概述
NETCONF = The Network Configuration Protocol
SDN = Software Define Network
NETCONF协议分为传输层、消息层、操作层和内容层。其中,内容层是唯一没有标准化的层,于是一种新的建模语言YANG产生了,它的目标是对NETCONF数据模型、操作进行建模,覆盖NETCONF协议的操作层和内容层
接下来就对NETCONF1.1(RFC6241)版本进行详细分析。
1. NETCONF1.1协议详解
NETCONF采用的是C/S的模式,分为4层,由下至上分别是传输层,消息层,操作层和内容层:
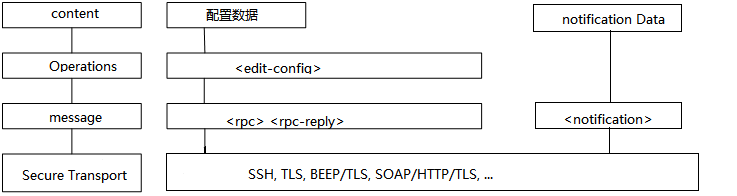
在详细介绍这四层之前,需要提前建立一个概念,NETCONF认为网络的模型数据可以分为两大类,即状态数据和配置数据。状态数据一般指server(设备)的固有属性数据和当前运行的状态数据等,这类数据仅能查询。而配置数据则是指由用户(以某种方式)配置到server上的数据。而配置数据本身又可以存在多个数据库,标准中提到了<running/>库用于保存当前已经生效的配置;<candidate/>用于保存可以提交为生效的数据;以及<startup/>用于保存启动时的配置数据。
1.1. 传输层
NETCONF的第一大优势就是其从协议层面就已经规定其传输层必须使用带有安全加密的通信协议,例如SSH,TLS等。相比与其它也允许明文传输的协议来说其在协议层面就已经对数据安全做了第一道守护。由于NETCONF协议规定必须要支持SSH,所以目前SSH是NETCONF使用最广泛的传输层协议。
NETCONF的协议内容是承载在安全传输层之上的,所以NETCONF本身是一个应用层协议,所以NETCONF协议中并没有规定建链和保活相关的内容。
1.2. 消息层
NETCONF中定义了三种消息类型,分别是hello, rpc和rpc-reply, notification。
1.2.1. <hello>
<hello>仅用于回话刚刚建立时netconf-server和netconf-client之间进行能力交换。
server和client需要在回话建立后互相发送<hello>消息,并在<hello>消息中携带自身支持的能力,以及支持的netconf协议的版本号,server和client根据自身和对方的能力信息协商使用的netconf版本。
一般来说,C/S双方互发<hello>且协商版本成功后,认为netconf会话建立成功。
1.2.1.1. 几种常用的能力
(1) XPath Capability
该能力表示client可以在filter中使用XPath表达式作为过滤条件
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:xpath:1.0
(2) Writable-Running Capability
该能力表示server支持直接对<running/>库进行修改操作。
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:writable-running:1.0
(3) Candidate Configuration Capability
该能力表示server具有一个candidate数据库,并且可以将candidate数据库中的配置提交生效并更新running数据库
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:candidate:1.0
(4) Rollback-on-Error Capability
该能力表示server在执行client发送的配置数据出错后可以进行回滚
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:rollback-on-error:1.0
(5) Validate Capability
该能力表示server可以校验client发送的配置数据是否正确
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:validate:1.1
(6) Distinct startup Capability
该能力表示server有一个startup数据库,用于保存启动配置
Capability Identifier:
urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:startup:1.0
1.2.2. <rpc>和<rpc-reply>
<rpc>是由netconf-client发起的发送到netconf-server的消息。用于client请求server执行某项具体的操作。
<rpc>包含一个强制属性”message-id”,这个id是一个单调递增的正整数,同一会话内不能重复。该id用于<rpc>和<rpc-reply>的配对。
<rpc-reply>是有netconf-server发送给netconf-client的rpc响应。不能主动发起,仅能在收到<rpc>之后回复,切必须携带与收到的rpc相同的message-id。
在<rpc-reply>定义了两种默认的元素分别是<ok>和<rpc-error>。<ok>表示未定义响应内容的rpc执行成功,而<rpc-error>表示rpc执行失败。
RPC的一条重要特性Pipelining,流水线
NETCONF<rpc>requests MUST be processed serially by the managed device. Additional<rpc>requests MAY be sent before previous ones have been completed. The managed device MUST send responses only in the order the requests were received.
简单的翻译一下就是:
NETCONF的RPC请求必须由设备串行处理。其他<rpc>请求可以在之前的请求完成之前发送。设备必须仅按接收请求的顺序发送响应
换言之,RPC消息是一个队列(queue),遵循先进先出原则。
1.2.3. <notification>
在netconf的1.0版本中还没有加入Notification相关的内容,而在1.1版本已经将RFC5277(NETCONF Event Notifications)添加在内了。支持Notification上报的netconf-server需在能力交换时上报能力:
“urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:notification:1.0”
几个关键的知识点:
1. Netconf的通知采用的是订阅发布机制,server仅会向发送过订阅请求的client发送通知。
2. Netconf的通知是以Stream进行分类的,不同类的Stream以不同的stream-name进行区分。netconf-server默认需要支持的stream-name是”NETCONF”。
3. client不能重复下发订阅,即同一Stream的订阅不能重复下发,也不能同时订阅多个Stream,订阅可以设置定时取消,如果没有设置终止时间,取消订阅需要使用close-session或者kill-session。定时取消的订阅netconf的会话还是激活的,而使用close-session或者kill-session来取消的话,netconf会话会关闭。
Stream发现:
例如:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <get> <filter type="subtree"> <netconf xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netmod:notification"> <streams/> </netconf> </filter> </get> </rpc> <rpc-reply message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <data> <netconf xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netmod:notification"> <streams> <stream> <name>NETCONF</name> <description>default NETCONF event stream</description> <replaySupport>true</replaySupport> <replayLogCreationTime>2007-07-08T00:00:00Z</replayLogCreationTime> </stream> <stream> <name>SNMP</name> <description>SNMP notifications</description> <replaySupport>false</replaySupport> </stream> <stream> <name>syslog-critical</name> <description>Critical and higher severity</description> <replaySupport>true</replaySupport> <replayLogCreationTime>2007-07-01T00:00:00Z</replayLogCreationTime> </stream> </streams> </netconf> </data> </rpc-reply>
发起订阅:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns:netconf="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <create-subscription xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:notification:1.0"> <stream>SNMP</stream> </create-subscription> </rpc> <rpc-reply message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
通知:
<notification xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:notification:1.0"> <eventTime>2007-07-08T00:10:00Z</eventTime> <event xmlns="http://example.com/event/1.0"> <eventClass>state</eventClass> <reportingEntity> <card>Ethernet0</card> </reportingEntity> <operState>enabled</operState> </event> </notification>
1.3. 操作层
操作层仅承载在仅<rpc>和<rpc-reply>消息上,<hello>和<notification>消息无操作层。
NETCONF协议规定了9种简单的rpc操作,同时也支持用户自定义rpc操作。有关自定义操作的内容放到内容层来讲。
1.3.1. <get>
用于查询状态数据,另外如果server支持能力:urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:xpath:1.0则还可以使用filter进行条件查询,例如:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <get> <filter type="subtree"> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/stats"> <interfaces> <interface> <ifName>eth0</ifName> </interface> </interfaces> </top> </filter> </get> </rpc> <rpc-reply message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <data> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/stats"> <interfaces> <interface> <ifName>eth0</ifName> <ifInOctets>45621</ifInOctets> <ifOutOctets>774344</ifOutOctets> </interface> </interfaces> </top> </data> </rpc-reply>
1.3.2. <get-config>
用于查询配置数据,可以通过 <source/>来指定不同的配置库,例如:
<rpc message-id="101"xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <get-config> <source> <running/> </source> <filter type="subtree"> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/config"> <users/> </top> </filter> </get-config> </rpc> <rpc-reply message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <data> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/config"> <users> <user> <name>root</name> <type>superuser</type> <full-name>Charlie Root</full-name> <company-info> <dept>1</dept> <id>1</id> </company-info> </user> <!-- additional <user> elements appear here... --> </users> </top> </data> </rpc-reply>
1.3.3. <edit-config>
用于对指定配置数据库的内容进行修改,支持以下几种操作:
merge: 合并操作,此操作为默认操作。
replace: 替换操作,如果对象已经存在则替换,不存在则创建。
create: 创建操作,如果对象已经存在,则报错误“data-exists”。
delete: 删除操作,如果对象存在则删除,不存在则报错 “data-missing”。
remove: 删除操作,如果对象存在则删除,不存在则忽略。
举例:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <edit-config> <target> <running/> </target> <config xmlns:xc="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/config"> <interface xc:operation="replace"> <name>Ethernet0/0</name> <mtu>1500</mtu> <address> <name>192.0.2.4</name> <prefix-length>24</prefix-length> </address> </interface> </top> </config> </edit-config> </rpc> <rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <edit-config> <target> <running/> </target> <default-operation>none</default-operation> <config xmlns:xc="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <top xmlns="http://example.com/schema/1.2/config"> <protocols> <ospf> <area> <name>0.0.0.0</name> <interfaces> <interface xc:operation="delete"> <name>192.0.2.4</name> </interface> </interfaces> </area> </ospf> </protocols> </top> </config> </edit-config> </rpc>
1.3.4. <copy-config>
将一个库的数据复制到另一个库。
举例:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <copy-config> <target> <running/> </target> <source> <url>https://user:password@example.com/cfg/new.txt</url> </source> </copy-config> </rpc>
1.3.5. <delete-config>
删除一个数据库。但是<running/>库不能被删除。
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <delete-config> <target> <startup/> </target> </delete-config> </rpc>
1.3.6. <lock>
获取指定数据库的锁,当某个client获得了指定数据库的锁之后,在其没有释放该锁之前,其余client均不能获得该数据库的锁,也不能对其进行修改操作。同一client也不能在没有释放锁之前,重复申请锁。
获取锁的主要目的就是避免并发导致数据冲突。
举例:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <lock> <target> <running/> </target> </lock> </rpc>
1.3.7. <unlock>
释放指定数据库的锁。client只能释放自己持有的锁,不能释放其它client的锁。
举例:
<rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <unlock> <target> <running/> </target> </unlock> </rpc>
1.3.8. <close-session>
优雅关闭netconf会话,netconf-server将释放该client持有的锁和为其分配的资源,并优雅的关闭与该client链接。所有在<close-session>之后收到的操作均会被忽略。
1.3.9. <kill-session>
强制关闭netconf会话。
1.4. 内容层
开放但规范的内容层是netconf协议的精髓所在。其开放体现在netconf协议本身没有对内容层的数据结构做任何的限定。而其规范则体现在其内容层需要使用Yang语言对其数据进行建模。
在netconf出现之前,我们所熟知且常用的协议,均采用在协议中规定报文的结构体,并按字节流读取并解析的架构。为了更好的在字节流中表达更丰富的报文结构,我们采用TLV等方式来定义对象。但不知大家是否发现,这种方式几乎不具备任何扩展性,一旦扩充对象,或修改对象就需要变更代码。而如果对一个协议扩展了大量的私有数据,那么首先协议不在标准,其次协议栈的代码几乎是完全重写。
而netconf的出现可以说直接对上述问题进行了一次”降维“打击,它完全站在了一个更高的维度来解决上述问题。其内容层未指定具体的模型结构,而是指定了一套建模语言–yang。也就是说使用yang定义的数据模型,均可以作为netconf的内容层。所以扩展对netconf来说就是不断的增加和修改yang文件而已。
做一个比喻,传统基于字节流的协议可以比作一份具有特定可执行的程序,而NETCONF则是写程序的编程语言。
另外一点我们在上面将操作的时候提到netcon支持用户自定义操作。也就是说我们不必纠结标准制定的9个操作类型是否够用,完全可以根据实际的需求在yang文件中定义相应的rpc操作。
Netconf协议本身的一些扩展也是采用在标准中增加默认支持的yang文件的方式来实现的,比如yang-moudle-monitor。