apahce shiro:1.6.0
密码存储,应该加密/生成密码摘要存储,而不是存储明文密码。
1、编码/解码
Shiro 提供了 base64和 16进制字符串编码/解码的API支持, 方便一些编码解码操作。
String str = "hello"; #base64 String base64Encoded = Base64.encodeToString(str.getBytes()); String str2 = Base64.decodeToString(base64Encoded); #十六进制 String base64Encoded = Hex.encodeToString(str.getBytes()); String str2 = new String(Hex.decode(base64Encoded.getBytes()));
还有一个可能经常用到的类CodecSupport,提供了toBytes(str, "utf-8") / toString(bytes, "utf-8")用于在 byte数组/String之间转换。
2、散列算法
散列算法一般用于生成数据的摘要信息,是一种不可逆的算法,一般适合存储密码之类的数据,常见的散列算法如 MD5、SHA 等。

2.1 MD5散列举例
String str = "admin"; String salt = ""; String md5 = new Md5Hash(str, salt).toString();//21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3
可以到一些 md5 解密网站很容易的通过散列值得到密码“admin”,即如果直接对密码进行散列相对来说破解更容易;
此时我们可以加一些只有系统知道的干扰数据, 如用户名和 ID (即盐);这样散列的对象是“密码+用户名+ID”,这样生成的散列值相对来说更难破解:
String str = "admin"; String salt = "123"; String md5 = new Md5Hash(str, salt).toString();//d829b843a6550a947e82f2f38ed6b7a7
另外散列时还可以指定散列次数,如2次表示:md5(md5(str))
String str = "admin"; String salt = "123"; String md5 = new Md5Hash(str, salt, 2).toString();//6bdae6366c1e46d541eb0ca9547d974c
2.2 使用SHA算法(SHA1、SHA256、SHA512)生成相应的散列数据
String str = "admin"; String salt = "123"; String sha1 = new Sha1Hash(str, salt).toString();//28dca2a7b33b7413ad3bce1d58c26dd679c799f1 String sha256 = new Sha256Hash(str, salt).toString();//82a79f11b4acb52a642ef7e339dfce4aa92ff65ed2e7ab702d798dbe10eca0b8 String sha512 = new Sha512Hash(str, salt).toString();//cefbd13986ef4b4c6d57e681da43f7abc076d4d6236df728c1b57519763edd305ee8d6d3c94d5d853dbdc36c1a3169c5e7c4d8bccbf48fb31a6e0eb7758a9f8f
2.3 Shiro 还提供了通用的散列支持
通过调用 SimpleHash 时指定散列算法,其内部使用了 Java 的 MessageDigest 实现
String str = "admin"; String salt = "123"; //内部使用 MessageDigest String simpleHash = new SimpleHash("SHA-1", str, salt).toString();
2.4 为了方便使用,Shiro 提供了 HashService,默认提供了 DefaultHashService 实现
DefaultHashService hashService = new DefaultHashService(); //默认算法 SHA-512 hashService.setHashAlgorithmName("SHA-512"); //通过 hashAlgorithmName 属性修改算法 hashService.setPrivateSalt(new SimpleByteSource("123")); //通过 privateSalt 设置一个私盐,其在散列时自动与用户传入的公盐混合产生一个新盐,默认无 hashService.setGeneratePublicSalt(true);//是否生成公盐,默认 false hashService.setRandomNumberGenerator(new SecureRandomNumberGenerator());//用于生成公盐。默认就这个 hashService.setHashIterations(1); //生成 Hash 值的迭代次数 #构建一个 HashRequest,传入算法、数据、公盐、迭代次数 HashRequest request = new HashRequest.Builder() .setAlgorithmName("MD5").setSource(ByteSource.Util.bytes("hello")) .setSalt(ByteSource.Util.bytes("123")).setIterations(2).build(); String hex = hashService.computeHash(request).toHex();
2.5 SecureRandomNumberGenerator 用于生成一个随机数
SecureRandomNumberGenerator randomNumberGenerator = new SecureRandomNumberGenerator(); randomNumberGenerator.setSeed("123".getBytes()); String hex = randomNumberGenerator.nextBytes().toHex();
3、加密/解密
Shiro 还提供对称式加密/解密算法的支持,如 AES、Blowfish.
AesCipherService aesCipherService = new AesCipherService(); aesCipherService.setKeySize(128); //设置 key 长度 //生成 key Key key = aesCipherService.generateNewKey(); String text = "hello"; //加密 String encrptText = aesCipherService.encrypt(text.getBytes(), key.getEncoded()).toHex(); //解密 String text2 = new String(aesCipherService.decrypt(Hex.decode(encrptText), key.getEncoded()).getBytes()); Assert.assertEquals(text, text2);
4、PasswordService
Shiro 提供了PasswordService用于提供加密密码服务。
public interface PasswordService { //输入明文密码得到密文密码 String encryptPassword(Object plaintextPassword) throws IllegalArgumentException; }
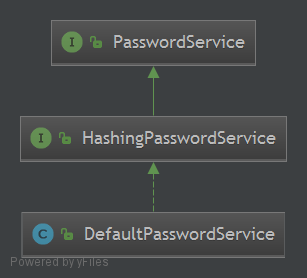
DefaultPasswordService配合PasswordMatcher 实现简单的密码加密与验证服务。实际使用:在Realm注入一个 passwordService 来加密密码用于后面的验证匹配或者在用户模块里新增用户和修改密码时可以使用passwordService 加密密码并存到数据库.

package com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter5.hash.realm; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordService; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; /** * <p>User: Zhang Kaitao * <p>Date: 14-1-27 * <p>Version: 1.0 */ public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { private PasswordService passwordService; public void setPasswordService(PasswordService passwordService) { this.passwordService = passwordService; } @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { return null; } @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( "wu", passwordService.encryptPassword("123"), getName()); } }
5、CredentialsMatcher
Shiro 提供了CredentialsMatcher用于提供验证密码服务。
public interface CredentialsMatcher { //匹配用户输入的 token 的凭证(未加密)与系统提供的凭证(已加密) boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info); }
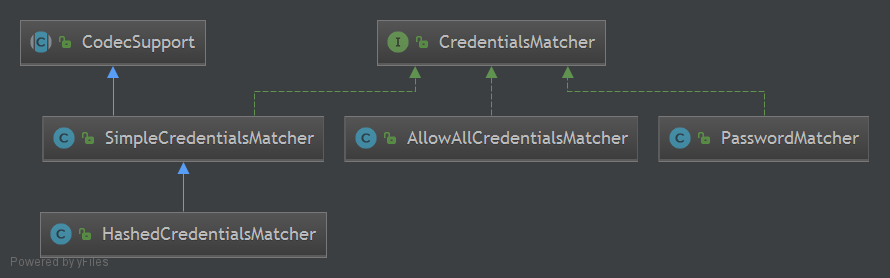
Shiro提供了CredentialsMatcher的散列实现HashedCredentialsMatcher, PasswordMatcher只用于密码验证且可以提供自己的盐, 而不是随机生成盐,所以生成密码散列值的算法需要自己写。
(1)生成密码散列值
此处我们使用 MD5 算法,"密码+盐(用户名+随机数)"的方式生成散列值
String algorithmName = "md5"; String username = "liu"; String password = "123"; String salt1 = username; String salt2 = new SecureRandomNumberGenerator().nextBytes().toHex(); int hashIterations = 2; SimpleHash hash = new SimpleHash(algorithmName, password, salt1 + salt2, hashIterations);
如果要写用户模块,需要在新增用户/重置密码时使用如上算法保存密码,将生成的密码及salt2 存入数据库(因为我们的散列算法是:md5(md5(密码+username+salt2)))。
(2)生成 Realm
此处就是把步骤1中生成的相应数据组装为SimpleAuthenticationInfo,通过SimpleAuthenticationInfo的credentialsSalt设置盐,HashedCredentialsMatcher会自动识别这个盐

package com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter5.hash.realm; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordService; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; /** * <p>User: Zhang Kaitao * <p>Date: 14-1-27 * <p>Version: 1.0 */ public class MyRealm2 extends AuthorizingRealm { @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { return null; } @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { String username = "liu"; //用户名及salt1 String salt2 = "0072273a5d87322163795118fdd7c45e"; String password = "be320beca57748ab9632c4121ccac0db"; //加密后的密码 SimpleAuthenticationInfo ai = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, password, getName()); ai.setCredentialsSalt(ByteSource.Util.bytes(username+salt2)); //盐是用户名+随机数 return ai; } }
(3)密码重试次数限制
如在 1 个小时内密码最多重试 5 次,如果尝试次数超过 5 次就锁定 1 小时,1 小时后可再次重试,如果还是重试失败,可以锁定如 1 天,以此类推,防止密码被暴力破解。我们通过继承 HashedCredentialsMatcher,且使用 Ehcache 记录重试次数和超时时间。

package com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter5.hash.credentials; import net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager; import net.sf.ehcache.Ehcache; import net.sf.ehcache.Element; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.ExcessiveAttemptsException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher; import javax.security.auth.login.AccountLockedException; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * <p>User: Zhang Kaitao * <p>Date: 14-1-28 * <p>Version: 1.0 */ public class RetryLimitHashedCredentialsMatcher extends HashedCredentialsMatcher { private Ehcache passwordRetryCache; public RetryLimitHashedCredentialsMatcher() { CacheManager cacheManager = CacheManager.newInstance(CacheManager.class.getClassLoader().getResource("ehcache.xml")); passwordRetryCache = cacheManager.getCache("passwordRetryCache"); } @Override public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //retry count + 1 Element element = passwordRetryCache.get(username); if(element == null) { element = new Element(username , new AtomicInteger(0)); passwordRetryCache.put(element); } AtomicInteger retryCount = (AtomicInteger)element.getObjectValue(); if(retryCount.incrementAndGet() > 5) { //if retry count > 5 throw throw new ExcessiveAttemptsException(); } boolean matches = super.doCredentialsMatch(token, info); if(matches) { //clear retry count passwordRetryCache.remove(username); } return matches; } }
如上代码逻辑比较简单, 即如果密码输入正确清除 cache 中的记录; 否则 cache 中的重试次数+1,如果超出 5 次那么抛出异常表示超出重试次数了。
