Volume
容器磁盘上的文件的生命周期是短暂的,这就使得在容器中运行重要应用时会出现一些问题。首先,当容器崩溃时, kubelet会重启它,但是容器中的文件将丢失--容器以干净的状态(镜像最初的状态)重新启动。其次,在 Pod中同时运行多个容器时,这些容器之间通常需要共享文件。Kubernetes中的volume抽象就很好的解决了这些问题
背景
Kubernetes中的卷有明确的寿命--与封装它的Pod相同。所以,卷的生命比Pod中的所有容器都长,当这个容器重启时数据仍然得以保存。当然,当Pod不再存在时,卷也将不复存在。也许更重要的是, Kubernetes支持多种类型的卷, Pod可以同时使用任意数量的卷
卷的类型
Kubernetes支持以下类型的卷:
-
awsElasticBlockstore azureDisk azureFile cephfs csi downwardAPI emptyDin
-
fc flocker gcePersistentDisk gitRepo glusterfs hostPath iscsi local nfs
-
persistentVolumeClaim projected portworxVolume quobyte rbd scalelo secret
-
storageos vsphereVolume
emptyDir
当Pod被分配给节点时,首先创建emptypir卷,并且只要该Pod在该节点上运行,该卷就会存在。正如卷的名字所述,它最初是空的。 Pod中的容器可以读取和写入emptypir卷中的相同文件,尽管该卷可以挂载到每个容器中的相同或不同路径上。当出于任何原因从节点中删除Pod时, emptyDir中的数据将被永久删除
emptyoir 的用法有:
-
暂存空间,例如用于基于磁盘的合并排序
-
用作长时间计算崩溃恢复时的检查点
-
Web服务器容器提供数据时,保存内容管理器容器提取的文件
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pd
spec:
containers:
- image: k8s.gcr.io/test-webserver
name; test-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /cache
name: cache-volume
volumes:
- name: cache-volume
emptyDir: {}
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pd
spec:
containers:
- image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
name: test-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /cache
name: cache-volume
- image: busybox
name: liveness-httpget-container
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 3600s"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /test
name: cache-volume
volumes:
- name: cache-volume
emptyDir: {}
kubectl exec test-pd -c test-container -it -- /bin/sh
kubectl exec test-pd -c liveness-httpget-container -it -- /bin/sh
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl exec test-pd -c test-container -it -- /bin/sh
/ # ls
bin dev home media proc run srv tmp var
cache etc lib mnt root sbin sys usr
/ # cd test
/bin/sh: cd: can't cd to test
/ # cd cache/
/cache # ls
index.html
/cache # date >> index.html
/cache # cat index.html
Tue Dec 3 20:20:59 UTC 2019
Tue Dec 3 20:21:49 UTC 2019
hostPath
hostPath卷将主机节点的文件系统中的文件或目录挂载到集群中
hostpath的用途如下:
-
运行需要访问Docker内部的容器;使用/var/lib/docker的hostpath
-
在容器中运行cAdvisor;使用/dev/cgroups的hostPath
-
允许pod指定给定的hostPath是否应该在pod运行之前存在,是否应该创建,以及它应该以什么形式存在
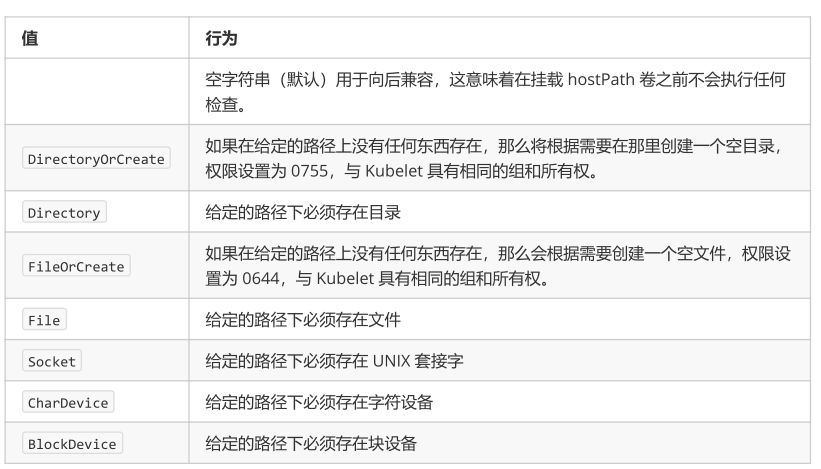
使用这种卷类型是请注意,因为:
-
由于每个节点上的文件都不同,具有相同配置(例如从podTemplate创建的)的pod在不同节点上的行为可能会有所不同
-
当Kubernetes按照计划添加资源感知调度时,将无法考虑nostPath使用的资源
-
在底层主机上创建的文件或目录只能由root写入。您需要在特权容器中以root身份运行进程,或修改主机上的文件权限以便写入hostPath卷
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pd2
spec:
containers:
- image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
name: test-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /test-pd
name: test-volume
volumes:
- name: test-volume
hostPath:
# directory location on host
path: /data
# this field is optional
type: Directory
[root@k8s-master01 volume]# kubectl exec test-pd2 -c test-container -it -- /bin/sh
/ # cd /test-pd/
/test-pd # date > index.html
/test-pd # cat index.html
Tue Dec 3 20:50:55 UTC 2019
2019年 12月 04日 星期三 04:51:17 CST
/test-pd # exit
[root@k8s-node01 ~]# mkdir /data
[root@k8s-node01 ~]# cd /data
[root@k8s-node01 data]# ls
index.html
[root@k8s-node01 data]# cat index.html
Tue Dec 3 20:50:55 UTC 2019
[root@k8s-node01 data]# date >> index.html
[root@k8s-node01 data]# cat index.html
Tue Dec 3 20:50:55 UTC 2019
2019年 12月 04日 星期三 04:51:17 CST
CrashLoopBackOff:
running: