写在前面
注:因为变量名中有下划线,所以有些地方使用的是代码块而没有使用 \(\text{LateX}\) 渲染,恳请管理大大原谅。
转了一圈题解发现没有用莫队的?
唯一一个涉及到的貌似还被卡了?
那么我就来一发回滚莫队吧。
Solution
一开始把题目读错了,以为求的是一段区间内最远的两个相同的数的距离,
这不就回滚莫队板子嘛。
调半天发现是求最近的两个相同的数的距离,想想怎么用莫队维护。
跟着回滚莫队的做法,先进行离散化、分块、排序这一类基本操作。
然后每次轮到一个新块时,我们不是要移动两端点到块的右端嘛。
我们要查询的区间因此就分成了两块,暂且称作左块和右块。
题目要求是求最近的,那么只需统计相邻的两个相同的数的贡献。
开四个数组 cntr[x], cntr_pre[x], cntl_t[x], cntl_pre_t[x],分别表示一个数 \(x\) 在右块的最小的位置,\(x\) 在右块中上一次出现的位置,\(x\) 在左块中的最大位置,\(x\) 在左块中上一次出现的位置。
画成图大体是这个样子:
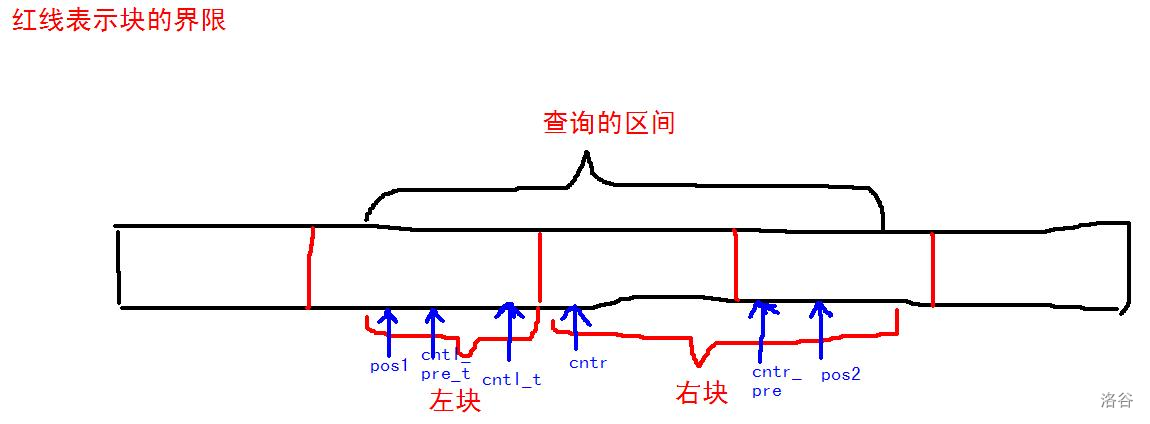
假设图中标记的都是一个数:
- 如果在左块中又枚举到一个数 \(pos_1\),它对答案的贡献显然是
cntl_pre_t - pos1。 - 如果在右块中又枚举到一个数 \(pos_2\),它对答案的贡献显然是
pos2 - cntr_pre。 - 因为左块和右块之间可能也会有贡献,所以还需要统计
cntr - cntl_t。
一些小细节:
- 注意没有相同的数时要输出 \(-1\);
- 在左块或者右块中统计答案时,如果其中某一个值不存在就不要统计答案了。
Code
/*
Work by: Suzt_ilymics
Knowledge: ??
Time: O(??)
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define LL long long
#define orz cout<<"lkp AK IOI!"<<endl
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 5e5+5;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
struct Ques{
int l, r, bh;
}q[MAXN];
int n, m;
int L = 1, R = n, preL = 0, Ans, Res, _L;
int a[MAXN], date[MAXN], date_num = 0;
int lef[MAXN], rig[MAXN], bel[MAXN];
int cntr[MAXN], cntr_pre[MAXN], cntl_t[MAXN], cntl_pre_t[MAXN];
int ans[MAXN];
int read(){
int s = 0, f = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + ch - '0' , ch = getchar();
return f ? -s : s;
}
bool cmp(Ques x, Ques y) { return bel[x.l] == bel[y.l] ? x.r < y.r : x.l < y.l; } //按块排序
void Init() {
n = read(), m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = date[i] = read();
sort(date + 1, date + n + 1); date[0] = -INF; //离散化
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) if(date[i] != date[i - 1]) date[++date_num] = date[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = lower_bound(date + 1, date + date_num + 1, a[i]) - date;
for(int i = 1; i <= date_num; ++i) cntr[i] = cntr_pre[i] = ans[i] = INF;
for(int i = date_num + 1; i <= m; ++i) ans[i] = INF; //初始化为极大值
int len = sqrt(n + 0.5);//分块
int block_num = n / len;
for(int i = 1; i <= block_num; ++i) lef[i] = rig[i - 1] + 1, rig[i] = rig[i - 1] + len;
if(rig[block_num] < n) {
++ block_num;
lef[block_num] = rig[block_num - 1] + 1;
rig[block_num] = n;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= block_num; ++i)
for(int j = lef[i]; j <= rig[i]; ++j)
bel[j] = i;
}
void Add(int pos, int &ans_) {
int x = a[pos];
cntr[x] = min(cntr[x], pos); //更新右块中x的最小的位置
if(cntr_pre[x] != INF) ans_ = min(ans_, pos - cntr_pre[x]); // 只有x在右块中出现过才统计答案
cntr_pre[x] = pos; // 更新
}
void Add_tem(int pos, int &ans_, int type) {
int x = a[pos];
cntl_t[x] = max(cntl_t[x], pos); // 更新左块中x的最大位置
if(cntl_pre_t[x]) ans_ = min(ans_, cntl_pre_t[x] - pos); //只有x在左块中出现过才统计答案
cntl_pre_t[x] = pos; //更新
if(cntr[x] != INF && cntl_t[x] && type) ans_ = min(ans_, cntr[x] - cntl_t[x]); //统计左右块之间的贡献
}
void Del(int pos) { cntr[a[pos]] = cntr_pre[a[pos]] = INF; }
void Del_tem(int pos) { cntl_t[a[pos]] = cntl_pre_t[a[pos]] = 0; }
int main()
{
Init();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) q[i].l = read(), q[i].r = read(), q[i].bh = i;
sort(q + 1, q + m + 1, cmp);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { //回滚莫队基操?
if(preL != bel[q[i].l]) {
while(R > rig[bel[q[i].l]]) Del(R--);
while(L <= rig[bel[q[i].l]]) Del(L++);
Ans = INF, R = rig[bel[q[i].l]], preL = bel[q[i].l];
}
if(bel[q[i].l] == bel[q[i].r]) {
for(int j = q[i].r; j >= q[i].l; --j) Add_tem(j, ans[q[i].bh], 0); //倒序枚举方便统计答案
for(int j = q[i].r; j >= q[i].l; --j) Del_tem(j);
} else {
while(R < q[i].r) Add(++R, Ans);
_L = L, Res = Ans;
while(_L > q[i].l) Add_tem(--_L, Res, 1);
ans[q[i].bh] = Res;
while(_L < L) Del_tem(_L++);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) printf("%d\n", ans[i] == INF ? -1 : ans[i]);
return 0;
}