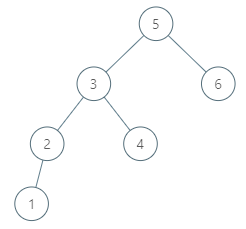
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
You will have direct access to the node but not to the root of the tree. Each node will have a reference to its parent node.
Example 1:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":1},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"3","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":3},"val":2}
p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of Node type.
Example 2:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":1},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":6},"val":5}
p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Example 3:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"7","left":{"$id":"8","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"7"},"right":null,"val":9},"parent":{"$ref":"6"},"right":null,"val":13},"val":7},"val":6},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"9","left":{"$id":"10","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":17},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"11","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":20},"val":18},"val":15}
p = 15
Output: 17
Example 4:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"7","left":{"$id":"8","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"7"},"right":null,"val":9},"parent":{"$ref":"6"},"right":null,"val":13},"val":7},"val":6},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"9","left":{"$id":"10","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":17},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"11","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":20},"val":18},"val":15}
p = 13
Output: 15
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
null. - It's guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
- Remember that we are using the
Nodetype instead ofTreeNodetype so their string representation are different.
Follow up:
Could you solve it without looking up any of the node's values?
M1: look up node's value, time = O(height), space = O(1)
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public Node left; public Node right; public Node parent; }; */ class Solution { public Node inorderSuccessor(Node x) { if(x.right != null) { Node candidate = x.right; while(candidate.left != null) { candidate = candidate.left; } return candidate; } else { Node candidate = x.parent; while(candidate != null && candidate.val < x.val) { candidate = candidate.parent; } return candidate; } } }
M2: don't look up node's value, time = O(height), space = O(1)
if the current node has a right child, then the successor is somewhere lower in the tree -> go to the right once, and then as many times to the left as you could, return the last node
if no right child, then the successor is somewhere upper in the tree -> go up until the node that is left child of its parent, the answer is the parent
class Solution { public Node inorderSuccessor(Node x) { if(x.right != null) { // the successor is somewhere lower in the right subtree x = x.right; while(x.left != null) { x = x.left; } return x; } while(x.parent != null && x == x.parent.right) { // the successor is somewhere upper in the tree x = x.parent; } return x.parent; } }