题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
题目描述:
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
你是否可以使用 O(1) 空间解决此题?
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
解题:采用双指针法
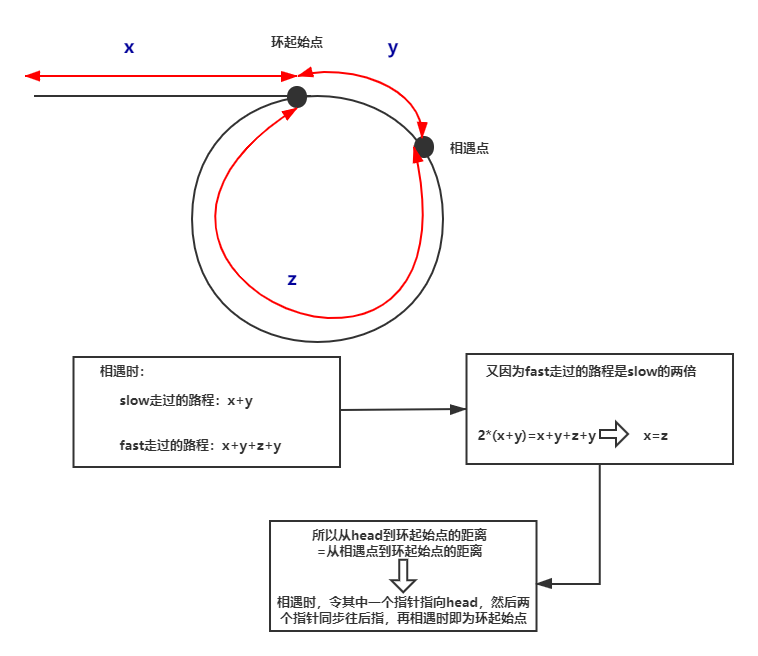
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
ListNode *index1 = head;
ListNode *index2 = slow;
while(index1 != index2)
{
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
方法二:哈希表
遍历链表中的每个节点,并将它记录下来;一旦遇到了此前遍历过的节点,就可以判定链表中存在环。借助哈希表可以很方便地实现。
C++ 11中对unordered_set描述大体如下:无序集合容器(unordered_set)是一个存储唯一(unique,即无重复)的关联容器(Associative container),容器中的元素无特别的秩序关系,该容器允许基于值的快速元素检索,同时也支持正向迭代。
问题:如果链表中有重复值,其实本没有环,是否会产生错误?
回答:visited.insert(head),head是指针,存放的是地址,所以hash值是对象的内存地址。hash值根据对象内存地址生成(不改写的情况下),两个内容一样的节点内存地址是不一样的,所以即时链表中存在重复元素,也可以保证答案正确。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> visited;
while (head != nullptr) {
if (visited.count(head)) {
return head;
}
visited.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/solution/huan-xing-lian-biao-ii-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)