概念相关
(因为前面期末考试的原因很久没有更了,也没有时间写题目了,暑假因为要集训和多校赛的话,会更的比较频繁,逃~)顾名思义,字典树,就是由一个个字符组成的一棵树。我们从根节点出发,在我们面临下一个单词的输入的时候,我们去新建一个节点存放当前的字符序列,ch[p][c]表示的是当前节点是上一个字符的下一个字符,所以这里我们应该会有感觉,我们在插入和查找字符串的时候,都是通过从根点沿着trie一直走,当我们走到这个字符串的末尾的时候,打上标记就代表这个字符串是存在于这棵树里面的。关于我们查找的次数我们同样可以进行处理,只需要这个点上面打上标记可以了。下面是字典树的结构示意图。在应用方面,我们可以用字典树来进行字串的统计,检索查询,对字符串集合进行字典序的排列等,操作性十分的高。
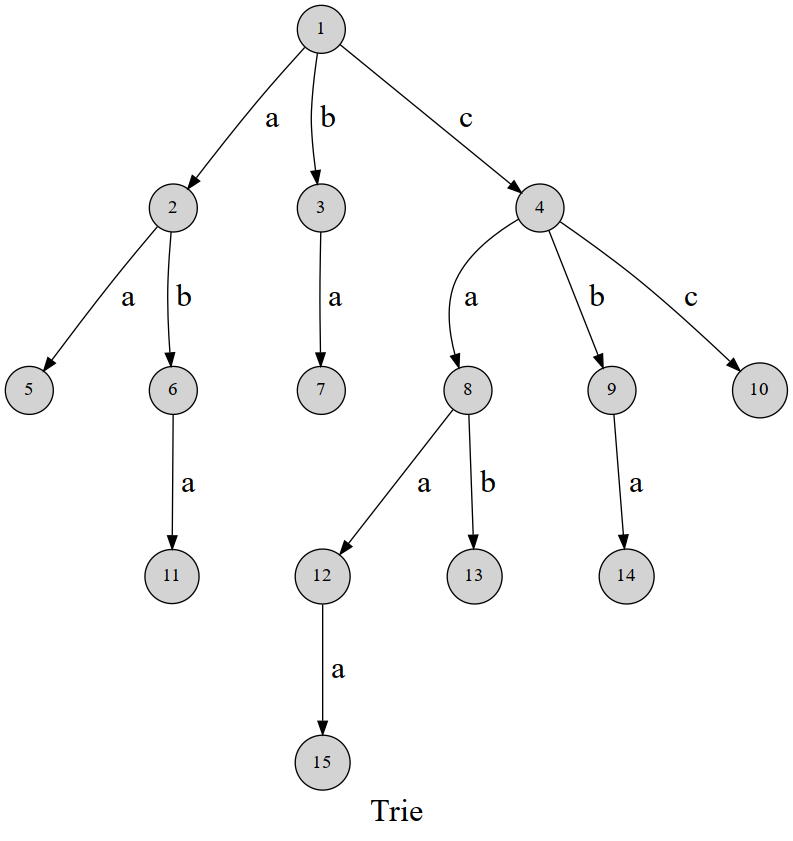
字典树的优缺点
我们掌握了一个数据结构我们当然要了解他的作用和优缺点。首先我们来关注一下字典树操作的时间复杂度,插入和查找都是线性的时间,这个复杂度十分优秀了,这里我们要提一下它和hash的区别,hash的话查询和比较操作是常数级别的复杂度,但是我们知道字符hash的话,还是取决于hash函数的好坏,并且hash函数或多或少都是会发生hash碰撞的,而字典树的结构则具有唯一性,当然了,我们既然说到这里,字典树的唯一性是什么带来的哪?没错,是他开的巨大的数组,所以来说字典树其实采用了一种以时间换空间的思想。
代码实现
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N=500005;
struct trie {
int ch[N][26],cnt;
bool exist [N];
void insert (char *s,int len) {
int p=0;
for (int i=0;i<len;i++) {
int c=s[i]-'a';
if (!ch[p][c]) ch[p][c]=++cnt;
p=ch[p][c];
}
exist[p]=1;
}
bool find (char *s,int len) {
int p=0;
for (int i=0;i<len;i++) {
int c=s[i]-'a';
if (!ch[p][c]) return 0;
p=ch[p][c];
}
return exist[p];
}
};
字典树的简单应用
给你n个学生的名字,我进行m次点名,第一次点到的输出OK,重复点到的输出RE,不存在的学生输出Never。
思路
这个我们很容易想,我们读入字符串同时把他丢进trie tree里面,然后我们点名的时候去查找这个字符串是否存在就可以了,点过一次后记得把tag标志打成2,这样在下次点名的时候我们就可以做出相对应的输出了。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include<vector>
#include <functional>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=500010;
char s[60];
int n,m,ch[N][26],cnt,tag[N];
int main() {
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf ("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int i=1;s[i];i++) {
int c=s[i]-'a';
if (!ch[u][c]) ch[u][c]=++cnt; //没有就新建节点
u=ch[u][c];
}
tag[u]=1;
}
cin>>m;
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
scanf ("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int j=1;s[j];j++) {
int c=s[j]-'a';
u=ch[u][c]; //沿着trie搜索,直到没有下一个根点为止
if (!u) break;
}
if (tag[u]==1) {
tag[u]=2;
puts("OK");
}
else if (tag[u]==2) puts("RE");
else puts("Never");
}
return 0;
}