实现mypwd
任务详情
1 学习pwd命令
2 研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
3 实现mypwd
4 测试mypwd
实现过程
一、查阅资料学习pwd
- 命令语法
pwd [OPTION]... - 命令参数
| 参数 | 长参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| -L | --logical(无效) | 当目录为连接路径时,显示连接路径 |
| -P | --physical(无效) | 显示实际物理路径,而非使用连接(link)路径 |
| --help | 显示命令在线帮助(该参数无法使用) | |
| --version | 显示命令版本信息(该参数无法使用) |
二、通过man命令查看pwd
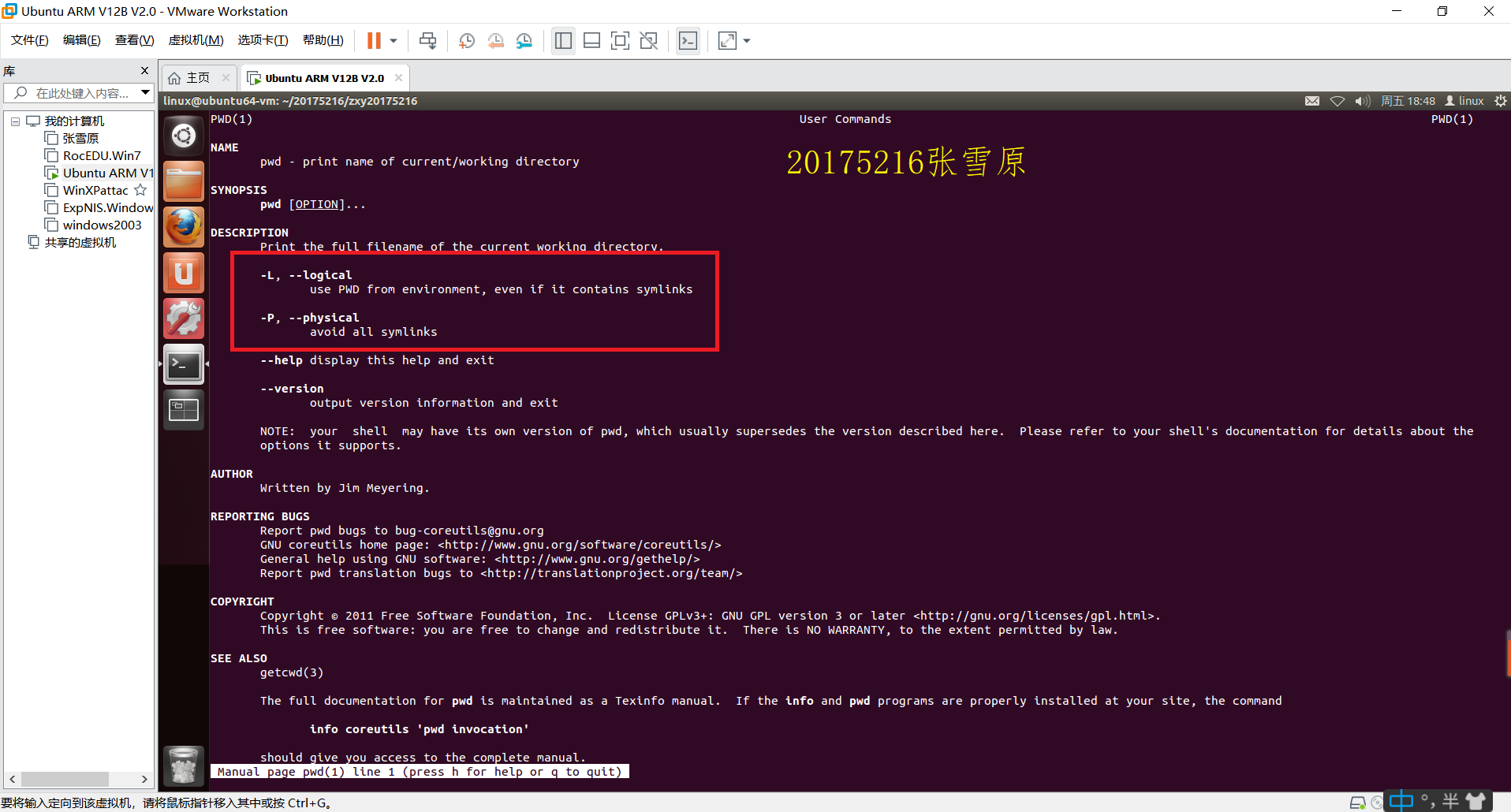
由图可知pwd命令的用途是显示工作目录的路径名称。pwd 命令将当前目录的全路径名称(从根目录)写入标准输出。全部目录使用 /(斜线)分隔。第一个 / 表示根目录,最后一个目录是当前目录。
pwd [-L]如果 PWD 环境变量包含了不包含文件名 .(点)或 ..(点点)的当前目录的绝对路径名,则显示 PWD 环境变量的值。否则,-L标志与-P标志一样运行。pwd [-p]显示当前目录的绝对路径名。与-P标志一起显示的绝对路径不包含在路径名的绝对路径中涉及到符号链接类型的文件的名称。
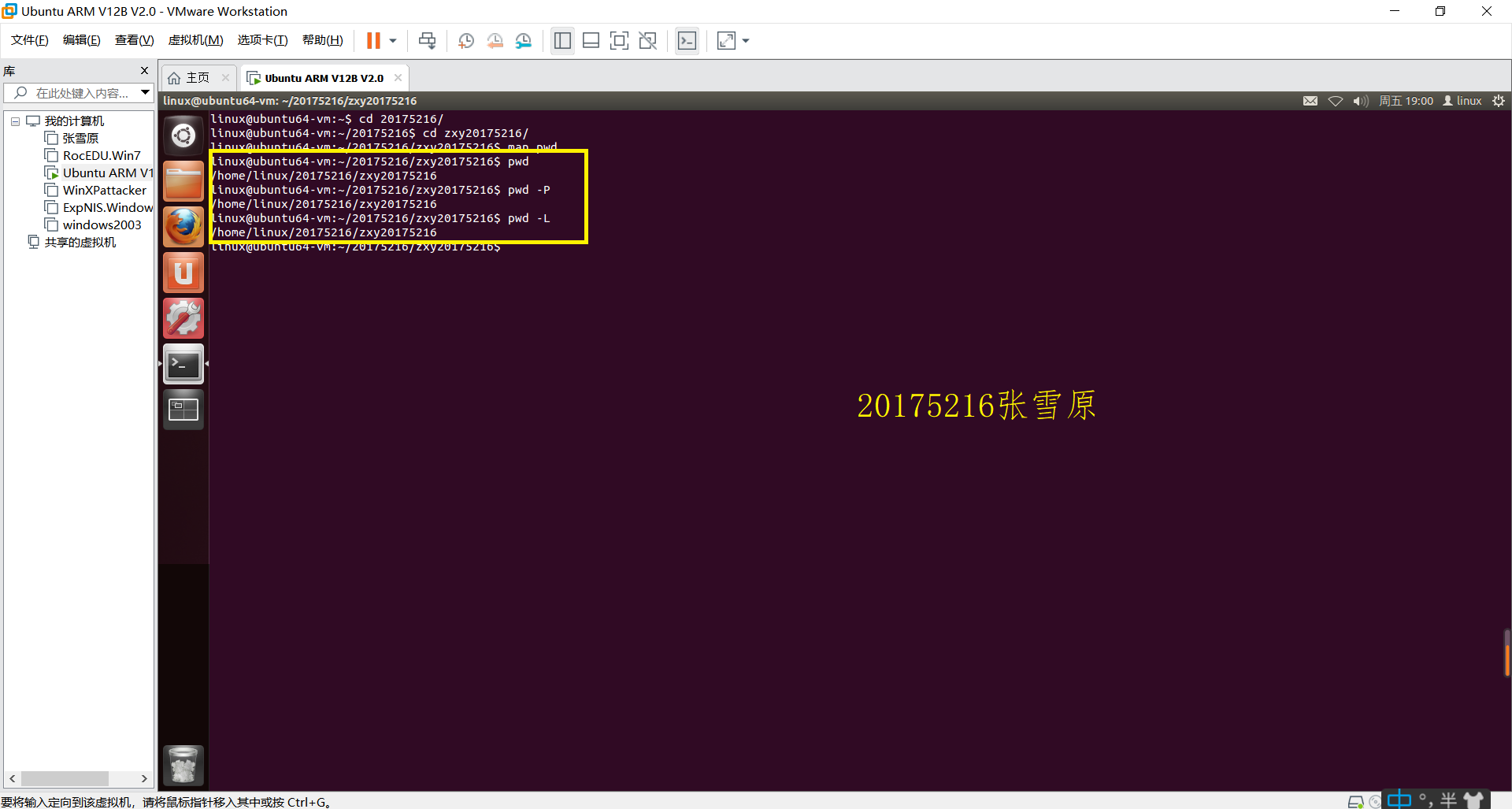
三、执行pwd命令
四、研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
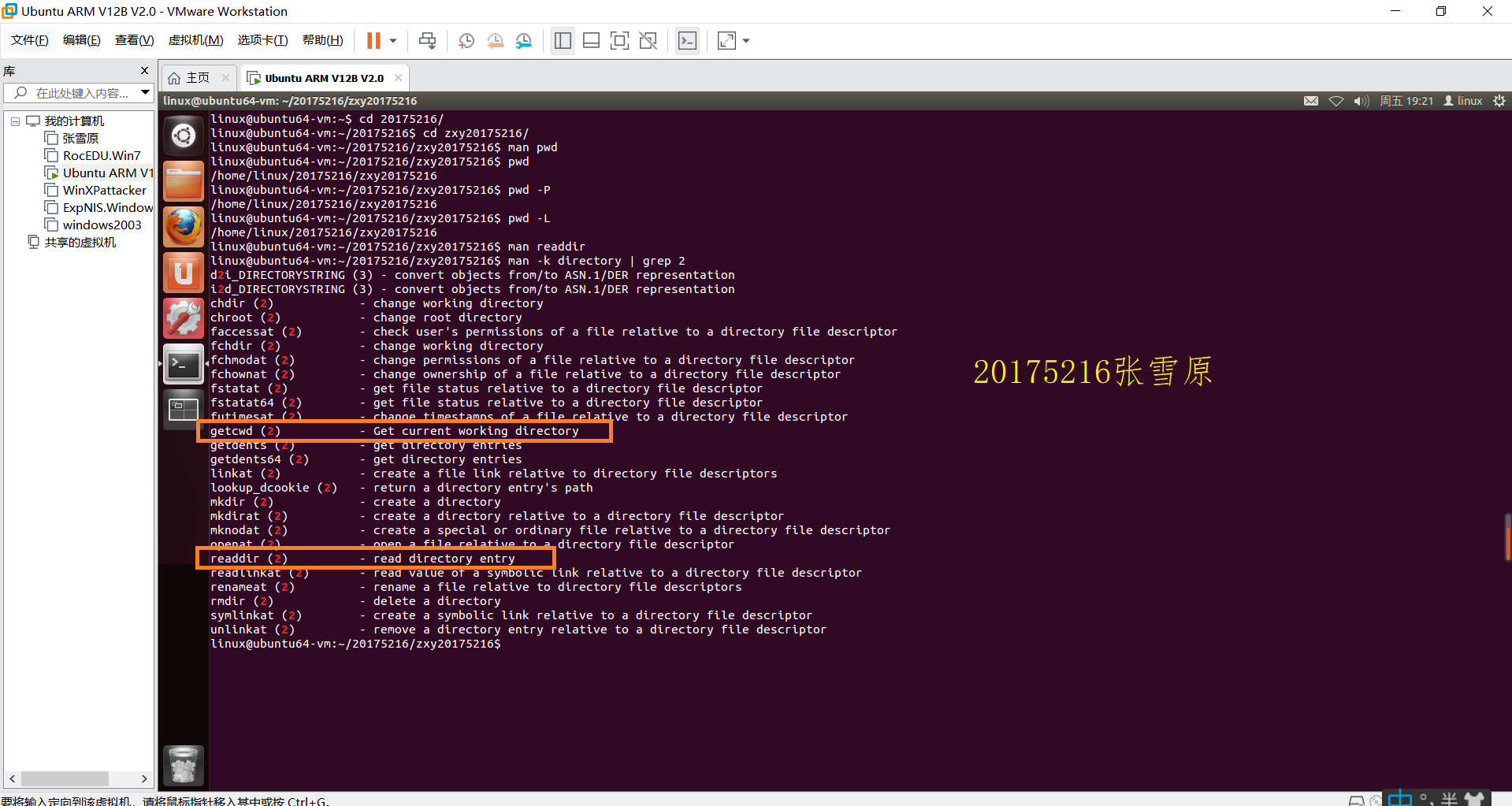
- 命令
readdir也符合要求,用于打开并读取当前目录文件
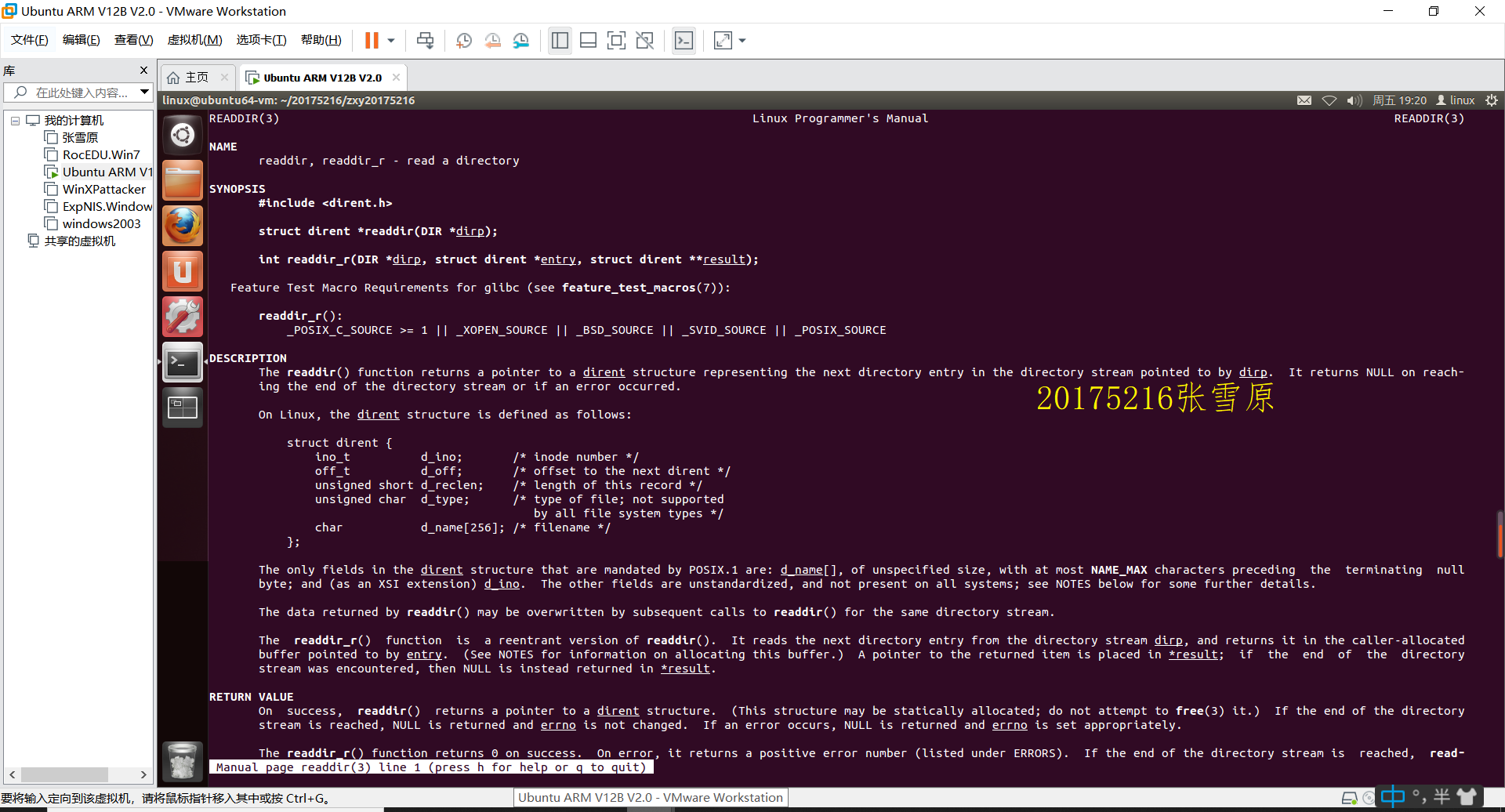
从详细资料中发现readdir符合我们的需求,这需要头文件#inlude<dirent.h>,并且readdir定义的是一个结构体,可知该函数返回一个dirent结构体指针,dirent结构体成员如下,
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* filename */
};
- 发现
getcwd()函数符合条件后,查看其用法

- 找到需要的头文件和函数参数
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
- 伪代码
1、用“.”获取当前目录的i-node(inode)
2、用“..”获取父级目录的i-node(up_inode)
3、判断当前目录的i-node和父级目录的i-node是否相同
4、相同:到达根目录,输出完整路径,退出程序
5、不同:还未到根目录,切换至父级目录,返回第一步再次执行相同操作直至两个i-node相同
五、实验代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char this_name[20]=".",father_name[20]="..";
char name[16][32];
struct dirent *this_dir=NULL,*father_dir=NULL,*temp=NULL;
DIR *dir=NULL;
int i=0;
unsigned long int this_ino;
while(1)
{
dir = opendir(this_name);
if(dir == NULL)
printf("error open");
while(1)
{
this_dir = readdir(dir);
if(strcmp(this_dir->d_name,".")==0)
break;
}
this_ino=this_dir->d_ino;
closedir(dir);
dir = opendir(father_name);
while(1)
{
father_dir = readdir(dir);
if(father_dir->d_name[0]=='.'&&father_dir->d_name[1]=='.')
break;
}
if(this_dir->d_ino==father_dir->d_ino)
break;
closedir(dir);
dir=opendir(father_name);
while((temp=readdir(dir))!=NULL)
{
if(temp->d_ino==this_ino)
{
bzero(name[i],32);
strcat(name[i++],temp->d_name);
break;
}
}
closedir(dir);
strcat(this_name,"/..");
strcat(father_name,"/..");
}
for(i--;i>=0;i--)
printf("/%s",name[i]);
printf("
");
}
六、测试结果
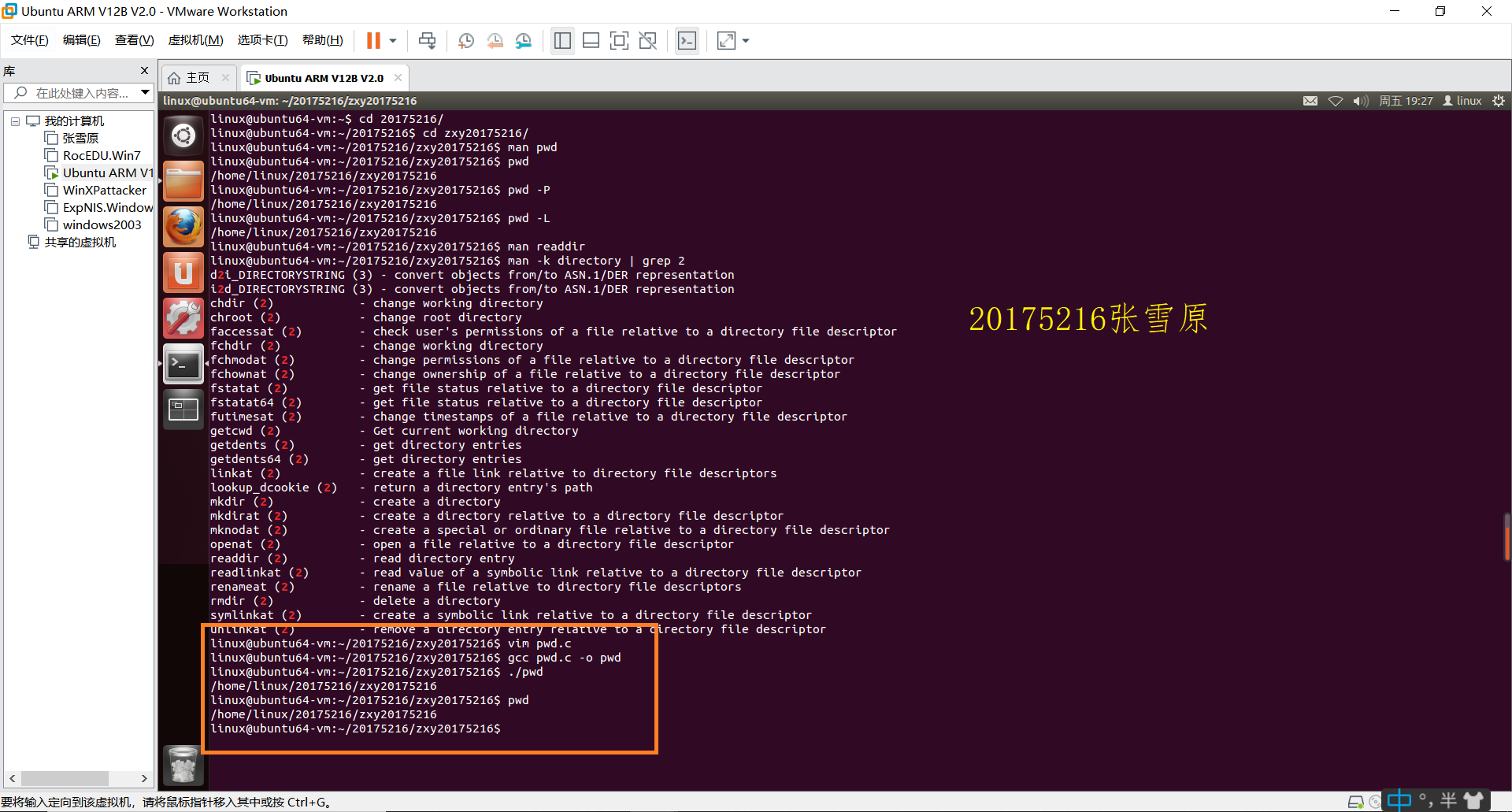
码云链接:https://gitee.com/besti20175216/20175216_snow_plains/blob/master/20175216zxy/mystate.c