内置函数
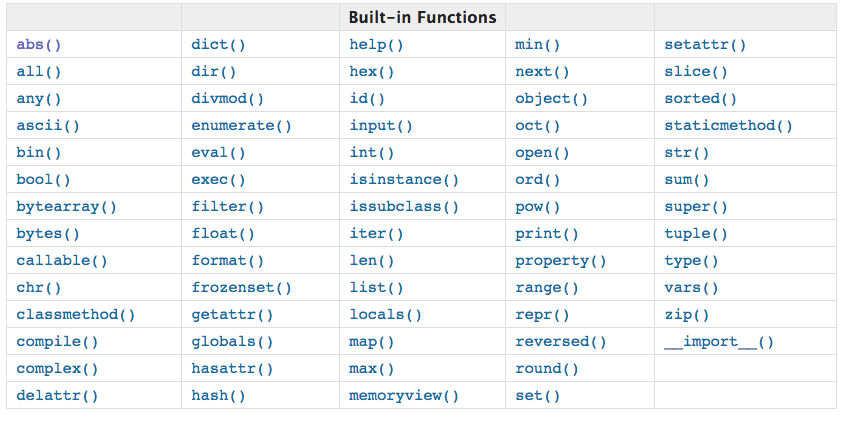
上面就是内置函数的表,68个函数都在这儿了。这个表的顺序是按照首字母的排列顺序来的,你会发现都混乱的堆在一起。比如,oct和bin和hex都是做进制换算的,但是却被写在了三个地方。。。这样非常不利于大家归纳和学习。那我把这些函数分成了7大类。
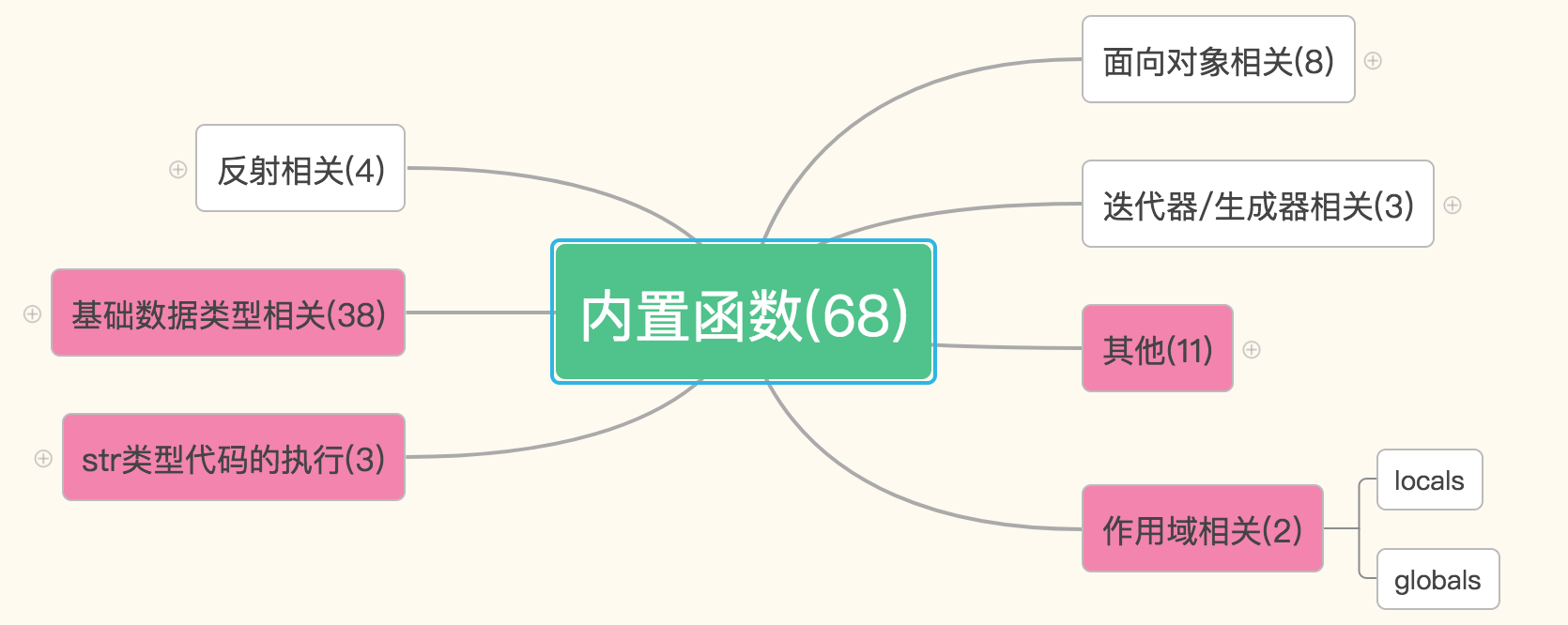
我们今天就要学习用粉红色标注出来的这四大块——53个方法。还有15个方法欠着怎么办呢?我们讲完内置函数会还你们3个,剩下12个也会在两周之内陆续还给你们的,我保证(认真脸)。那这样,我们今天就主要关注我们要学习的这53个方法。
作用域相关
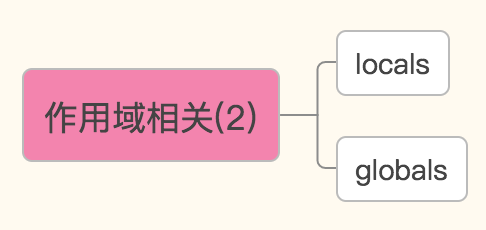
基于字典的形式获取局部变量和全局变量
globals()——获取全局变量的字典
locals()——获取执行本方法所在命名空间内的局部变量的字典
其他
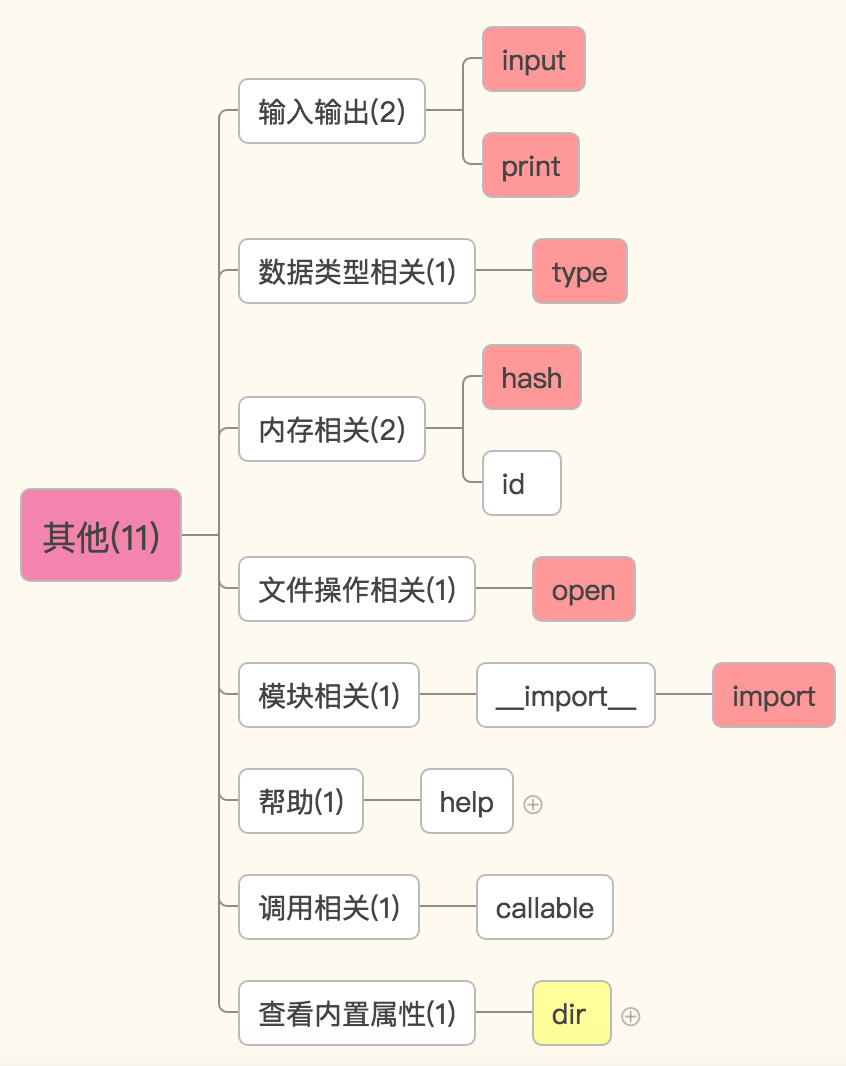
input() 输入
s = input("请输入内容 : ") #输入的内容赋值给s变量 print(s) #输入什么打印什么。数据类型是str
print() 输出
## 源码 def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end=' ', file=None): # known special case of print """ print(value, ..., sep=' ', end=' ', file=sys.stdout, flush=False) file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件 sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格 end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符 flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存 """
## 例子 with open('print_test.txt', 'w') as f: print('testtest', 'test2test2', file=f, sep='---', end=' and ') print('second!!!', file=f)
print_test.txt文件:
testtest---test2test2 and second!!!
## 打印进度条 import time for i in range(0, 101, 2): time.sleep(0.1) char_num = i//2 # 打印多少个'*' per_str = ' {}% : {} '.format(i, '*' * char_num) if i == 100 else ' {}% : {}'.format(i, '*' * char_num) print(per_str, end='', flush=True) # 可以把光标移动行首但不换行
数据类型相关:
type(o) 返回变量o的数据类型
内存相关:
id(o) o是参数,返回一个变量的内存地址
hash(o) o是参数,返回一个可hash变量的哈希值,不可hash的变量被hash之后会报错。
t = (1,2,3) l = [1,2,3] print(hash(t)) #可hash print(hash(l)) #会报错 ''' 结果: TypeError: unhashable type: 'list' '''
hash函数会根据一个内部的算法对当前可hash变量进行处理,返回一个int数字。
*每一次执行程序,内容相同的变量hash值在这一次执行过程中不会发生改变。
文件操作相关
open() 打开一个文件,返回一个文件操作符(文件句柄)
操作文件的模式有r,w,a,r+,w+,a+ 共6种,每一种方式都可以用二进制的形式操作(rb,wb,ab,rb+,wb+,ab+)
模块操作相关
__import__导入一个模块
导入模块 import time __import__ os = __import__('os') print(os.path.abspath('.'))
帮助方法
在控制台执行help()进入帮助模式。可以随意输入变量或者变量的类型。输入q退出
或者直接执行help(o),o是参数,查看和变量o有关的操作。。。
和调用相关
callable(o),o是参数,看这个变量是不是可调用。
如果o是一个函数名,就会返回True
def func():pass print(callable(func)) #参数是函数名,可调用,返回True print(callable(123)) #参数是数字,不可调用,返回False
查看参数所属类型的所有内置方法
dir() 默认查看全局空间内的属性,也接受一个参数,查看这个参数内的方法或变量
print(dir(list)) #查看列表的内置方法 print(dir(int)) #查看整数的内置方法
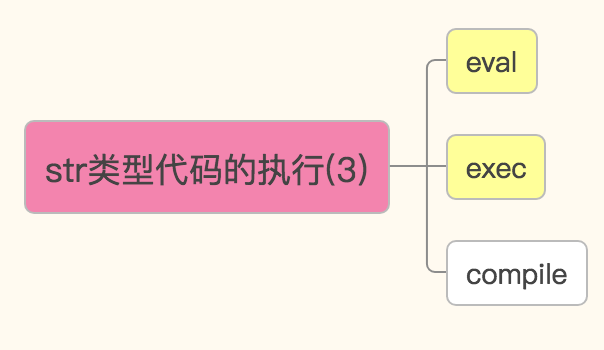
eval() 将字符串类型的代码执行并返回结果(单行,有返回值)
print(eval('1+2+3+4')) Output: 10
exec()将自字符串类型的代码执行(多行,无返回值)
code = ''' print(123) a = 20 print(a) ''' a = 10 exec(code,{'print':print},) print(a) Output: 123 20 10
compile 将字符串类型的代码编译。代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval()进行求值。
参数说明:
1. 参数source:字符串或者AST(Abstract Syntax Trees)对象。即需要动态执行的代码段。
2. 参数 filename:代码文件名称,如果不是从文件读取代码则传递一些可辨认的值。当传入了source参数时,filename参数传入空字符即可。
3. 参数model:指定编译代码的种类,可以指定为 ‘exec’,’eval’,’single’。当source中包含流程语句时,model应指定为‘exec’;当source中只包含一个简单的求值表达式,model应指定为‘eval’;当source中包含了交互式命令语句,model应指定为'single'。
>>> #简单求值表达式用eval >>> code2 = '1 + 2 + 3 + 4' >>> compile2 = compile(code2,'','eval') >>> eval(compile2) >>> #交互语句用single >>> code3 = 'name = input("please input your name:")' >>> compile3 = compile(code3,'','single') >>> name #执行前name变量不存在 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#29>", line 1, in <module> name NameError: name 'name' is not defined >>> exec(compile3) #执行时显示交互命令,提示输入 please input your name:'pythoner' >>> name #执行后name变量有值 "'pythoner'"
和数字相关
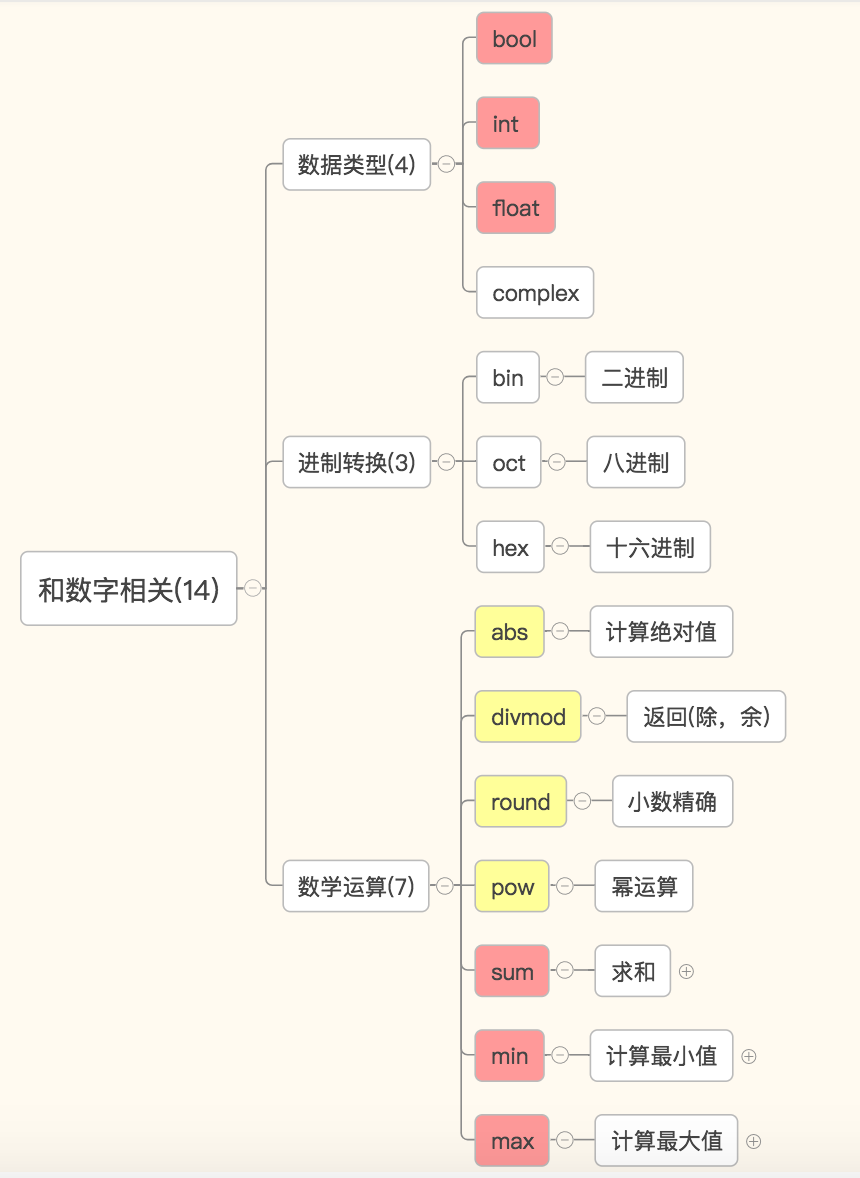
数字——数据类型相关:bool,int,float,complex
数字——进制转换相关:bin,oct,hex
数字——数学运算:abs,divmod,min,max,sum,round,pow
## divmod # divmod() 函数把除数和余数运算结果结合起来,返回一个包含商和余数的元组(a // b, a % b) res = divmod(10, 3) print(res) Output: (3, 1)
## pow() 方法返回 xy(x的y次方) 的值。 print(pow(2, 3)) Output: 8 ## round() 方法返回浮点数x的四舍五入值。 print(round(1.61284567)) Output: 2 print(round(1.61284567,3)) Output:1.613
和数据结构相关
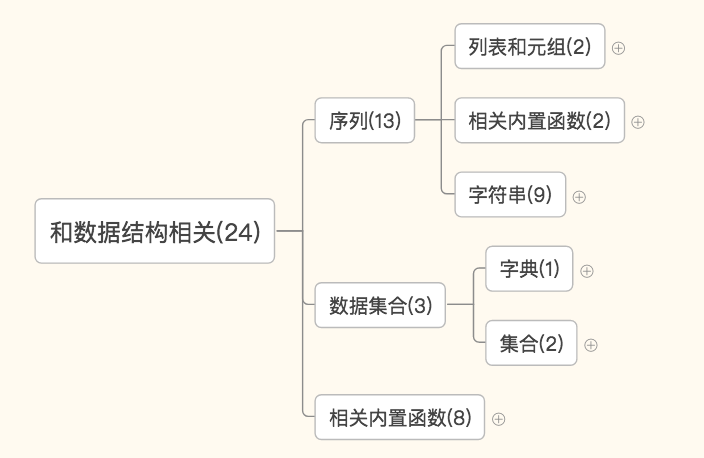
序列——列表和元组相关的:list和tuple
序列——字符串相关的:str,format,bytes,bytearry,memoryview,ord,chr,ascii,repr
## bytearray() 方法返回一个新字节数组。这个数组里的元素是可变的,并且每个元素的值范围: 0 <= x < 256。 ret = bytearray('alex',encoding='utf-8') print(id(ret)) print(ret[0]) ret[0] = 65 print(ret) print(id(ret)) Output: 1913856888704 97 bytearray(b'Alex') 1913856888704
序列:reversed,slice
## reversed l = (1,2,23,213,5612,342,43) print(l) print(list(reversed(l)))
Output:
(1, 2, 23, 213, 5612, 342, 43)
[43, 342, 5612, 213, 23, 2, 1]
## slice l = (1,2,23,213,5612,342,43) sli = slice(1,5,2) print(l[sli]) Output: (2, 213)
数据集合——字典和集合:dict,set,frozenset
数据集合:len,sorted,enumerate,all,any,zip,filter,map
filter和map:http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/7266192.html