概述
- 属于行为型模式
- 定义一系列算法,并将每种算法分别放入独立的类中,以使算法的对象能够相互替换
- 找出负责用许多不同方法完成特殊任务的类,然后将其中的算法抽取到一组被称为策略的独立类中
结构
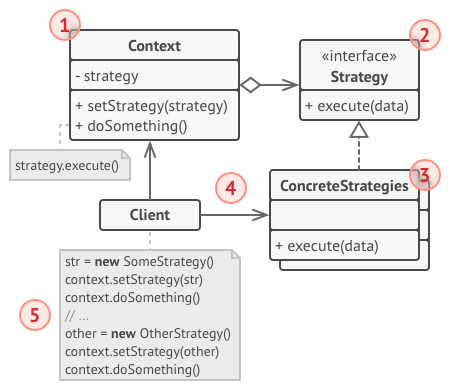
- 上下文类:维护指向具体策略的引用,仅通过策略接口与该对象进行交流
- 策略接口:所有具体策略的通用接口,声明了一个上下文用于执行策略的方法
- 具体策略:实现了上下文所用算法的各种不同变体
- 客户端:创建一个特定策略对象并将其传递给上下文,上下文提供一个设置器以便客户端在运行时替换相关策略
场景
- 假如你要前往机场,可以选择乘坐公共汽车,预约出租车或骑自行车,可根据预算或时间等因素选择其中一种策略
示例1

1 enum TaxBase { 2 CN_Tax, 3 US_Tax, 4 DE_Tax, 5 FR_Tax //更改 6 }; 7 8 class SalesOrder{ 9 TaxBase tax; 10 public: 11 double CalculateTax(){ 12 //... 13 14 if (tax == CN_Tax){ 15 //CN*********** 16 } 17 else if (tax == US_Tax){ 18 //US*********** 19 } 20 else if (tax == DE_Tax){ 21 //DE*********** 22 } 23 else if (tax == FR_Tax){ //更改 24 //... 25 } 26 27 //.... 28 } 29 30 };
- 静态看没有问题,动态看有问题,比如后期还要支持日本、法国等其他国家
- 更改代码的过程,违反了开闭原则,考虑重构,用扩展的方式应对变化

1 class TaxStrategy{ 2 public: 3 virtual double Calculate(const Context& context)=0; 4 virtual ~TaxStrategy(){} 5 }; 6 7 8 class CNTax : public TaxStrategy{ 9 public: 10 virtual double Calculate(const Context& context){ 11 //*********** 12 } 13 }; 14 15 class USTax : public TaxStrategy{ 16 public: 17 virtual double Calculate(const Context& context){ 18 //*********** 19 } 20 }; 21 22 class DETax : public TaxStrategy{ 23 public: 24 virtual double Calculate(const Context& context){ 25 //*********** 26 } 27 }; 28 29 30 31 //扩展 32 //********************************* 33 class FRTax : public TaxStrategy{ 34 public: 35 virtual double Calculate(const Context& context){ 36 //......... 37 } 38 }; 39 40 41 class SalesOrder{ 42 private: 43 TaxStrategy* strategy; 44 45 public: 46 SalesOrder(StrategyFactory* strategyFactory){ 47 this->strategy = strategyFactory->NewStrategy(); 48 } 49 ~SalesOrder(){ 50 delete this->strategy; 51 } 52 53 public double CalculateTax(){ 54 //... 55 Context context(); 56 57 double val = 58 strategy->Calculate(context); //多态调用 59 //... 60 } 61 62 };
- 实现多态性,必须要靠指针,而不是具体对象
- 42销售类,44策略指针,支持多态性
- 48采用工厂模式创建实例,因为是堆对象,要写虚构函数47,56多态调用
- 使类型在运行时根据需要在各个算法间切换(41, 56)
- SalesOrder 类全程不变,实现了复用,后期可通过扩展子类实现变化
示例2
商场促销策略

- 简单工厂模式实现

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <math.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class CashSuper{ 7 public: 8 virtual double acceptCash(double money) = 0; 9 }; 10 // 正常收费类 11 class CashNormal:public CashSuper{ 12 public: 13 double acceptCash(double money){ 14 return money; 15 } 16 }; 17 // 返利收费类 18 class CashReturn:public CashSuper{ 19 private: 20 double moneyCondition; 21 double moneyReturn; 22 public: 23 CashReturn(double moneyCondition, double moneyReturn){ 24 this->moneyCondition = moneyCondition; 25 this->moneyReturn = moneyReturn; 26 } 27 double acceptCash(double money){ 28 double result = money; 29 if(moneyCondition) 30 result = money - floor(money/moneyCondition)*moneyReturn; 31 return result; 32 } 33 }; 34 // 打折收费类 35 class CashRebate:public CashSuper{ 36 private: 37 double moneyRebate; 38 public: 39 CashRebate(double moneyRebate){ 40 this->moneyRebate = moneyRebate; 41 } 42 double acceptCash(double money){ 43 return money*moneyRebate; 44 } 45 }; 46 // 工厂类 47 class CashFactory{ 48 public: 49 static CashSuper* Create(int type){ 50 CashSuper* cs; 51 switch(type){ 52 case 1:{ 53 cs = new CashNormal(); 54 break; 55 } 56 case 2:{ 57 cs = new CashReturn(300, 100); 58 break; 59 } 60 case 3:{ 61 cs = new CashRebate(0.8); 62 break; 63 } 64 default:; 65 } 66 return cs; 67 } 68 }; 69 70 int main(){ 71 double total = 0; 72 double totalPrice = 0; 73 74 CashSuper* cc1 = CashFactory::Create(1); 75 totalPrice = cc1->acceptCash(300); 76 total += totalPrice; 77 cout << "Type:正常收费 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 78 << total << endl; 79 totalPrice = 0; 80 81 CashSuper* cc2 = CashFactory::Create(2); 82 totalPrice = cc2->acceptCash(300); 83 total += totalPrice; 84 cout << "Type:正常收费 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 85 << total << endl; 86 totalPrice = 0; 87 88 CashSuper* cc3 = CashFactory::Create(3); 89 totalPrice = cc3->acceptCash(300); 90 total += totalPrice; 91 cout << "Type:正常收费 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 92 << total << endl; 93 totalPrice = 0; 94 95 return 0; 96 }

- 策略模式实现
- 菱形+箭头代表聚合(如雁群和大雁)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <math.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class CashSuper{ 7 public: 8 virtual double acceptCash(double money) = 0; 9 }; 10 // 正常收费类 11 class CashNormal:public CashSuper{ 12 public: 13 double acceptCash(double money){ 14 return money; 15 } 16 }; 17 // 返利收费类 18 class CashReturn:public CashSuper{ 19 private: 20 double moneyCondition; 21 double moneyReturn; 22 public: 23 CashReturn(double moneyCondition, double moneyReturn){ 24 this->moneyCondition = moneyCondition; 25 this->moneyReturn = moneyReturn; 26 } 27 double acceptCash(double money){ 28 double result = money; 29 if(moneyCondition) 30 result = money - floor(money/moneyCondition)*moneyReturn; 31 return result; 32 } 33 }; 34 // 打折收费类 35 class CashRebate:public CashSuper{ 36 private: 37 double moneyRebate; 38 public: 39 CashRebate(double moneyRebate){ 40 this->moneyRebate = moneyRebate; 41 } 42 double acceptCash(double money){ 43 return money*moneyRebate; 44 } 45 }; 46 // 策略类 47 class CashContext{ 48 private: 49 CashSuper* cs; 50 public: 51 CashContext(CashSuper* csuper):cs(NULL){ 52 this->cs = csuper; 53 } 54 ~CashContext(){ 55 if(cs != NULL){ 56 delete cs; 57 cs = NULL; 58 } 59 } 60 double GetResult(double money){ 61 return cs->acceptCash(money); 62 } 63 }; 64 65 int main(){ 66 double total = 0; 67 double totalPrice = 0; 68 69 CashContext* cc1 = NULL; 70 cc1 = new CashContext(new CashNormal()); 71 totalPrice = cc1->GetResult(300); 72 total += totalPrice; 73 cout << "Type:正常收费 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 74 << total << endl; 75 totalPrice = 0; 76 77 CashContext* cc2 = NULL; 78 cc2 = new CashContext(new CashReturn(300,100)); 79 totalPrice = cc2->GetResult(300); 80 total += totalPrice; 81 cout << "Type:满300返100 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 82 << total << endl; 83 totalPrice = 0; 84 85 CashContext* cc3 = NULL; 86 cc3 = new CashContext(new CashRebate(0.8)); 87 totalPrice = cc3->GetResult(300); 88 total += totalPrice; 89 cout << "Type:打8折 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 90 << total << endl; 91 totalPrice = 0; 92 93 if(cc1 != NULL){ 94 delete cc1; 95 cc1 = NULL; 96 } 97 if(cc2 != NULL){ 98 delete cc2; 99 cc2 = NULL; 100 } 101 if(cc3 != NULL){ 102 delete cc3; 103 cc3 = NULL; 104 } 105 return 0; 106 }
-
- 不足:要在客户端判断用哪种算法(此处写法为示意,实际程序中需要用判断语句决定用哪种算法)
- 改进:和简单工厂模式结合,把判断过程写入策略类中
- 改进的策略模式实现

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <math.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class CashSuper{ 7 public: 8 virtual double acceptCash(double money) = 0; 9 }; 10 // 正常收费类 11 class CashNormal:public CashSuper{ 12 public: 13 double acceptCash(double money){ 14 return money; 15 } 16 }; 17 // 返利收费类 18 class CashReturn:public CashSuper{ 19 private: 20 double moneyCondition; 21 double moneyReturn; 22 public: 23 CashReturn(double moneyCondition, double moneyReturn){ 24 this->moneyCondition = moneyCondition; 25 this->moneyReturn = moneyReturn; 26 } 27 double acceptCash(double money){ 28 double result = money; 29 if(moneyCondition) 30 result = money - floor(money/moneyCondition)*moneyReturn; 31 return result; 32 } 33 }; 34 // 打折收费类 35 class CashRebate:public CashSuper{ 36 private: 37 double moneyRebate; 38 public: 39 CashRebate(double moneyRebate){ 40 this->moneyRebate = moneyRebate; 41 } 42 double acceptCash(double money){ 43 return money*moneyRebate; 44 } 45 }; 46 // 策略类 47 class CashContext{ 48 private: 49 CashSuper* cs; 50 public: 51 CashContext(int type):cs(NULL){ 52 switch(type){ 53 case 1:{ 54 cs = new CashNormal(); 55 break; 56 } 57 case 2:{ 58 cs = new CashReturn(300, 100); 59 break; 60 } 61 case 3:{ 62 cs = new CashRebate(0.8); 63 break; 64 } 65 default:; 66 } 67 } 68 ~CashContext(){ 69 if(cs != NULL){ 70 delete cs; 71 cs = NULL; 72 } 73 } 74 double GetResult(double money){ 75 return cs->acceptCash(money); 76 } 77 }; 78 79 int main(){ 80 double total = 0; 81 double totalPrice = 0; 82 83 CashContext* cc1 = NULL; 84 cc1 = new CashContext(1); 85 totalPrice = cc1->GetResult(300); 86 total += totalPrice; 87 cout << "Type:正常收费 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 88 << total << endl; 89 totalPrice = 0; 90 91 CashContext* cc2 = NULL; 92 cc2 = new CashContext(2); 93 totalPrice = cc2->GetResult(300); 94 total += totalPrice; 95 cout << "Type:满300返100 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 96 << total << endl; 97 totalPrice = 0; 98 99 CashContext* cc3 = NULL; 100 cc3 = new CashContext(3); 101 totalPrice = cc3->GetResult(300); 102 total += totalPrice; 103 cout << "Type:打8折 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 104 << total << endl; 105 totalPrice = 0; 106 107 if(cc1 != NULL){ 108 delete cc1; 109 cc1 = NULL; 110 } 111 if(cc2 != NULL){ 112 delete cc2; 113 cc2 = NULL; 114 } 115 if(cc3 != NULL){ 116 delete cc3; 117 cc3 = NULL; 118 } 119 return 0; 120 }

-
- 策略模式和简单工厂模式的区别:可直接在客户端接受用户输入判断算法
- 改进后的策略模式和简单工厂模式的区别:简单工厂模式需要在客户端中用CashSuper和CashFactory两个类,改进的策略模式只要用CashContext即可,降低了耦合
**错误代码**
1 CashSuper csuper = CashFactory.Create(2); 2 totalPrice = csuper.acceptCash(300); 3 total += totalPrice; 4 cout << "Type:满300返100 totalPrices:" << totalPrice << " total:" 5 << total << endl; 6 totalPrice = 0;
- 1行,csuper是CashSuper的指针类型,应加*;CashFactory是类名,应用::
- 2行,csuper是指针变量,应用->
示例3

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <typeinfo> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 /** 7 * The Strategy interface declares operations common to all supported versions 8 * of some algorithm. 9 * 10 * The Context uses this interface to call the algorithm defined by Concrete 11 * Strategies. 12 */ 13 class Strategy 14 { 15 public: 16 virtual ~Strategy() {} 17 virtual std::string DoAlgorithm(const std::vector<std::string> &data) const = 0; 18 }; 19 20 /** 21 * The Context defines the interface of interest to clients. 22 */ 23 24 class Context 25 { 26 /** 27 * @var Strategy The Context maintains a reference to one of the Strategy 28 * objects. The Context does not know the concrete class of a strategy. It 29 * should work with all strategies via the Strategy interface. 30 */ 31 private: 32 Strategy *strategy_; 33 /** 34 * Usually, the Context accepts a strategy through the constructor, but also 35 * provides a setter to change it at runtime. 36 */ 37 public: 38 Context(Strategy *strategy = nullptr) : strategy_(strategy) 39 { 40 } 41 ~Context() 42 { 43 delete this->strategy_; 44 } 45 /** 46 * Usually, the Context allows replacing a Strategy object at runtime. 47 */ 48 void set_strategy(Strategy *strategy) 49 { 50 delete this->strategy_; 51 this->strategy_ = strategy; 52 } 53 /** 54 * The Context delegates some work to the Strategy object instead of 55 * implementing +multiple versions of the algorithm on its own. 56 */ 57 void DoSomeBusinessLogic() const 58 { 59 // ... 60 std::cout << "Context: Sorting data using the strategy (not sure how it'll do it) "; 61 std::string result = this->strategy_->DoAlgorithm(std::vector<std::string>{"a", "e", "c", "b", "d"}); 62 std::cout << result << " "; 63 // ... 64 } 65 }; 66 67 /** 68 * Concrete Strategies implement the algorithm while following the base Strategy 69 * interface. The interface makes them interchangeable in the Context. 70 */ 71 class ConcreteStrategyA : public Strategy 72 { 73 public: 74 std::string DoAlgorithm(const std::vector<std::string> &data) const override 75 { 76 std::string result; 77 std::for_each(std::begin(data), std::end(data), [&result](const std::string &letter) { 78 result += letter; 79 }); 80 std::sort(std::begin(result), std::end(result)); 81 82 return result; 83 } 84 }; 85 class ConcreteStrategyB : public Strategy 86 { 87 std::string DoAlgorithm(const std::vector<std::string> &data) const override 88 { 89 std::string result; 90 std::for_each(std::begin(data), std::end(data), [&result](const std::string &letter) { 91 result += letter; 92 }); 93 std::sort(std::begin(result), std::end(result)); 94 for (int i = 0; i < result.size() / 2; i++) 95 { 96 std::swap(result[i], result[result.size() - i - 1]); 97 } 98 99 return result; 100 } 101 }; 102 /** 103 * The client code picks a concrete strategy and passes it to the context. The 104 * client should be aware of the differences between strategies in order to make 105 * the right choice. 106 */ 107 108 void ClientCode() 109 { 110 Context *context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyA); 111 std::cout << "Client: Strategy is set to normal sorting. "; 112 context->DoSomeBusinessLogic(); 113 std::cout << " "; 114 std::cout << "Client: Strategy is set to reverse sorting. "; 115 context->set_strategy(new ConcreteStrategyB); 116 context->DoSomeBusinessLogic(); 117 delete context; 118 } 119 120 int main() 121 { 122 ClientCode(); 123 return 0; 124 }

示例4

1 public interface Strategy { 2 public int doOperation(int num1, int num2); 3 } 4 5 public class OperationAdd implements Strategy{ 6 @Override 7 public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) { 8 return num1 + num2; 9 } 10 } 11 12 public class OperationSubstract implements Strategy{ 13 @Override 14 public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) { 15 return num1 - num2; 16 } 17 } 18 19 public class OperationMultiply implements Strategy{ 20 @Override 21 public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) { 22 return num1 * num2; 23 } 24 } 25 26 public class Context { 27 private Strategy strategy; 28 29 public Context(Strategy strategy){ 30 this.strategy = strategy; 31 } 32 33 public int executeStrategy(int num1, int num2){ 34 return strategy.doOperation(num1, num2); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public class StrategyPatternDemo { 39 public static void main(String[] args) { 40 Context context = new Context(new OperationAdd()); 41 System.out.println("10 + 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5)); 42 43 context = new Context(new OperationSubstract()); 44 System.out.println("10 - 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5)); 45 46 context = new Context(new OperationMultiply()); 47 System.out.println("10 * 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5)); 48 } 49 }
10 + 5 = 15 10 - 5 = 5 10 * 5 = 50
总结
- 动机:软件构建过程中,某些对象使用的算法多种多样,经常改变
- 若将这些代码写在对象中,将会使对象变得异常复杂,且支持不用的算法会带来性能负担
- 如何在运行时根据需要透明地更改对象的算法,将其与对象本身解耦
- 复用:保证编译后的二进制代码不用改变,不是粘贴代码片段
- 每次扩展,在新文件中添加一个新类即可
- 定义一系列算法,把它们封装起来,使它们可以相互替换(变化),使得算法可以独立于使用它的客户程序(稳定)而变化
- 提供了条件判断语句外的另一种选择,减低了耦合,含有许多条件判断语句的代码通常都需要Stragegy模式
- 当 if else 稳定不变时则不用,如性别、每周七天等
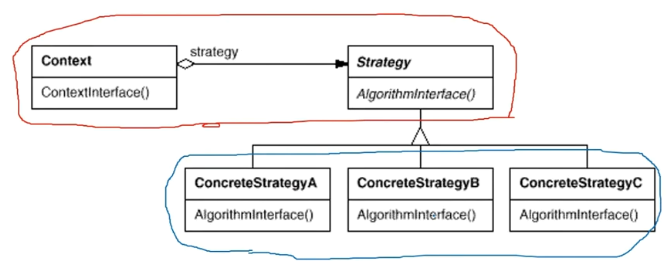
- Context指向Strategy,Context通过Strategy接口调用一系列算法,ConcreteStrategyA/B/C实现具体的算法
- 优点:适合类中的成员以方法为主,算法经常变动的情况;简化了单元测试(每个算法可以通过自己的类接口单独测试)
- 缺点:需要客户端判断使用哪种算法
参考
