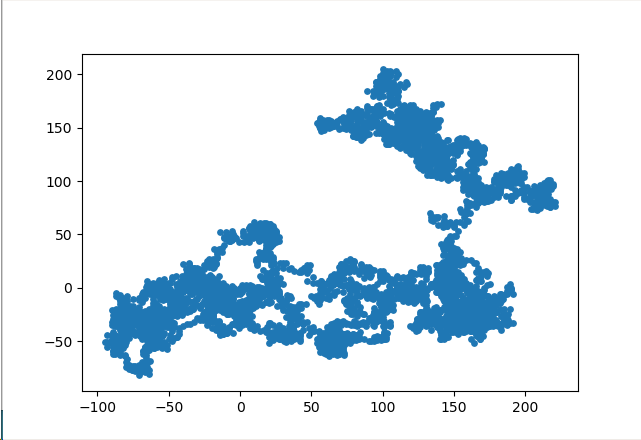
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=5000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__":
#只要程序处于活动状态,就不断地模拟随机漫步 while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
呈现的图像:
还处于活动状态:

按 y 则会继续生成:
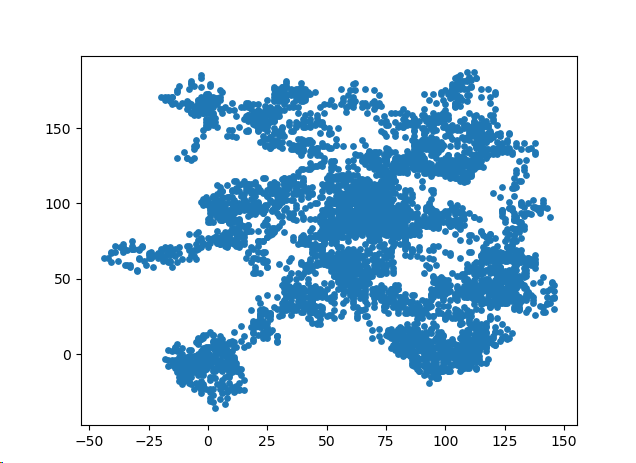
给点着色:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=5000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__": while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=15) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
图像呈现:

图像可以看到是一个渐变的过程
重新绘制起点和终点
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=5000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__": while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=15) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none') plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
图像呈现: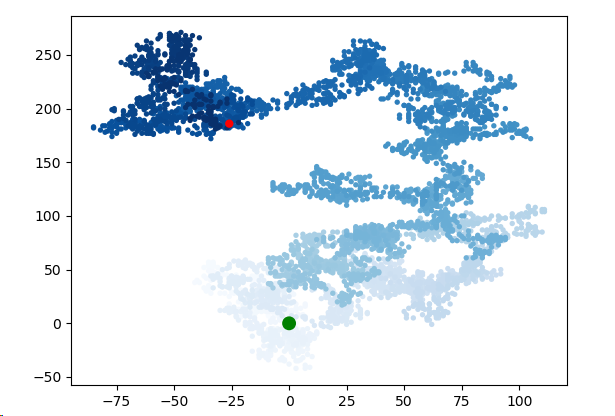
隐藏我们的坐标轴:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=5000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__": while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=15) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none') plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
图像呈现:
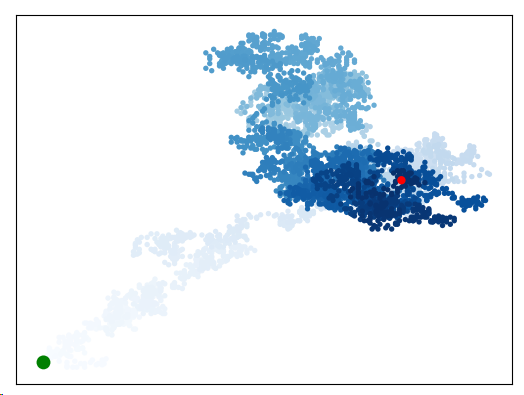
增加点数:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=50000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__": while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=1) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none') plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
图像呈现:

犹如一朵云
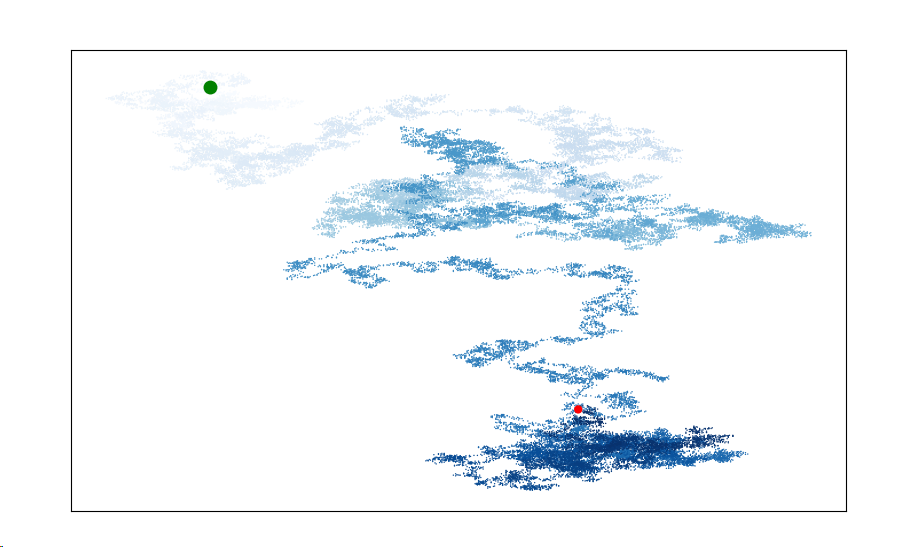
调整尺寸大小:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class Randomwalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=50000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values = [ 0 ] self.y_values = [ 0 ] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance if x_step == 0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) if __name__ == "__main__": while True: rw = Randomwalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=1) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none') plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
图像呈现: