本项目是基于jieba、TfidfVectorizer、LogisticRegression的搜狐新闻文本分类,jieba中文叫做结巴,是一款中文分词工具,TfidfVectorizer中文叫做词袋向量化模型,是用来文章内容向量化的工具,LogisticRegression中文叫做逻辑回归模型,是一种基础、常用的分类方法。
开发环境:jupyter notebook
1.数据准备
训练集共有24000条样本,12个分类,每个分类2000条样本。
测试集共有12000条样本,12个分类,每个分类1000条样本。
在jupyter notebook中新建tfidfVectorizerTest文件
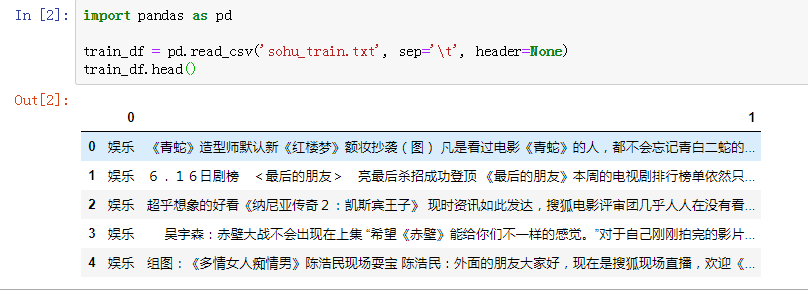
加载训练集到变量train_df中,并打印训练集前5行,代码如下。
read_csv方法中有3个参数,第1个参数是加载文本文件的路径,第2个关键字参数sep是分隔符,第3个关键字参数header是文本文件的第1行是否为字段名。
1 import pandas as pd 2 3 train_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_train.txt', sep=' ', header=None) 4 train_df.head()
运行结果如下图所示:
查看训练集每个分类的名字以及样本数量,代码如下:
1 for name, group in train_df.groupby(0): 2 print(name,len(group))
运行结果如下图所示:

加载测试集并查看每个分类的名字以及样本数量,代码如下:
1 test_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_test.txt', sep=' ', header=None) 2 for name, group in test_df.groupby(0): 3 print(name, len(group))
运行结果如下图所示:

载入停顿词赋值给变量stopWord_list,代码如下:
1 with open('stopwords.txt', encoding='utf8') as file: 2 stopWord_list = [k.strip() for k in file.readlines()]
2.分词
需要安装jieba库,cmd中安装命令:pip install jieba
对训练集的24000条样本循环遍历,使用jieba库的cut方法获得分词列表赋值给变量cutWords。
判断分词是否为停顿词,如果不为停顿词,则添加进变量cutWords中。
代码如下:
import jieba import time train_df.columns = ['分类', '文章'] stopword_list = [k.strip() for k in open('stopwords.txt', encoding='utf8').readlines() if k.strip() != ''] cutWords_list = [] i = 0 startTime = time.time() for article in train_df['文章']: cutWords = [k for k in jieba.cut(article) if k not in stopword_list] i += 1 if i % 1000 == 0: print('前%d篇文章分词共花费%.2f秒' %(i, time.time()-startTime)) cutWords_list.append(cutWords)
运行结果如下:
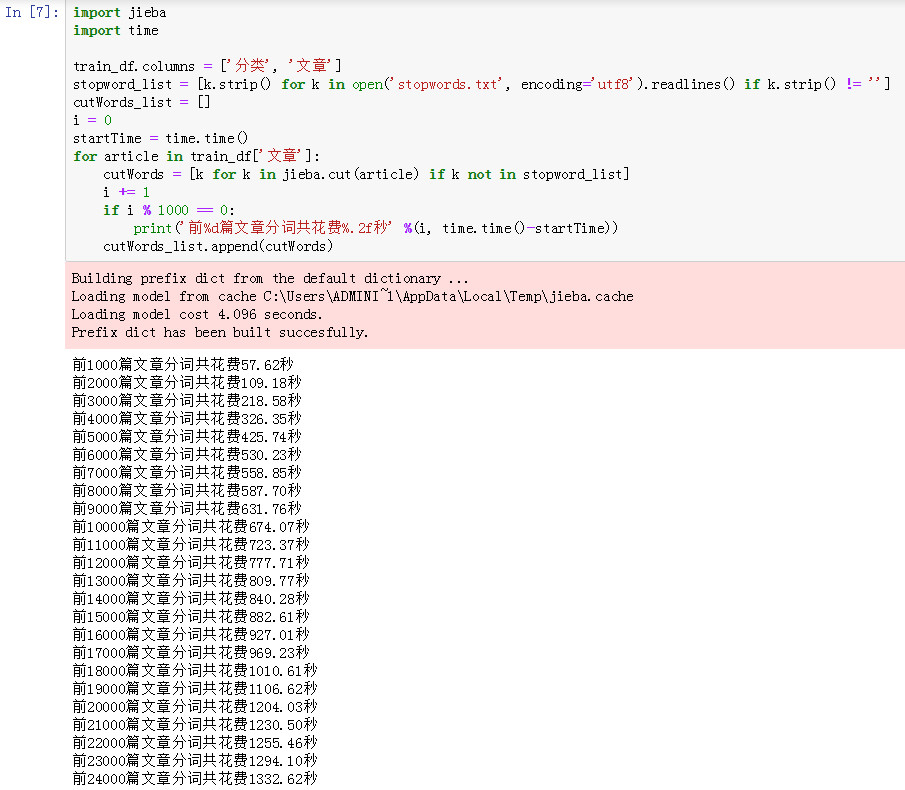
从上面的运行结果可以看出,对24000篇文章进行分词共使用1332.62秒。
将分词结果保存为本地文件cutWords_list.txt,代码如下:
1 with open('cutWords_list.txt', 'w') as file: 2 for cutWords in cutWords_list: 3 file.write(' '.join(cutWords) + ' ')
载入分词文件的代码如下:
1 with open('cutWords_list.txt') as file: 2 cutWords_list = [k.split() for k in file.readlines()]
3.TfidfVectorizer模型
调用sklearn.feature_extraction.text库的TfidfVectorizer方法实例化模型对象。
TfidfVectorizer方法需要4个参数。
第1个参数是分词结果,数据类型为列表,其中的元素也为列表;
第2个关键字参数stop_words是停顿词,数据类型为列表;
第3个关键字参数min_df是词频低于此值则忽略,数据类型为int或float;
第4个关键字参数max_df是词频高于此值则忽略,数据类型为Int或float。
查看TfidfVectorizer方法的更多参数用法,官方文档链接:http://sklearn.apachecn.org/cn/0.19.0/modules/generated/sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer.html
1 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer 2 3 tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(cutWords_list, stop_words=stopWord_list, min_df=40, max_df=0.3)
4.特征工程
第1行代码查看向量化的维数,即特征的维数;
第2行代码调用TfidfVectorizer对象的fit_transform方法获得特征矩阵赋值给X;
第3行代码查看特征矩阵的形状。
1 X = tfidf.fit_transform(train_df[1]) 2 print('词表大小:', len(tfidf.vocabulary_)) 3 print(X.shape)
运行结果如下:

5.模型训练
5.1 标签编码
调用sklearn.preprocessing库的LabelEncoder方法对文章分类做标签编码。
最后一行代码查看预测目标的形状。
1 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder 2 import pandas as pd 3 4 train_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_train.txt', sep=' ', header=None) 5 labelEncoder = LabelEncoder() 6 y = labelEncoder.fit_transform(train_df[0]) 7 y.shape
5.2 逻辑回归模型
调用sklearn.linear_model库的LogisticRegression方法实例化模型对象。
调用sklearn.model_selection库的train_test_split方法划分训练集和测试集。
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 2 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 3 4 train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2) 5 logistic_model = LogisticRegression(multi_class='multinomial', solver='lbfgs') 6 logistic_model.fit(train_X, train_y) 7 logistic_model.score(test_X, test_y)
运行结果如下:

5.3 保存模型
保存模型需要先安装pickle库,安装命令:pip install pickle
调用pickle库的dump方法保存模型,需要2个参数。
第1个参数是保存的对象,可以为任意数据类型,因为有3个模型需要保存,所以下面代码第1个参数是字典。
第2个参数是保存的文件对象,数据类型为_io.BufferedWriter
1 import pickle 2 3 with open('tfidf.model', 'wb') as file: 4 save = { 5 'labelEncoder' : labelEncoder, 6 'tfidfVectorizer' : tfidf, 7 'logistic_model' : logistic_model 8 } 9 pickle.dump(save, file)
5.4 交叉验证
在进行此步的时候,不需要运行此步之前的所有步骤,即可以重新运行jupyter notebook。
调用pickle库的load方法加载保存的模型对象,代码如下:
1 import pickle 2 3 with open('tfidf.model', 'rb') as file: 4 tfidf_model = pickle.load(file) 5 tfidfVectorizer = tfidf_model['tfidfVectorizer'] 6 labelEncoder = tfidf_model['labelEncoder'] 7 logistic_model = tfidf_model['logistic_model']
调用pandas的read_csv方法加载训练集数据。
调用TfidfVectorizer对象的transform方法获得特征矩阵。
调用LabelEncoder对象的transform方法获得预测目标值。
代码如下:
1 import pandas as pd 2 3 train_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_train.txt', sep=' ', header=None) 4 X = tfidfVectorizer.transform(train_df[1]) 5 y = labelEncoder.transform(train_df[0])
调用sklearn.linear_model库的LogisticRegression方法实例化逻辑回归模型对象。
调用sklearn.model_selection库的ShuffleSplit方法实例化交叉验证对象。
调用sklearn.model_selection库的cross_val_score方法获得交叉验证每一次的得分。
最后打印每一次的得分以及平均分,代码如下:
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 2 from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit 3 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 4 5 logistic_model = LogisticRegression(multi_class='multinomial', solver='lbfgs') 6 cv_split = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, test_size=0.3) 7 score_ndarray = cross_val_score(logistic_model, X, y, cv=cv_split) 8 print(score_ndarray) 9 print(score_ndarray.mean())
结果如下:

6.模型评估
绘制混淆矩阵,代码如下:
1 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 2 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionCV 3 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix 4 import pandas as pd 5 6 train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2) 7 logistic_model = LogisticRegressionCV(multi_class='multinomial', solver='lbfgs') 8 logistic_model.fit(train_X, train_y) 9 predict_y = logistic_model.predict(test_X) 10 pd.DataFrame(confusion_matrix(test_y, predict_y), 11 columns=labelEncoder.classes_, 12 index=labelEncoder.classes_)
结果如下图所示:

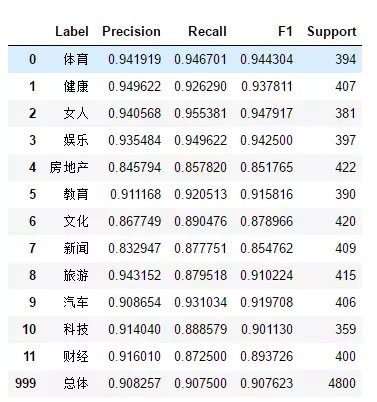
绘制precision、recall、f1-score、support报告表,代码如下:
1 import numpy as np 2 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_fscore_support 3 4 def eval_model(y_true, y_pred, labels): 5 # 计算每个分类的Precision, Recall, f1, support 6 p, r, f1, s = precision_recall_fscore_support(y_true, y_pred) 7 # 计算总体的平均Precision, Recall, f1, support 8 tot_p = np.average(p, weights=s) 9 tot_r = np.average(r, weights=s) 10 tot_f1 = np.average(f1, weights=s) 11 tot_s = np.sum(s) 12 res1 = pd.DataFrame({ 13 u'Label': labels, 14 u'Precision': p, 15 u'Recall': r, 16 u'F1': f1, 17 u'Support': s 18 }) 19 res2 = pd.DataFrame({ 20 u'Label': ['总体'], 21 u'Precision': [tot_p], 22 u'Recall': [tot_r], 23 u'F1': [tot_f1], 24 u'Support': [tot_s] 25 }) 26 res2.index = [999] 27 res = pd.concat([res1, res2]) 28 return res[['Label', 'Precision', 'Recall', 'F1', 'Support']] 29 30 predict_y = logistic_model.predict(test_X) 31 eval_model(test_y, predict_y, labelEncoder.classes_)
结果如下图所示:
7.模型测试
模型测试,即对一个全新的测试集进行预测。
调用pandas库的read_csv方法读取测试集文件。
调用TfidfVectorizer对象的transform方法获得特征矩阵。
调用LabelEncoder对象的transform方法获得预测目标值。
下面一段代码能够成功运行的前提,是本文第5.4节和第6节已经运行。
import pandas as pd test_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_test.txt', sep=' ', header=None) test_X = tfidfVectorizer.transform(test_df[1]) test_y = labelEncoder.transform(test_df[0]) predict_y = logistic_model.predict(test_X) eval_model(test_y, predict_y, labelEncoder.classes_)
结果如下图所示:

经过交叉验证,模型平均得分为0.8711。
模型评估时,使用LogisticRegressionCV模型,得分提高了3%,为0.9076。
最后在测试集上的f1-score指标为0.8990,总体来说这个分类模型较优秀。
数据集放在网盘,如下:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Rc1363FR2skA8Tn7CxEi3g
提取码:xbrr