视图引擎与视图
多数情况下控制器action方法返回ViewResult对象,MVC内建action调用器ControllerActionInvoker负责调用控制器action方法并调用视图引擎处理ViewResut,由视图引擎将ViewResult转化为ViewEngineResult对象,ViewEngineResult对象内含实现IView接口的视图对象,最终MVC框架调用视图对象的Render的方法渲染输出结果。下面还是以例子来演示这个过程,先来看看相关接口和类的定义与实现:
public interface IViewEngine { ViewEngineResult FindPartialView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string partialViewName, bool useCache); ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache); void ReleaseView(ControllerContext controllerContext, IView view); } public interface IView { void Render(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer); } public class ViewEngineResult { public ViewEngineResult(IEnumerable<string> searchedLocations) { if (searchedLocations == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("searchedLocations"); } SearchedLocations = searchedLocations; } public ViewEngineResult(IView view, IViewEngine viewEngine) { if (view == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("view");} if (viewEngine == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("viewEngine");} View = view; ViewEngine = viewEngine; } public IEnumerable<string> SearchedLocations { get; private set; } public IView View { get; private set; } public IViewEngine ViewEngine { get; private set; } }
IViewEngine的两个Find方法查找请求的视图返回ViewEngineResult对象,ViewEngineResult有两个函数,一个接受IView和IViewEngine作为参数,另一个传入一系列视图文件搜索路径列表作为参数。
先从自定义视图类开始:
public class DebugDataView : IView { public void Render(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer) { Write(writer, "---Routing Data---"); foreach (string key in viewContext.RouteData.Values.Keys) { Write(writer, "Key: {0}, Value: {1}", key, viewContext.RouteData.Values[key]); } Write(writer, "---View Data---"); foreach (string key in viewContext.ViewData.Keys) { Write(writer, "Key: {0}, Value: {1}", key, viewContext.ViewData[key]); } } private void Write(TextWriter writer, string template, params object[] values) { writer.Write(string.Format(template, values) + "<p/>"); } }
DebugDataView只是简单的输出一些路径映射和视图数据。接下来是自定义视图引擎:
public class DebugDataViewEngine : IViewEngine { public ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache) { if (viewName == "DebugData") { return new ViewEngineResult(new DebugDataView(), this); } else { return new ViewEngineResult(new string[] { "No view (Debug Data View Engine)" }); } } public ViewEngineResult FindPartialView(ControllerContext controllerContext,string partialViewName, bool useCache) { return new ViewEngineResult(new string[] { "No view (Debug Data View Engine)" }); } public void ReleaseView(ControllerContext controllerContext, IView view) { // do nothing } }
DebugDataViewEngine中最主要的是FindView方法,如果当前请求的是DebugData视图,我们直接创建一个DebugDataView并以它构建ViewEngineResult返回,其他情况下返回一个包含虚假搜索路径的ViewEngineResult(真实实现的话我们需要搜索模板文件等)。要使用自定义的视图引擎我们还需要在App_start中注册:
ViewEngines.Engines.Add(new DebugDataViewEngine());
在一个应用可以注册多个视图引擎,action调用器依次调用这些视图引擎的FindView方法,一旦某一个搜索引擎返回包含IView对象的ViewEngineResult结果调用停止,所以视图引擎注册的先后顺序是有影响的,可能存在两个视图引擎都可以处理同一个视图名称。如果我们想自定义的视图引擎优先处理可以将其插入列表首位:
ViewEngines.Engines.Insert(0, new DebugDataViewEngine());
如果某个action方法返回DebugData视图,比如:
return View("DebugData");
最后的结果就是调用DebugDataView.RenderData输出结果。如果我们请求一个未实现的视图,得到的结果就是:
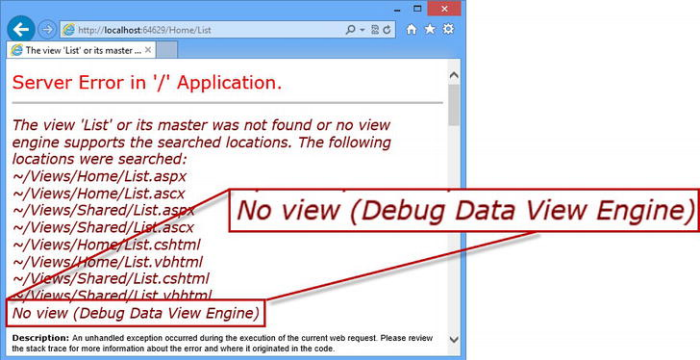
错误显示一系列视图模板的搜索路径,包含DebugDataViewEngine给出的虚假路径"No view (Debug Data View Engine)"。结果中其他一些路径来自于默认的Razor和ASPX视图引擎,你可以调用ViewEngines.Engines.Clear()清除默认视图引擎后仅注册自定义的视图引擎。
简单总结上面的示例可以说视图引擎完成从视图名称到视图对象的转换,而视图对象则负责具体的输出响应。
Razor视图引擎
只有极少数情况下我们需要自定义视图引擎,MVC已经为我们提供了Razor和ASPX引擎,Razor在MVC3中引入用以替代ASPX引擎,所以推荐使用Razor引擎。Razor引擎处理的是.cshtml视图文件,一个简单的Index.cshtml:
@model string[] @{
Layout = null; ViewBag.Title = "Index"; } This is a list of fruit names: @foreach (string name in Model) { <span><b>@name</b></span> }
在启动应用程序后,Razor引擎将cshtml文件转换为c#类的定义,我们可以在C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319Temporary ASP.NET Files oot下找到这些临时文件,比如上面的index.cshtml转成c#的.cs文件可能是这样的:
namespace ASP { using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Net; using System.Web; using System.Web.Helpers; using System.Web.Security; using System.Web.UI; using System.Web.WebPages; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Mvc.Ajax; using System.Web.Mvc.Html; using System.Web.Optimization; using System.Web.Routing; public class _Page_Views_Home_Index_cshtml : System.Web.Mvc.WebViewPage<string[]> { public _Page_Views_Home_Index_cshtml() { }
public override void Execute() { ViewBag.Title = "Index"; WriteLiteral(" This is a list of fruit names: "); foreach (string name in Model) { WriteLiteral(" <span><b>"); Write(name); WriteLiteral("</b></span> "); } } } }
它从 WebViewPage<T>扩展,T是视图数据模型类型,上面的例子string[]。理解Razor如何处理cshtml有助于我们后续理解html帮助函数是如何工作的。
当我们请求一个视图比如Index时,Razor引擎遵循约定规则在下列路径查找视图文件:
• ~/Views/Home/Index.cshtml • ~/Views/Home/Index.vbhtml • ~/Views/Shared/Index.cshtml • ~/Views/Shared/Index.vbhtml
实际上Razor并非真正的搜索这些磁盘文件,因为这些模板已经编译为c#类。RazorViewEngine的下列属性和模板搜索相关:
| 属性 | 默认值 | |
|
ViewLocationFormats |
搜索视图、部分视图和布局文件 |
~/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml, |
|
AreaViewLocationFormats |
区域搜索视图、部分视图和布局文件 |
~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml, |
这里{0}表示视图名称,{1}表示控制器名称,{2}标识区域名称。我们可以子类化RazorViewEngine后修改上述属性更改Razor的搜索方式,当然必须注册子类化的视图引擎到引擎列表。
Razor模板文件
Razor模板文件混合了HTML和C#的语句,以一个例子来具体分析:
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ Layout = null; } <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>Index</title> </head> <body> <div> @Model.Name </div> </body> </html>
第一行@model Razor.Models.Product 指定了视图的模型对象类型,后续我们可以使用@Model来引用该对象(注意M大写)。模型对象类型不是必须的,视图文件中完全可以没有这行,带模型类型的视图我们称之为强类型视图(Strong typed)。
第二行以“@{”开始一个Razor代码块,类似C#的代码块,最后也要以“}”结尾。
“Layout = null;”表示视图不使用布局文件,布局文件存放在ViewLayouts目录下,可以为多个视图文件共享。布局文件名一般以下划线“_”开始,比如_BasicLayout.cshtml,以下划线开头的不会返回给用户,这样可以帮助我们区分哪些是支持文件。布局文件其实也是一个Razor模板文件,比如:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>Product Information</h1> <div style="padding: 20px; border: solid medium black; font-size: 20pt"> @RenderBody() </div> <h2>Visit <a href="http://apress.com">Apress</a></h2> </body> </html>
最重要的是这里的 @RenderBody()(后面我们知道称为HTML帮助函数),它的作用是将视图的渲染结果插入到这里。使用布局文件后视图可以简化为:
@model Razor.Models.Product
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Product Name";
Layout = "~/Views/_BasicLayout.cshtml";
}
Product Name: @Model.Name
实际上我们不需要在每个视图文件中指定Layout,MVC会搜索一个名为 _ViewStart.cshtml的文件,它的内容会自动插入到所有视图文件中,所以如果我们要为所有视图文件指定布局文件可以在 _ViewStart.cshtml中定义:
@{
Layout = "~/Views/_BasicLayout.cshtml";
}
Razor语法
我们可以很方便的在视图中插入视图模型数据或者ViewData的数据:
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoExpression"; } <table> <thead> <tr><th>Property</th><th>Value</th></tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr><td>Name</td><td>@Model.Name</td></tr> <tr><td>Price</td><td>@Model.Price</td></tr> <tr><td>Stock Level</td><td>@ViewBag.ProductCount</td></tr> </tbody> </table>
这些值也可以很方便的应用到标记属性上:
<div data-discount="@ViewBag.ApplyDiscount" data-express="@ViewBag.ExpressShip" data-supplier="@ViewBag.Supplier"> The containing element has data attributes </div> Discount:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.ApplyDiscount" /> Express:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.ExpressShip" /> Supplier:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.Supplier" />
可以使用条件语句:
<td> @switch ((int)ViewBag.ProductCount) { case 0: @: Out of Stock break; case 1: <b>Low Stock (@ViewBag.ProductCount)</b> break; default: @ViewBag.ProductCount break; } </td>
注意“@:Out of Stock ”一行的“@:”,它阻止Razor将后续语句解释为代码。上面的switch换成if:
<td> @if (ViewBag.ProductCount == 0) { @:Out of Stock } else if (ViewBag.ProductCount == 1) { <b>Low Stock (@ViewBag.ProductCount)</b> } else { @ViewBag.ProductCount } </td>
枚举数据:
@model Razor.Models.Product[] @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoArray"; Layout = "~/Views/_BasicLayout.cshtml"; } @if (Model.Length > 0) { <table> <thead><tr><th>Product</th><th>Price</th></tr></thead> <tbody> @foreach (Razor.Models.Product p in Model) { <tr> <td>@p.Name</td> <td>$@p.Price</td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> } else { <h2>No product data</h2> }
在引用数据类型时我们用了完整的命名空间,可以将命名空间如果c#一样using引入:
@using Razor.Models @model Product[] @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoArray"; Layout = "~/Views/_BasicLayout.cshtml"; } @if (Model.Length > 0) { <table> <thead><tr><th>Product</th><th>Price</th></tr></thead> <tbody> @foreach (Productp in Model) { <tr> <td>@p.Name</td> <td>$@p.Price</td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> } else { <h2>No product data</h2> }
添加动态内容到Razor视图
除了静态的HTML,我们可以在视图模板中嵌入动态内容,动态内容在运行时输出,比如上面的内联@if、@Model等;还可以嵌入HTML帮助函数,比如布局文件中用到的@RenderBody()。除此之外我们还可以嵌入节(Sections)、分部视图(Partial views)和子动作(Child actions )。
- 使用节的例子
@model string[] @{ ViewBag.Title = "Index"; } @section Header { <div class="view"> @foreach (string str in new [] {"Home", "List", "Edit"}) { @Html.ActionLink(str, str, null, new { style = "margin: 5px" }) } </div> } @section Body { <div class="view"> This is a list of fruit names: @foreach (string name in Model) { <span><b>@name</b></span> } </div> } @section Footer { <div class="view"> This is the footer </div> }
这里定义了Header、Body、Footer三个节,我们可以在布局文件中引用这些节:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <style type="text/css"> div.layout { background-color: lightgray;} div.view { border: thin solid black; margin: 10px 0;} </style> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title> </head> <body> @RenderSection("Header") <div class="layout"> This is part of the layout </div> @RenderSection("Body") <div class="layout"> This is part of the layout </div> @if (IsSectionDefined("Footer")) { @RenderSection("Footer") } else { <h4>This is the default footer</h4> } @RenderSection("scripts", false) <div class="layout"> This is part of the layout </div> </body> </html>
注意@RenderSection("scripts", false)多了个参数false,其作用是表示scripts节可选的,如果视图中没有定义scripts节则不需要输出。如果这里不加这个false参数Razor会提示节未找到错误。
- 使用分部视图的例子
分部视图可以在添加视图窗口中选中“Create as partial view”创建 - MyPartial.cshtml:
<div> This is the message from the partial view. @Html.ActionLink("This is a link to the Index action", "Index") </div>
我们在另一个视图文件中引用它:
@{ ViewBag.Title = "List"; Layout = null; } <h3>This is the /Views/Common/List.cshtml View</h3> @Html.Partial("MyPartial")
分部视图也可以是强类型的:
@model IEnumerable<string> <div> This is the message from the partial view. <ul> @foreach (string str in Model) { <li>@str</li> } </ul> </div>
在引用时传入相应的模型对象:
@{ ViewBag.Title = "List"; Layout = null; } <h3>This is the /Views/Common/List.cshtml View</h3> @Html.Partial("MyStronglyTypedPartial", new [] {"Apple", "Orange", "Pear"})
- 使用子动作的例子
子动作调用的是一个控制的action方法,我们先定义一个这样一个action方法:
public class HomeController : Controller { ... [ChildActionOnly] public ActionResult Time() { return PartialView(DateTime.Now); } }
注意这里使用了ChildActionOnly标识这个action方法,表示仅用于被调用而不能作为标准Action方法访问。它对应一个分部视图:
@model DateTime <p>The time is: @Model.ToShortTimeString()</p>
我们在视图中引用它:
@{ ViewBag.Title = "List"; Layout = null; } <h3>This is the /Views/Common/List.cshtml View</h3> @Html.Partial("MyStronglyTypedPartial", new [] {"Apple", "Orange", "Pear"}) @Html.Action("Time")
如果要调用的子动作不在同一个控制器,我们还需要指定其控制器:
...
@Html.Action("Time", "MyController")
...
如果子动作有参数,调用时我们也可以指定参数:
...
@Html.Action("Time", new { time = DateTime.Now })
...
以上为对《Apress Pro ASP.NET MVC 4》第四版相关内容的总结,不详之处参见原版 http://www.apress.com/9781430242369。