理论知识部分:
1.程序与进程:
程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。
进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。
2.多线程
多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。
3.进程:
线程是比进程执行更小的单位。线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程中,同一进程的各线程间共享进程空间的数据。每个线程有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程, 是一个动态的概念。线程创建、销毁和切换的负荷远小于进程,又称 为轻量级进程(lightweight process)。
4.Java实现多线程:
-创建Thread类的子类
-在程序中定义实现Runnable接口的类
5.用Thread类的子类创建线程:
首先需从Thread类派生出一个子类,在该子类中 重写run()方法。
class hand extends Thread { public void run() {……} }
然后用创建该子类的对象
Lefthand left=new Lefthand();
Righthand right=new Righthand();
最后用start()方法启动线程
left.start();
right.start();
6.用Runnable()接口实现线程
首先设计一个实现Runnable接口的类;
然后在类中根据需要重写run方法;
再创建该类对象,以此对象为参数建立Thread 类的对象;
调用Thread类对象的start方法启动线程,将 CPU执行权转交到run方法。
7.线程的终止
调用interrupt()方法;
8.
8、测试线程是否被中断的方法
Java提供了几个用于测试线程是否被中断的方法。
-static boolean interrupted()
– 检测当前线程是否已被中断 ,并重置状态 “interrupted”值为false。
-boolean isInterrupted()
– 检测当前线程是否已被中断 ,不改变状态 “interrupted”值 。
9、线程的状态
-利用各线程的状态变换,可以控制各个线程轮流使用CPU,体现多线程的并行性特征。
-线程有如下7种状态:
New (新建)
Runnable (可运行)
Running(运行)
Blocked (被阻塞)
Waiting (等待)
Timed waiting (计时等待)
Terminated (被终止)
10、新创建线程
-new(新建)
线程对象刚刚创建,还没有启动,此时线程还处于不可运行状态。例如: Thread thread=new Thread(r); 此时线程thread处于新建状态,有了相应的内存空间以及其它资源。
11、可运行线程
- runnable(可运行状态)
此时线程已经启动,处于线程的run()方法之中。
此时的线程可能运行,也可能不运行,只要 CPU一空闲,马上就会运行。
调用线程的start()方法可使线程处于“可运行”状态。例如: thread.start();
12、被阻塞线程和等待线程
- blocked (被阻塞)
一个正在执行的线程因特殊原因,被暂停执行, 进入阻塞状态。
阻塞时线程不能进入队列排队,必须等到引起阻塞的原因消除,才可重新进入排队队列。
引起阻塞的原因很多,不同原因要用不同的方法解除。
-sleep(),wait()是两个常用引起线程阻塞的方法。
13、线程阻塞的三种情况
- 等待阻塞 -- 通过调用线程的wait()方法,让线程等待某工作的完成。
- 同步阻塞 -- 线程在获取synchronized同步锁失败(因为锁被其它线程所占用),它会进入同步阻塞状态。
-其他阻塞 -- 通过调用线程的sleep()或join() 或发出了I/O请求时,线程会进入到阻塞状态。当 sleep()状态超时、join()等待线程终止或者超 时、或者I/O处理完毕时,线程重新转入就绪状态。
14、被终止的线程
Terminated (被终止) 线程被终止的原因有二:
一是run()方法中最后一个语句执行完毕而自然死亡。
二是因为一个没有捕获的异常终止了run方法而意外死亡。
可以调用线程的 stop 方 法 杀 死 一 个 线 程(thread.stop();),但是,stop方法已过时, 不要在自己的代码中调用它。
15、多线程调度
-Java 的线程调度采用优先级策略:
优先级高的先执行,优先级低的后执行;
多线程系统会自动为每个线程分配一个优先级,缺省时,继承其父类的优先级;
任务紧急的线程,其优先级较高;
同优先级的线程按“先进先出”的队列原则;
16、Thread类有三个与线程优先级有关的静态量:
MAX_PRIORITY:最大优先权,值为10;
MIN_PRIORITY:最小优先权,值为1;
NORM _PRIORITY:默认优先权,值为5。
实验部分:
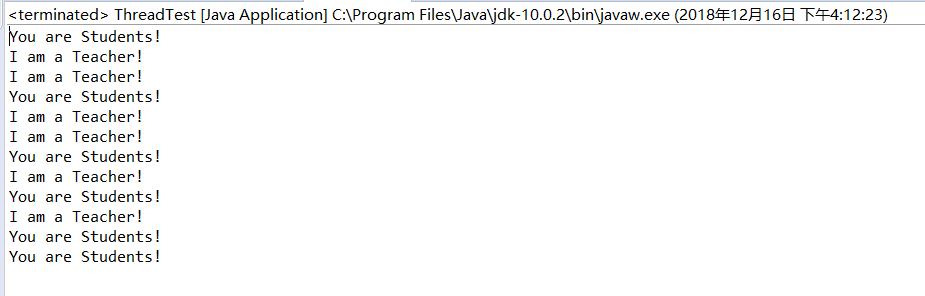
测试程序1:
class Lefthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{ left=new Lefthand();
right=new Righthand();
left.start();
right.start();
}
}
用runable接口实习
class Lefthand implements Runnable{
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ Thread.sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ Thread.sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Thread left;
static Thread right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Runnable lefthand = new Lefthand();
left=new Thread(lefthand);
left.start();
Runnable righthand = new Righthand();
right=new Thread(righthand);
right.start();
}
}
或
class Lefthand implements Runnable{
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ Thread.sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ Thread.sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Runnable lefthand = new Lefthand();
Thread left=new Thread(lefthand);
left.start();
Runnable righthand = new Righthand();
Thread right=new Thread(righthand);
right.start();
}
}
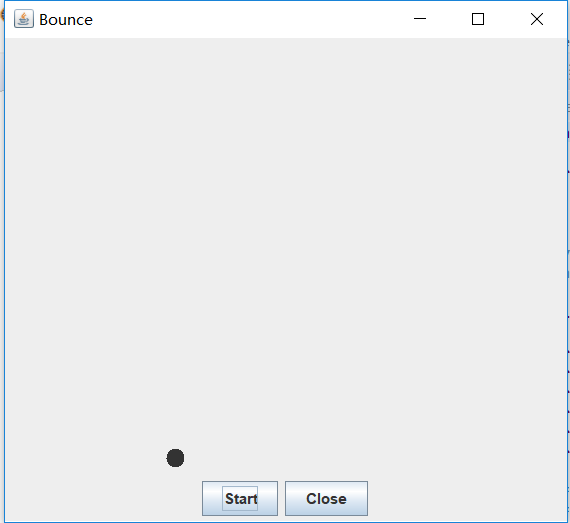
测试程序2:
package bounce;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* Shows an animated bouncing ball.
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bounce
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package bounceThread;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 画球的部件。
* @version 1.34 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BallComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350;
private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 向面板中添加一个球。
* @param b把球加到面板上
*/
public void add(Ball b)
{
balls.add(b);
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
for (Ball b : balls)
{
g2.fill(b.getShape());
}
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
package bounceThread;
import java.awt.geom.*;
/**
从长方形边缘上移动和弹跳的球
* @version 1.33 2007-05-17
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Ball
{
private static final int XSIZE = 15;
private static final int YSIZE = 15;
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
private double dx = 1;
private double dy = 1;
/**
将球移动到下一个位置,如果球碰到其中一条边,则反向移动
*/
public void move(Rectangle2D bounds)
{
x += dx;
y += dy;
if (x < bounds.getMinX())
{
x = bounds.getMinX();
dx = -dx;
}
if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX())
{
x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE;
dx = -dx;
}
if (y < bounds.getMinY())
{
y = bounds.getMinY();
dy = -dy;
}
if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY())
{
y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE;
dy = -dy;
}
}
/**
获取球在当前位置的形状。
*/
public Ellipse2D getShape()
{
return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE);
}
}
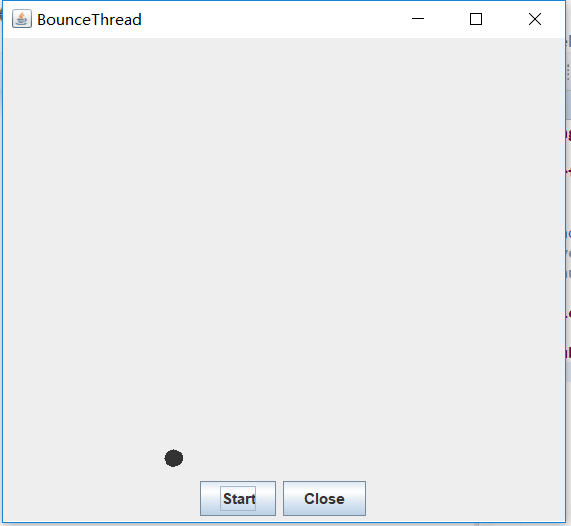
package bounceThread;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 显示动画弹跳球。
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BounceThread
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setTitle("BounceThread");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* 带有面板和按钮的框架。
*/
class BounceFrame extends JFrame
{
private BallComponent comp;
public static final int STEPS = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 5;
/**
* 使用组件构造框架,以显示弹跳球和开始和关闭按钮
*/
public BounceFrame()
{
comp = new BallComponent();
add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());
addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0));
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
/**
* 将按钮添加到容器中。
* @param c the container
* @param title the button title
* @param listener the action listener for the button
*/
public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(title);
c.add(button);
button.addActionListener(listener);
}
/**
* 在画布上添加一个弹跳球,并启动一根线使其弹跳
*/
public void addBall()
{
Ball ball = new Ball();
comp.add(ball);
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++)
{
ball.move(comp.getBounds());
comp.repaint();
Thread.sleep(DELAY);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
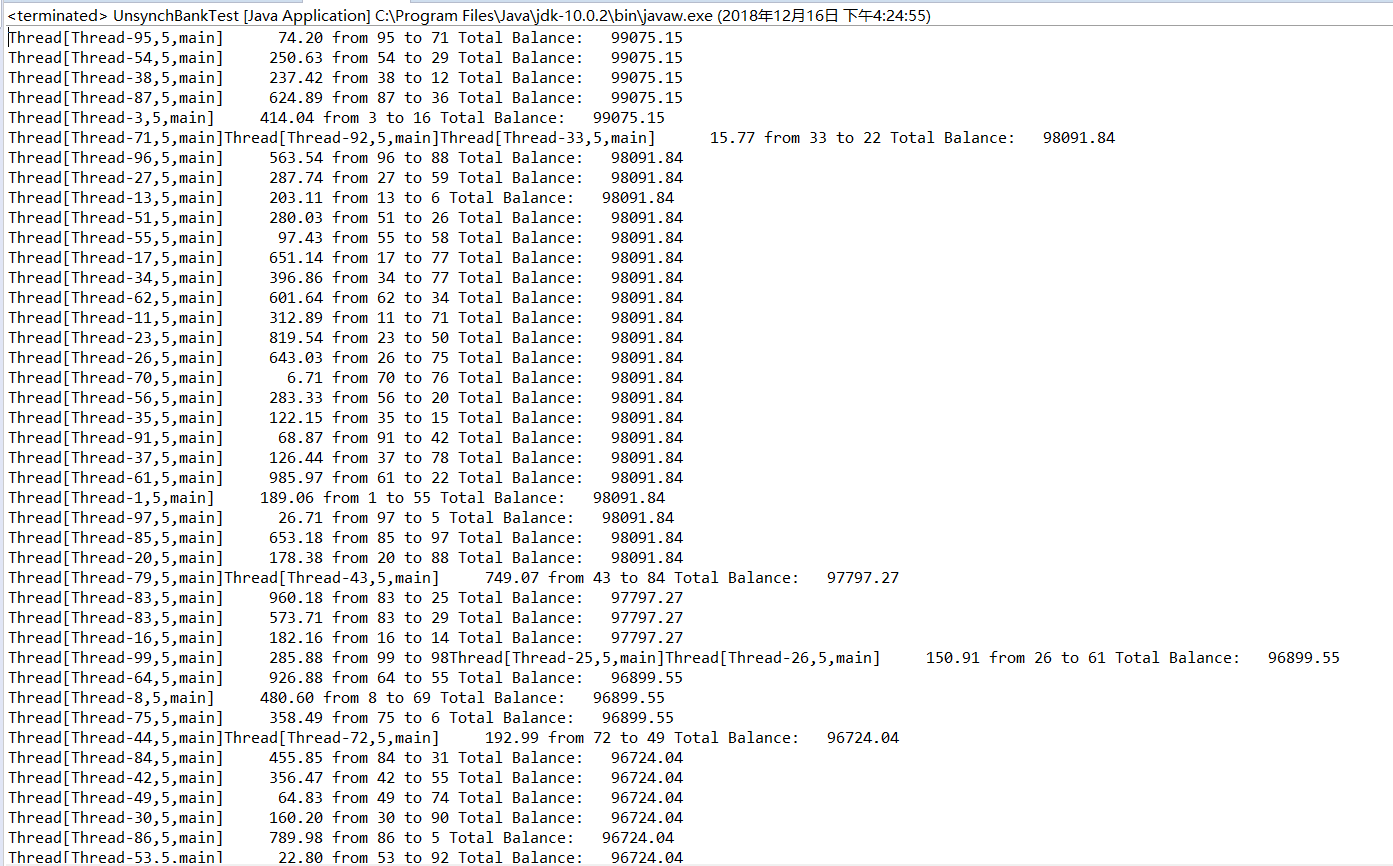
测试程序3:
class Race extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Race[] runner=new Race[4];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( );
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( );
runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY);
runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);}
public void run( ) {
for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++);
System.out.println(getName()+"线程的优先级是"+getPriority()+"已计算完毕!");
}
}

测试程序4
package unsynch;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 有许多银行账户的银行。
* @version 1.30 2004-08-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bank
{
private final double[] accounts;
/**
*构建了银行。
* @param n账户数量
* @param 每个帐户的初始余额
*/
public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
{
accounts = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
}
/**
* 把钱从一个账户转到另一个账户。
* @param 从账户转出
* @param 到账转到
* @param 转帐金额
*/
public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount)
{
if (accounts[from] < amount) return;
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
accounts[from] -= amount;
System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
accounts[to] += amount;
System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
}
/**
* 获取所有帐户余额的总和。
* @return 总平衡
*/
public double getTotalBalance()
{
double sum = 0;
for (double a : accounts)
sum += a;
return sum;
}
/**
* 获取银行中的帐户编号。
* @return 账户数量
*/
public int size()
{
return accounts.length;
}
}
package unsynch;
/**
* 当多个线程访问一个数据结构时,这个程序显示数据损坏。
* @version 1.31 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class UnsynchBankTest
{
public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 10;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
{
int fromAccount = i;
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
while (true)
{
int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
}
综合编程练习
1 .
package 第十六周;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Aaa extends JFrame {
private JTextField name;
private JTextField psw;
public Aaa() {
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2, 5, 2));
JPanel panel_1 = new JPanel();
panel.add(panel_1);
JLabel label = new JLabel("Name:");
panel_1.add(label);
name = new JTextField();
panel_1.add(name);
name.setColumns(10);
JPanel panel_4 = new JPanel();
panel.add(panel_4);
JLabel Label4 = new JLabel("Qualification:");
panel_4.add(Label4);
String[] nians = { "Graduate", "Academic degree", "Foundation degree", "Ungraduate" };
final JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox(nians);
panel_4.add(comboBox);
JPanel panel_2 = new JPanel();
panel.add(panel_2);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("Address:");
panel_2.add(label2);
psw = new JTextField();
panel_2.add(psw);
psw.setColumns(10);
JPanel panel_5 = new JPanel();
panel.add(panel_5);
JLabel Label5 = new JLabel("Hobby:");
panel_5.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2, 0, 0));
panel_5.add(Label5);
final JCheckBox cb1 = new JCheckBox("Reading");
panel_5.add(cb1);
JLabel reginfo1 = new JLabel(" ");
panel_5.add(reginfo1);
final JCheckBox cb2 = new JCheckBox("Singing");
panel_5.add(cb2);
JLabel reginfo2 = new JLabel(" ");
panel_5.add(reginfo2);
final JCheckBox cb3 = new JCheckBox("Dancing");
panel_5.add(cb3);
JPanel panel_3 = new JPanel();
panel.add(panel_3);
panel_3.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2, 0, 0));
JLabel Label3 = new JLabel("Sex:");
panel_3.add(Label3);
final JRadioButton rb1 = new JRadioButton("Female");
panel_3.add(rb1);
JLabel reginfo3 = new JLabel(" ");
panel_3.add(reginfo3);
JRadioButton rb2 = new JRadioButton("Male");
panel_3.add(rb2);
ButtonGroup bg = new ButtonGroup();
bg.add(rb1);
rb1.setSelected(true);
bg.add(rb2);
JPanel panel1 = new JPanel();
getContentPane().add(panel1, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
panel1.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1, 5, 2));
JPanel panel_6 = new JPanel();
panel1.add(panel_6);
JButton jbreg = new JButton("Validate");
panel_6.add(jbreg);
JButton jbrest = new JButton("Reset");
panel_6.add(jbrest);
JPanel panel_7 = new JPanel();
//getContentPane().add(panel_7, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
JLabel reginfo4 = new JLabel(" ");
panel_7.add(reginfo4);
setSize(480,400);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setTitle("信息采集");
jbreg.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String id = name.getText();
sb.append("Name:" + id);
if (name != null) {
System.out.println("Name:"+id);
}
String pas = psw.getText();
sb.append("Address:" + pas);
if (pas != null) {
System.out.println("Adress:"+pas);
}
System.out.println("Sex:");
if (rb1.isSelected()) {
sb.append("Sex:" + "Female");
System.out.println(rb1.getText());
} else {
sb.append("Sex:" + "Male");
System.out.println(rb2.getText());
}
sb.append("Qualification:" + comboBox.getSelectedItem().toString());
sb.append("Hobby:");
System.out.println("Hobby:");
if (cb1.isSelected()) {
sb.append(cb1.getText());
System.out.println(cb1.getText());
}
if (cb2.isSelected()) {
sb.append(cb2.getText());
System.out.println(cb2.getText());
}
if (cb3.isSelected()) {
sb.append(cb3.getText());
System.out.println(cb3.getText());
}
reginfo4.setText(sb.toString());
}
});
jbrest.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
name.setText("");
psw.setText("");
rb1.setSelected(true);
comboBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
cb1.setSelected(false);
cb2.setSelected(false);
cb3.setSelected(false);
reginfo4.setText(" ");
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Aaa().setVisible(true);
}
}
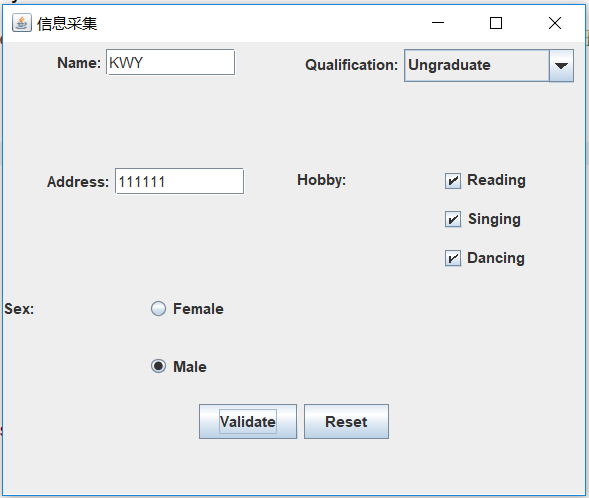

点击重置:

2.
package 第十六周;
public class ThreadTest {
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args) {
left = new Lefthand();
right = new Righthand();
left.start();
right.start();
}
}
class Lefthand extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i+":lefthand.你好!");
try {
sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Lefthand error.");
}
}
}
}
class Righthand extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i+":righthand.你好!");
try {
sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Righthand error.");
}
}
}
}
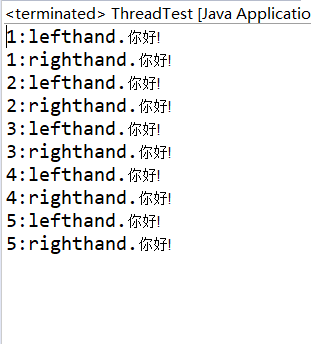
实验总结:
本周我们学习了线程,我明白了在java中,线程的重要性。但是有些问题我还是不太理解,比如如何判断线程终止,其次,在编程练习1中我的布局还是存在一些问题,我会再去继续改正。