__declspec(dllimport)和__declspec(dllexport)经常是成对的,在动态链接库中__declspec(dllexport)导出dll中的成员,__declspec(dllimport)导入外部dll中的成员。
但是有时候不使用dllimport和dllexport也能实现个基本的导出导入功能, 它们具有的功能如下:
1.dllimport/dllexport可以导入或者导出动态链接库中的全局变量,当然是用extern也可以实现同样的功能;
2.dllimport/dllexport的作用主要体现在导出类的静态成员方面,如果不使用它们,无法在正常是用外部dll中类的静态成员函数;
3.隐式使用dll时,不加dllimport/dllexport也是可以,使用上没什么区别,只是在生成的二进制代码上稍微有点效率损失;
4.使用dllimport/dllexport还可以体现编程语言的对称美。
以下是一个Demo实例:
====================================.h文件如下[DllExport.h]:================================================

#ifdef DLLEXPORT_EXPORTS #define DLLEXPORT_API __declspec(dllexport) #else #define DLLEXPORT_API __declspec(dllimport) #endif // class从dll中导出Demo class DLLEXPORT_API CDllExport { public: CDllExport(void); }; //变量从dll中导出Demo extern DLLEXPORT_API int nDllExport; //函数从dll中导出Demo DLLEXPORT_API int fnDllExport(void);
====================================.cpp文件如下[DllExport.cpp]:==============================================

#include "DllExport.h" // 变量从Dll中导出Demo DLLEXPORT_API int nDllExport=0; // 函数从Dll中导出Demo DLLEXPORT_API int fnDllExport(void) { return 42; } // 类从Dll中导出Demo,以下为导出类的构造函数 CDllExport::CDllExport() { return; }
====================================调用文件如下[DemoEntry.cpp]:=============================================

#include"DllExport.h" #include<iostream> int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { int returncnt= fnDllExport(); std::cout<<returncnt<<std::endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
====================================================================================================
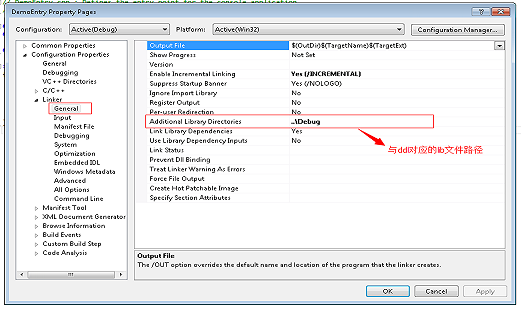
调用Dll过程编译器设置如下:

同样,使用.def文件也可以导出dll中的函数供外部调用,关于.def的使用如下:
1.LIBRARY语句说明.def文件相应的DLL;
2.EXPORTS语句后列出要导出函数的名称。可以在.def文件中的导出函数名后加@n,表示要导出函数的序号为n(在进行函数调用时,这个序号将发挥其作用);
3.def文件中的注释由每个注释行开始处的分号 (;) 指定,且注释不能与语句共享一行
以下是使用.def 文件导出DLL的Demo实例:
====================================.cpp文件如下[APIExport.cpp]:=============================================

int nTest=1;//全局变量 int AddAndMulti(int a,int b) { return (a+b)*nTest; } int _stdcall SubAndMulti(int a,int b) { return (a-b)*nTest; } int _cdecl Multiply(int a,int b) { return a*b; }
====================================.def文件如下[DllExport.def]:==============================================

LIBRARY DllExport_def EXPORTS AddAndMulti @3 SubAndMulti @5 Multiply @1 nTest DATA
====================================.cpp调用代码[DllLoadEntry.cpp]:============================================

// DllLoadEntry.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; //引用dll中的全局变量 extern int _declspec(dllimport) nTest; //声明函数,需与Dll中的函数定义一致(包括其函数调用修饰词) int AddAndMulti(int a,int b); int _stdcall SubAndMulti(int a,int b); int _cdecl Multiply(int a,int b); //#pragma comment(lib,"DllExport_def.lib") int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { nTest=2; cout<<AddAndMulti(1,2)<<endl; cout<<SubAndMulti(3,4)<<endl; cout<<Multiply(4,5)<<endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
====================================================================================================
编译环境设置如下:


当然也可以在代码中添加 #pragma comment(lib,"DllExport_def.lib")实现同样的效果,DLL和调用的exe在同一个目录下。
def和__declspec的使用区别:
VC++编译器会对__declspec导出的函数进行一定的变化,如下:__declspec(dllexport) int __stdcall Add()会转换为Add@0(),对于外部调用程序也是VC++时,只需要将编译产生的lib文件提供给调用者即可,而如果提供给语言程序调用,就不是那么方便了。此时,使用.def文件就可以让编译器不会对导出的函数名称进行修改。
