题目描述
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根节点开始往下一直到叶节点所经过的节点形成一条路径。
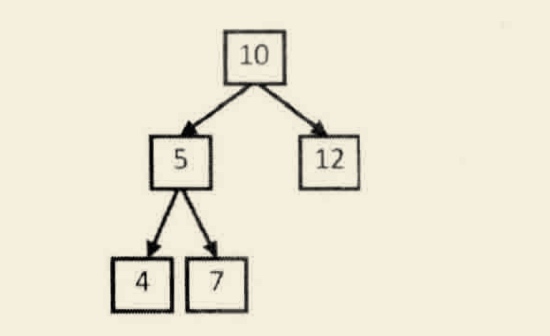
输入上图二叉树以及22,可以打印出两条路径,[10,12] 和[10,5,7]
思路分析
递归的前序遍历二叉树 ,将沿途路径中的值添加到list中,每次与target相减,当target减为0且遍历到子结点时,这条路径就是符合条件的路径,继续寻找。
测试用例
- 功能测试:二叉树中有一条、多条符合要求的路径;二叉树中没有符合要求的路径。
- 特殊输入测试:指向二叉树根节点的指针为nullptr指针。
Java代码
public class Offer34 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
test2();
test3();
}
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) {
return Solution1(root,target);
}
private static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Solution1(TreeNode root,int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(root==null)
return pathList;
ArrayList<Integer> nodeList=new ArrayList<Integer>();
findPathCore(root,target,pathList,nodeList);
return pathList;
}
private static void findPathCore(TreeNode root,int target,ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList, ArrayList<Integer> nodeList) {
if(root == null) return;
nodeList.add(root.val);
target-=root.val;
if(target==0 && root.left==null && root.right==null) {
int i=0;
while(i<pathList.size() && nodeList.size()<pathList.get(i).size()) {
i++;
}
pathList.add(i,new ArrayList<Integer>(nodeList));
}else {
findPathCore(root.left, target,pathList,nodeList);
findPathCore(root.right, target,pathList,nodeList);
}
nodeList.remove(nodeList.size()-1);
}
private static void test1() {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(8);
TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(10);
TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(7);
TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(9);
TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(11);
root.left=node1;
root.right=node2;
node1.left=node3;
node1.right=node4;
node2.left=node5;
node2.right=node6;
TreeNode.preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> findPath = FindPath(root, 27);
System.out.println(findPath);
}
private static void test2() {
}
private static void test3() {
}
}