【声明】
欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→
文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4140466.html
联系方式:smyhvae@163.com
一、http协议回顾:
在上一篇文章中:JavaWeb学习之Servlet(一)----MyEclipse及Tomcat的配置,我们通过在浏览器输入url,就能看到在MyEclipse中编写的Servlet资源,效果如下:
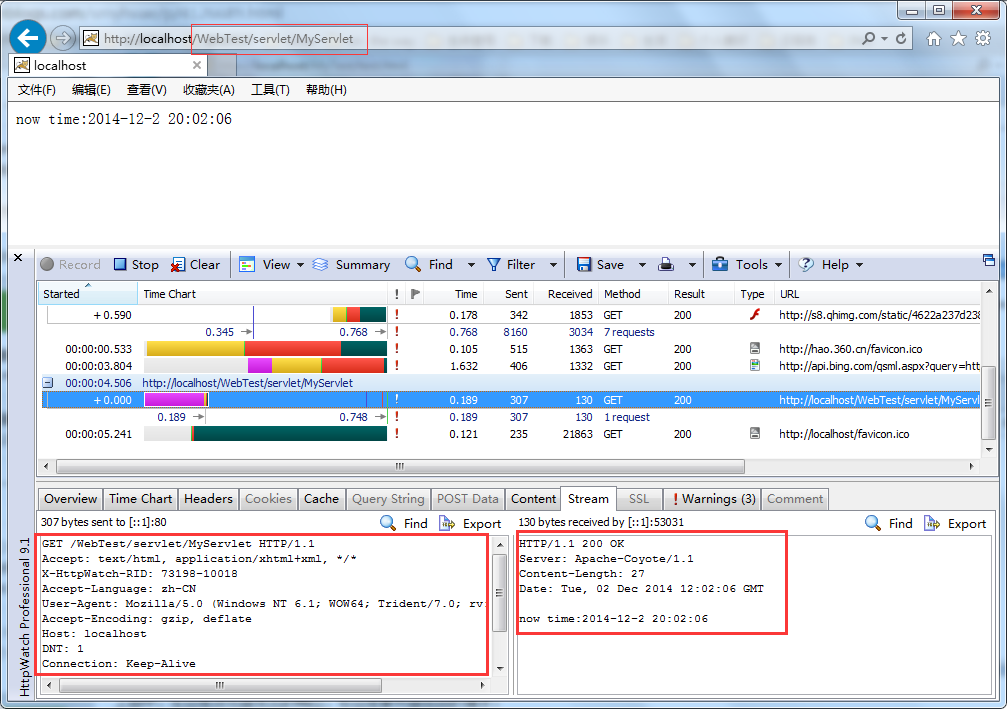
上图中,整个过程是这样的:浏览器中输入url后,会通过hosts文件/dns服务器解析为IP地址,进而找到对应ip地址的服务器。
在这期间,浏览器会通过http协议发出请求。服务器端收到请求后,做了下面这些事:
(1)分析出当前请求的是哪台虚拟主机:
- 查看Host请求头分析出访问的是哪台虚拟主机
- 如果没有Host请求头(在浏览器地址栏直接输入ip地址而不是url),则访问缺省虚拟主机
(2)分析当前请求访问的是当前虚拟主机的哪个Web应用:
- 从请求行中请求的资源部分来分析
(3)分析当前请求要访问的是这个Web应用的哪个资源:
- 从请求行的资源部分分析出访问的是哪个资源
(4)查找web.xml文件,查看有没有对应的虚拟路径,如果有则用这个虚拟路径对应的资源做响应
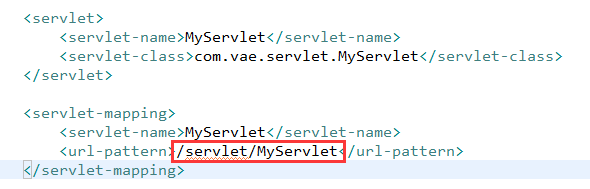
(5)服务器从response对象中获取之前写入的数据(这就是写在Servlet当中的java代码),组织成http响应消息发给浏览器。
注:第(5)句话便是本文要学习的重点。
二、Servet的运行过程及生命周期
Servlet程序是由WEB服务器调用,web服务器收到客户端的ServletWeb服务器首先检查是否已经装载并创建了该Servlet的实例对象。如果是,则直接执行第(4)步,否则,执行第(2)步。
访问请求后:
(1)装载并创建该Servlet的一个实例对象。
(2)调用Servlet实例对象的init()方法。
(3)创建一个用于封装HTTP请求消息的HttpServletRequest对象和一个代表HTTP响应消息的HttpServletResponse对象,然后调用Servlet的service()方法并将请求和响应对象作为参数传递进去。
(4)WEB应用程序被停止或重新启动之前,Servlet引擎将卸载Servlet,并在卸载之前调用Servlet的destroy()方法。
Servet的生命周期:
Servlet 的生命周期定义了一个Servlet如何被加载、初始化,以及它怎样接收请求、响应请求、提供服务。
生命周期如下:
- (1)通常情况下,服务器会在Servlet第一次被调用时创建该Servlet类的实例对象(servlet出生),创建出对象后立即调用init()方法做初始化操作;
- (2)一旦被创建出来,该Servlet实例就会驻留在内存中,为后续对这个Servlet的请求做服务,每次对这个Servlet的访问都会导致Servlet中Service方法执行;
- (3)当web应用被移除容器或者关闭服务器时,随着web应用的销毁,Servlet也会被销毁(servlet死亡)。在销毁之前服务器会调用Servlet的destroy方法做一些善后的工作。
有3个方法代表了Servlet的生命周期:
- init方法,负责初始化Servlet对象。
- service方法,负责响应客户的请求(调用doGet或doPost等方法)。
- destroy方法,当Servlet对象退出生命周期时,负责释放占用的资源。
注:在Servlet的整个生命周期内,Servlet的init方法只有在servlet被创建时被调用一次,每次对这个Servlet的访问都会导致Servlet中Service方法执行。
例如:现在浏览器连续访问Servlet 10次,内存中只有一个Sevlet对象。Servlet对象由服务器创建(创建一次),request和response由Servlet容器创建(创建10次)
来看一段代码:
1 package com.vae.servlet;
2 import java.io.IOException;
3 import java.io.PrintWriter;
4 import javax.servlet.ServletException;
5 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
8 //一般实现一个Servlet,只要继承HttpServlet类即可
9 public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
10 //Servlet初始化时调用的方法
11 @Override
12 public void init() throws ServletException {
13 super.init();
14 System.out.println("init....");
15 }
16
17 //Servlet被销毁时调用的方法
18 @Override
19 public void destroy() {
20 super.destroy();
21 System.out.println("destroy...");
22 }
23 //-------doGet/doPost 核心的业务处理方法(由service方法来调用)------------
24 @Override
25 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
26 throws ServletException, IOException {
27 //super.doGet(req, resp);
28 doPost(req, resp);
29 System.out.println("do service...");
30 }
31
32 @Override
33 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
34 throws ServletException, IOException {
35 //super.doPost(req, resp);
36 }
37 }
运行程序,输入url,此时,一按回车,马上就会在后台打出日志:
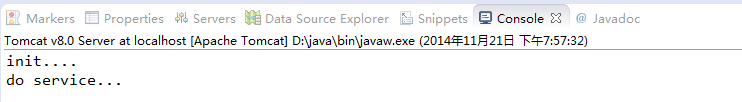
然后连续刷新三次网页,日志如下:
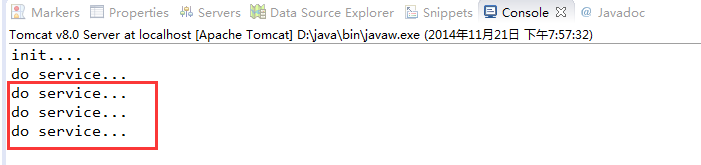
可以看到,Servelet只会初始化一次,之后的话,我们多次访问的是同一个Sevlet对象。此时,即使关掉网页,Servlet也不会销毁,只有关掉Tomcat服务器才会销毁Servlet。
需要注意的是,前台可能有get和post两种请求,但是在后台做的处理是一样的。例如:前台输入用户名密码,在后台验证的时候是不区分哪一种请求方式的。于是,如果在doGet()方法中写了代码内容,我们可以在doPost()方法中加一句:"doGet(req,resp);"即可,就可以进行重复利用(毕竟执行的都是同一段逻辑)。
三、Servlet的继承结构:
- Servlet接口:定义了Servlet应该具有的基本方法
- GenericServlet:抽象类,实现了Servlet接口。通用基本Servlet实现,对于不常用的方法在这个实现类中进行了基本的实现,将Service设计为了抽象方法,需要子类去实现
- HttpServlet:抽象类,继承了GenericServlet类。在通用Servlet的基础上基于HTTP协议进行了进一步的强化:复写了GenericServlet中的Service方法,Service方法体内的代码会自动判断用户的请求方式,如为GET请求,则调用HttpServlet的doGet方法,如为Post请求,则调用doPost方法。因此,开发人员在编写Servlet时,通常只需要继承HttpServlet,然后覆写doGet或doPost方法,而不要去覆写service方法。
四、修改Servlet模板:
使用MyEclipse创建Servlet时,根据默认的Servlet模板生成的Servlet代码如下:

1 import java.io.IOException;
2 import java.io.PrintWriter;
3
4 import javax.servlet.ServletException;
5 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
8
9
10 public class Servlet2 extends HttpServlet {
11
12 /**
13 * The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
14 *
15 * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get.
16 *
17 * @param request the request send by the client to the server
18 * @param response the response send by the server to the client
19 * @throws ServletException if an error occurred
20 * @throws IOException if an error occurred
21 */
22 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
23 throws ServletException, IOException {
24
25 response.setContentType("text/html");
26 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
27 out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
28 out.println("<HTML>");
29 out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
30 out.println(" <BODY>");
31 out.print(" This is ");
32 out.print(this.getClass());
33 out.println(", using the GET method");
34 out.println(" </BODY>");
35 out.println("</HTML>");
36 out.flush();
37 out.close();
38 }
39
40 /**
41 * The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
42 *
43 * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to post.
44 *
45 * @param request the request send by the client to the server
46 * @param response the response send by the server to the client
47 * @throws ServletException if an error occurred
48 * @throws IOException if an error occurred
49 */
50 public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
51 throws ServletException, IOException {
52
53 response.setContentType("text/html");
54 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
55 out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
56 out.println("<HTML>");
57 out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
58 out.println(" <BODY>");
59 out.print(" This is ");
60 out.print(this.getClass());
61 out.println(", using the POST method");
62 out.println(" </BODY>");
63 out.println("</HTML>");
64 out.flush();
65 out.close();
66 }
67
68 }
在实际开发中,这些生成的代码和注释一般我们都用不到的,每次都要手工删除这些注释和代码,很麻烦,因此可以根据开发的实际情况修改Servlet的模板代码,改成符合实际开发需求的模板代码。
MyEclipse 10修改Servlet模板的步骤如下:
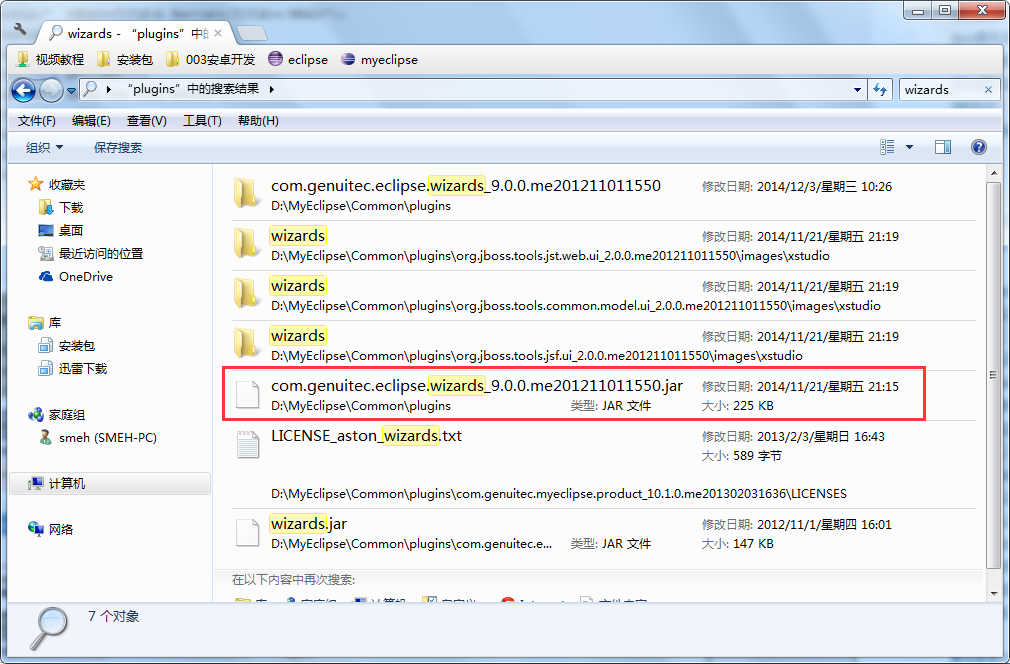
关闭MyEclipse,找到MyEclipse安装目录下的Commonplugins文件夹,比如:D:MyEclipse10Commonplugins,然后找到com.genuitec.eclipse.wizards_9.0.0.me201108091322.jar这个jar文件,如下图所示:
用压缩工具打开,注意是打开而不是解压这个jar包,如下图所示:
上图中,打开Jar包中的Templates文件夹中的Servlet.java文件,可以看到里面的模板代码:

1 #---------------------------------------------#
2 # <aw:description>Template for Servlet</aw:description>
3 # <aw:version>1.1</aw:version>
4 # <aw:date>04/05/2003</aw:date>
5 # <aw:author>Ferret Renaud</aw:author>
6 #---------------------------------------------#
7
8 <aw:import>java.io.IOException</aw:import>
9 <aw:import>java.io.PrintWriter</aw:import>
10
11 <aw:import>javax.servlet.ServletException</aw:import>
12 <aw:import>javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet</aw:import>
13 <aw:import>javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest</aw:import>
14 <aw:import>javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse</aw:import>
15
16 <aw:parentClass>javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet</aw:parentClass>
17
18 <aw:constructor name="c1">
19 /**
20 * Constructor of the object.
21 */
22 public <aw:className/>() {
23 super();
24 }
25
26 </aw:constructor>
27
28 <aw:method name="doGet">
29 /**
30 * The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
31 *
32 * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get.
33 *
34 * @param request the request send by the client to the server
35 * @param response the response send by the server to the client
36 * @throws ServletException if an error occurred
37 * @throws IOException if an error occurred
38 */
39 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
40 throws ServletException, IOException {
41 response.setContentType("text/html");
42 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
43 out.println(
44 "<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
45 out.println("<HTML>");
46 out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
47 out.println(" <BODY>");
48 out.print(" This is ");
49 out.print(this.getClass());
50 out.println(", using the GET method");
51 out.println(" </BODY>");
52 out.println("</HTML>");
53 out.flush();
54 out.close();
55 }
56
57 </aw:method>
58
59 <aw:method name="doPost">
60 /**
61 * The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
62 *
63 * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to post.
64 *
65 * @param request the request send by the client to the server
66 * @param response the response send by the server to the client
67 * @throws ServletException if an error occurred
68 * @throws IOException if an error occurred
69 */
70 public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
71 throws ServletException, IOException {
72 response.setContentType("text/html");
73 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
74 out.println(
75 "<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
76 out.println("<HTML>");
77 out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
78 out.println(" <BODY>");
79 out.print(" This is ");
80 out.print(this.getClass());
81 out.println(", using the POST method");
82 out.println(" </BODY>");
83 out.println("</HTML>");
84 out.flush();
85 out.close();
86 }
87
88 </aw:method>
89
90 <aw:method name="doPut">
91 /**
92 * The doPut method of the servlet. <br>
93 *
94 * This method is called when a HTTP put request is received.
95 *
96 * @param request the request send by the client to the server
97 * @param response the response send by the server to the client
98 * @throws ServletException if an error occurred
99 * @throws IOException if an error occurred
100 */
101 public void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
102 throws ServletException, IOException {
103
104 // Put your code here
105
106 }
107
108 </aw:method>
109
110 <aw:method name="doDelete">
111 /**
112 * The doDelete method of the servlet. <br>
113