今天学习了Spring的@Autowried注解,来写一篇博客来回想一下。
@Autowried注解是干什么的呢?
它可以对类成员变量、方法及构造函数进行标注,完成自动装配的工作。 通过 @Autowired的使用来消除 set ,get方法。
在没有用@Autowried注解之前的时候,我们对一个bean配置属性的时候,通常是这样的。
<property name="xxx" value="xxx"></property>
如果配置的属性比较多的时候,这中方式就比较繁琐,所以在Spring 2.5 引入了 @Autowired 注释
代码实现:
//人类
public class Person {
private Dog dog;
private Cat cat;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
}
//猫类
public class Cat implements animal {
public void shoot() {
System.out.println("miao~");
}
}
//动物接口
public interface animal {
//叫的方法
void shoot();
}
public class Dog implements animal{
public void shoot() {
System.out.println("giao~");
}
}
我们实现了一个人的类,他有一条狗和一只猫。并且都实现了shoot方法。
我们之前没有用注解的时候,配置文件要这样写:
<bean id="cat" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Person">
<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>
<property name="dog" ref="dog"></property>
</bean>
使用@Autowried注解后:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启对注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="cat" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Person"></bean>
</beans>
public class Person {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
}
我们只需要对person类中的成员变量(dog和cat)进行标识即可.
来测试一下:
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Person person = context.getBean("person", Person.class);
person.getDog().shoot();
person.getCat().shoot();
}
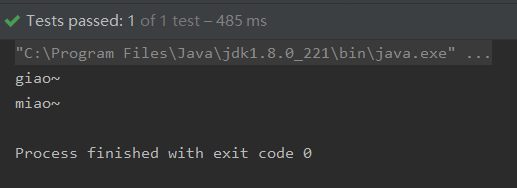
注意:
查阅资料发现:在使用@Autowired注解时,默认使用ByType(通过类型)来进行查找,如果没有查询到,抛出异常
如果查询结果为一个时,就将该bean装配给@Autowired指定的数据
如果查询结果为多个时,@Autowried注解会根据SetXxx中的xxx来查找(ByName通过名字)。
(如果查询到,就将该bean装配给@Autowired指定的数据.如果没有查询到,抛出异常。)
举例说明:
<!--开启对注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="cat" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="dog2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Person"></bean>
我们发现有多个查询结果.测试代码不变
测试一下:
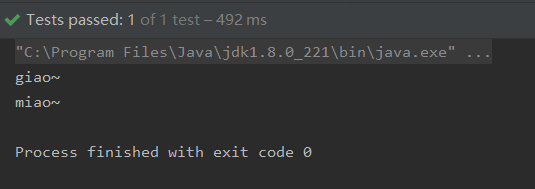
我们可以看到结果并没有发生改变,说明如果查询结果为多个时,@Autowried注解会根据SetXxx中的xxx来查找。
在来一个栗子:
<!--开启对注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="cat3" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog3" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="dog2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Person"></bean>
我们发现同样有多个查询结果.测试代码不变
测试一下:
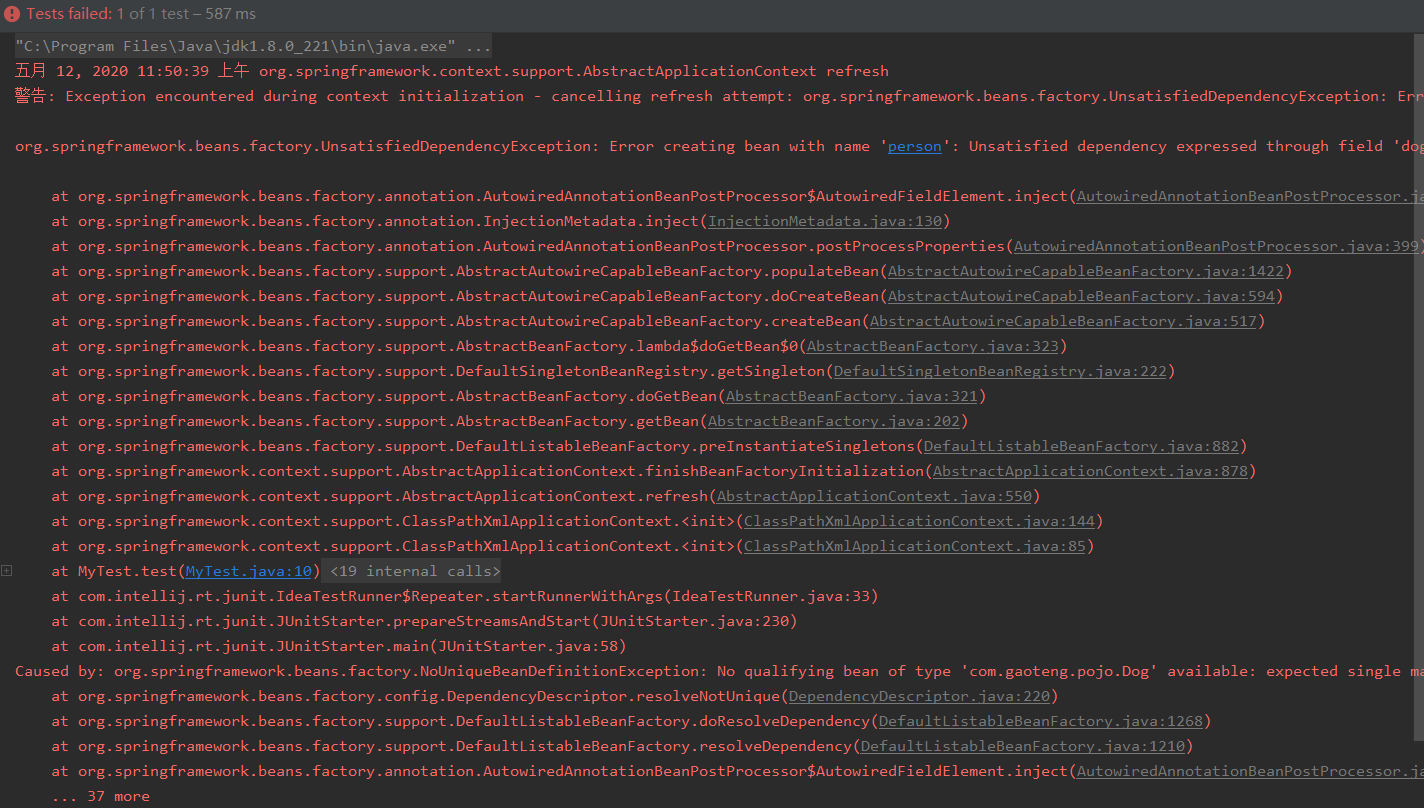
我们发现发生了异常,我们来截取异常的信息
Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'dog'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: dog2,dog3
翻译一下就是:
通过字段“ dog”表示不满意的依赖关系; 嵌套的异常是org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException:没有类型为'com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog'的合格bean:期望的单个匹配bean,但找到2:dog2,dog3.
如果@Autowried自动装配环境比较复杂时,自动装配无法通过一个@Autowired注解完成时,我们可以使用@Qualifier(value = "xxx")注解配合@Autowired使用,来指定一个唯一的bean对象的注入.
public class Person {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "dog2")
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "cat2")
private Cat cat;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
}
配置文件
<!--开启对注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="cat2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog2" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.gaoteng.pojo.Person"></bean>
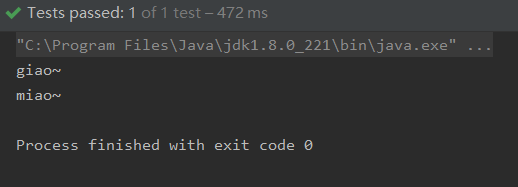
测试代码
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Person person = context.getBean("person", Person.class);
person.getDog().shoot();
person.getCat().shoot();
}
来测试一下:
与@Autowried注解作用很像的一个注解@Resource
@Resource默认按照名称(xxx)进行查找,找不到按类型.
public class Person {
@Resource
private Dog dog;
@Resource
private Cat cat;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
}
本篇博客参考以下博客:
@Autowired用法详解
在此特别感谢!