Java Thread系列(一)线程创建
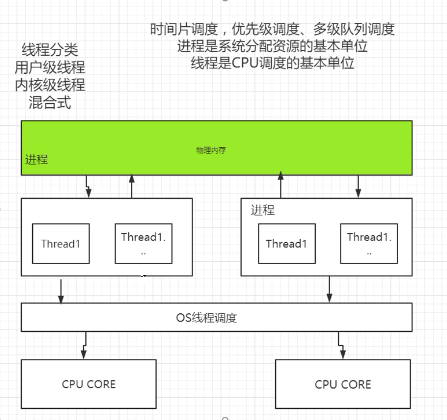
Java 中创建线程主要有三种方式:继承 Thread、实现 Runnable 接口、使用 ExecutorService、Callable、Future 实现由返回结果的多线程。 线程是 CPU 调度的最小单位。
一、继承 Thread 类创建线程类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("线程一" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread th = new MyThread();
th.start();
}
}
注意:通过 start() 方法才能启动的线程,直接调用的 run() 方法只是普通的方法。
二、实现 Runnable 接口创建线程
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public String ThreadName;
public MyRunnable(String tName){
ThreadName = tName;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.println(ThreadName);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable th1 = new MyRunnable("线程A");
MyRunnable th2 = new MyRunnable("线程B");
Thread myth1 = new Thread(th1);
Thread myth2 = new Thread(th2);
myth1.start();
myth2.start();
}
}
总结:使用 Runnable 接口创建线程有两个不足,一是不能同步返回线程执行的结果,二是 run() 方法不能抛出异常。下面介绍 Callable 接口解决这个问题。
三、使用 ExecutorService、Callable、Future 实现由返回结果的多线程
/**
* 有返回值的线程
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException,
InterruptedException {
System.out.println("----程序开始运行----");
Date date1 = new Date();
int taskSize = 5;
// 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(taskSize);
// 创建多个有返回值的任务
List<Future> list = new ArrayList<Future>();
for (int i = 0; i < taskSize; i++) {
Callable c = new MyCallable(i + " ");
// 执行任务并获取Future对象
Future f = pool.submit(c);
// System.out.println(">>>" + f.get().toString());
list.add(f);
}
// 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
// 获取所有并发任务的运行结果
for (Future f : list) {
// 从Future对象上获取任务的返回值,并输出到控制台
System.out.println(">>>" + f.get().toString());
}
}
}
class MyCallable implements Callable<Object> {
private String taskNum;
MyCallable(String taskNum) {
this.taskNum = taskNum;
}
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return taskNum;
}
}
《40个Java多线程问题总结》:http://www.importnew.com/18459.html
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!