于'�'时,while循环不会做拷贝,只能在循环结束时,添加上去
13 return ptrDest;
14 }
15
16 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
17 {
18 char strDest[] = "My name is Bob!";
19 char* strSour = "I love China!";
20 char* stringName = strcpy(strDest, strSour);
21
22 printf("%s
", stringName);
23
24 return 0;
25 }
注意:strDestination的长度一定要比strSource的长度长,不然会导致不可预知的内存错误
3、char *strcat( char *strDestination, const char *strSource );
将字符串strSource 添加到strDestination尾部。返回指针为strDestination的值。
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 char* strcat(char* strDestination, const char* strSource)
4 {
5 #if 0
6 if (strDestination == NULL || strSource == NULL)
7 {
8 return ;
9 }
10 #endif
11 //记录strDestination的地址
12 char* ptrDest = strDestination;
13 //字符串拼接,那就要从strDestination为'�'的位置开始
14 while(*ptrDest != '�')
15 {
16 ptrDest ++;
17 }
18
19 while(*strSource != '�')
20 {
21 *ptrDest = *strSource;
22 ptrDest ++;
23 strSource ++;
24 }
25
26 *ptrDest = '�';
27 return strDestination;
28 }
29
30 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
31 {
32 char strDest[100] = "My name is Bob! ";
33 const char strSour[] = "I love China very much!";
34
35 char* stringName = strcat(strDest, strSour);
36 printf("%s
", stringName);
37
38 return 0;
39 }
注意:strDestination的长度一定要比strSource的长度长,不然会导致不可预知的内存错误
写都写到这了,干脆我也做下联系把,写一下strncat吧
1 #include "stdafx.h"
2
3 char* strncat(char* strDestination, const char* strSource, int n)
4 {
5 #if 0
6 if (strDestination == NULL || strSource == NULL)
7 {
8 return ;
9 }
10 #endif
11 //记录strDestination的地址
12 char* ptrDest = strDestination;
13 //字符串拼接,那就要从strDestination为'�'的位置开始
14 while(*ptrDest != '�')
15 {
16 ptrDest ++;
17 }
18 /*
19 写法一:
20 while(*strSource != '�' && n != 0)
21 {
22 *ptrDest = *strSource;
23 ptrDest ++;
24 strSource ++;
25 n --;
26 }
27 */
28
29 //写法二:
30 for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
31 {
32 *ptrDest = *strSource;
33 ptrDest ++;
34 strSource ++;
35 }
36
37 *ptrDest = '�';
38 return strDestination;
39 }
40
41 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
42 {
43 char strDest[100] = "My name is Bob! ";
44 const char strSour[] = "I love China very much!";
45
46 char* stringName = strncat(strDest, strSour, 6);
47 printf("%s
", stringName);
48
49 return 0;
50 }
4、int strcmp(const char* strDestination, const char* strSource)
比较strDestination与strSource,如果小于则返回-1,如果相等,则返回0,如果大于则返回1.
方法一:
1 /************************************************************************/
2 /* Author: xiaoYu */
3 /* Time:2019-11-20 15:21:19 */
4 /************************************************************************/
5 #include "stdafx.h"
6
7 int strcmp(const char* strDestination, const char* strSource)
8 {
9 #if 0
10 if (strDestination == NULL || strSource == NULL)
11 {
12 return ;
13 }
14 #endif
15
16 while ((*strDestination != '�') && (strSource != '�'))
17 {
18 if (*strDestination == *strSource)
19 {
20 strDestination ++;
21 strSource ++;
22 }
23 else if (*strDestination < *strSource)
24 {
25 return -1;
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 return 1;
30 }
31 }
32
33 //当两个子串其中有一个碰到'�',我们在这加以判断
34 if (*strDestination < *strSource)
35 {
36 return -1;
37 }
38 else if (*strSource > *strSource)
39 {
40 return 1;
41 }
42 return 0;
43 }
44
45 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
46 {
47 const char strDest[] = "XiaoYu";
48 const char strSour[] = "XiaoYi";
49
50 int ret = strcmp(strDest, strSour);
51 printf("%d
", ret);
52
53 return 0;
54 }
方法二、
1 /************************************************************************/
2 /* Author: xiaoYu */
3 /* Time:2019-11-20 16:31:48 */
4 /************************************************************************/
5 #include "stdafx.h"
6
7 int strlen(const char* s)
8 {
9 int length = 0;
10 while (*s != '�')
11 {
12 s ++;
13 length ++;
14 }
15 return length;
16 }
17
18 int strcmp(const char* strDestination, const char* strSource)
19 {
20 #if 0
21 if (strDestination == NULL || strSource == NULL)
22 {
23 return ;
24 }
25 #endif
26 int length = 0;
27 int length1 = strlen(strDestination);
28 int length2 = strlen(strSource);
29
30 if (length1 < length2)
31 {
32 length = length2;
33 }
34 else
35 {
36 length = length1;
37 }
38
39 for (int i = 0; i <= length; i ++)
40 {
41 //两个子串相等但却不为'�'
42 /*if ((*(strDestination + i) == *(strSource + i)) && (*(strDestination + i) != '�'))
43 {
44 continue;
45 }*/
46 //用数组的写法吧,更加易读
47 if((strDestination[i] == strSource[i]) && (strSource[i] != '�'))
48 {
49 continue;
50 }
51 if (strDestination[i] == '�' && strSource[i] == '�')
52 {
53 return 0;
54 }
55
56 if (strDestination[i] > strSource[i])
57 {
58 return 1;
59 }
60 else
61 {
62 break;
63 }
64 }
65 return -1;
66 }
67
68 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
69 {
70 const char strDest[] = "XiaoYu";
71 const char strSour[] = "XiaoYz";
72
73 int ret = strcmp(strDest, strSour);
74 printf("%d
", ret);
75
76 return 0;
77 }
四、指针函数
写到这,发现就很尴尬了,因为上面的例子就已经给我写完了,哎,写博客还是不太会规划,嗯,既然上面字符串操作中都有写指针函数,那我在这里就简单描述一下什么是指针函数吧,大家例子参考上面就行了
我也就不照搬书面定义了,大家只需要记住,指针函数是一个函数,这个函数的返回值类型是指针类型,嗯,大家只需要记住这个就行了。
五、练习
1 /************************************************************************/
2 /* Author: xiaoYu */
3 /* Time:2019-11-20 16:44:57 */
4 /************************************************************************/
5 #include "stdafx.h"
6 #include<string.h>
7
8 /************************************************************************/
9 /* 模拟实现CE的数据搜索功能: */
10 /* 这一堆数据中存储了角色的名字信息(WOW),请列出角色名的内存地址 */
11 /************************************************************************/
12 char data[100] =
13 {
14 0x00,0x01,0x02,0x03,0x04,0x05,0x06,0x07,0x07,0x09,
15 0x00,0x20,0x10,0x03,0x03,0x0C,0x00,0x00,0x44,0x00,
16 0x00,0x33,0x00,0x47,0x0C,0x0E,0x00,0x0D,0x00,0x11,
17 0x00,0x00,0x00,0x02,0x64,0x00,0x00,0x00,0xAA,0x00,
18 0x00,0x00,0x64,0x10,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,
19 0x00,0x00,0x02,0x00,0x74,0x0F,0x41,0x00,0x00,0x00,
20 0x01,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x05,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x0A,0x00,
21 0x00,0x02,0x57,0x4F,0x57,0x00,0x06,0x08,0x00,0x00,
22 0x00,0x00,0x00,0x64,0x00,0x0F,0x00,0x00,0x0D,0x00,
23 0x00,0x00,0x23,0x00,0x00,0x64,0x00,0x00,0x64,0x00
24 };
25
26 char* FindRoleNameAddr(char* pData, char* pRoleName)
27 {
28 char* ptrData = data;
29 for (int i = 0; i < 97; i ++)
30 {
31 int* ptrAddr = (int*)(ptrData + i);
32 if (*ptrAddr == *pRoleName)
33 {
34 return (char*)ptrAddr;
35 }
36 }
37 return NULL;
38 }
39
40 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
41 {
42 char* pRoleName = "WOW";
43 char* pRoleNameAddr = FindRoleNameAddr(data, pRoleName);
44 printf("%s %x
", pRoleName, pRoleName);
45 return 0;
46 }