0.最近在复习C++,好多东西都忘了 ==!!
从博客中,书中看到的一些东西,在这里简单总结下,没有章法,看到哪,复习到哪
1. 引用
C++中引用 具备了 指针的 所有功能
区别:
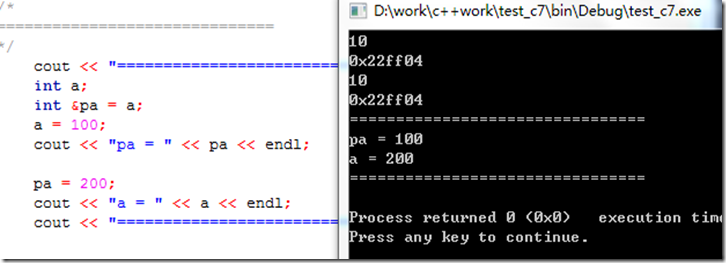
(1) 引用在定义时必须初始化.引用和变量共享同一块内存空间,而指针单独有内存空间
(2) 指针进行删除后,一般需要将其指向NULL,防止野指针,而引用至始而终都是它初始化时的地址,而且也不用删除,它会在作用域范围外由系统回收
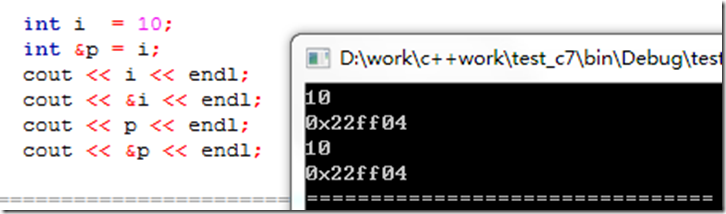
引用和它引用的变量指向的是同一块内存空间
当修改其中任意一个值时,两个值都改变,当对引用重新赋一个新值时,引用的值和原来引用指向的值都改变为这个新值,而引用地址不变
在C ++ 中还可以定义一个类的对象的引用,与对象共享一块内存
C++中 3 种传递函数参数的方式
(1)按值传递
(2)引用传递
(3)指针传递
3种方式的示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int a)
{
a = 10;
cout << "函数f()中 a = " << a << endl;
}
void g(int * a)
{
*a = 15;
cout << "函数g() 中 a = " << *a << endl;
}
void h(int &a)
{
a = 20;
cout << "函数h() 中 a = " << a << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1;
cout << "按值传递前 a = " << a << endl;
f(a);
cout << "按值传递后 a = " << a << endl;
cout << "按地址传递前 a = " << a << endl;
g(&a);
cout << "按地址传递后 a = " << a << endl;
cout << "按引用传递前 a = " << a << endl;
h(a);
cout << "按引用传递后 a = " << a << endl;
return 0;
}
可以看到按值传递,函数f()是不能修改a的
因为按值传递,只是把主函数a的值给了f函数的a值,这两个a的地址不是同一个地址,
在执行的过程中,会把主函数a的地址的数据拷贝给set函数a的地址
2 c++ 内存管理
内存分配方式
1. 从静态区分配,一般是全局变量和static类型变量
2.从栈区分配内存,一般是局部的变量,会随着所在函数的结束而自动释放
3.从堆中分配,一般是使用手动分配,使用malloc()函数和new来申请任意大小空间,不过要手动释放空间,相应的使用free()函数和delete释放,
如果不释放该空间,而且指向该空间的指针指向了别的空间.则该空间就无法释放,造成内存泄露,造成了内存浪费
动态内存释放问题与野指针
当我们使用free()和delete释放一块内存时,指针还是指向原来的地址,不过这时候的指针时野指针
1.指针销毁了,并不表示所指的空间也得到了释放 :内存泄露
2.内存被释放了,并不表示指针也被销毁了或指向NULL :野指针
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char *p = (char *)malloc(100);
memset(p,0,10);//一般申请内存后,最好使用memset初始化一下
strcpy(p,"hello world!");
if(p)
{
cout << "p:" << p << endl;
}
free(p);
// 所谓的野指针
cout << "p:" << p << endl;
if(p != NULL)
{
cout << "p不为空!" << endl;
}
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
指针的内存的传递
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
// 返回内存地址方式,这是正确的 !
//因为是动态内存分配,在堆上分配的
char * getMemory()
{
char *p = NULL;
p = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char));
memset(p,0,sizeof(char));
return p;
}
//常见错误是在栈上分配的被返回了,错误的
char *getMemory2()
{
char p [] = "hello world";
return p;
}
//通过指针的指针方式申请内存
void getMemory3(char ** p)
{
*p = NULL;
*p = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char));
if(*p)
{
cout << "p:" << p << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
char *p1 = NULL;
char *p2 = NULL;
char *p3 = NULL;
p1 = getMemory();
if(p1)
{
cout << "p1申请成功!" << endl;
}
p2 = getMemory2();
if(p2)
{
cout << "p2申请成功!" << endl;
cout << "p2:" << p2 << endl;
}
getMemory3(&p3);
if(p3)
{
cout << "p3申请成功!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3 动态数组(从csdn还是cnblogs中看到的,直接在这贴吧,网址找不到了)
1维
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int n1,i;
int *array;
printf("请输入所要创建的一维动态数组的长度:");
scanf("%d",&n1);
array=(int*)calloc(n1,sizeof(int));
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
array[i]=i+1;
printf("%d\t",array[i]);
}
free(array);//释放第一维指针
return 0;
}
2维
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int n1,n2;
int **array,i,j;
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的第一维长度:");
scanf("%d",&n1);
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的第二维长度:");
scanf("%d",&n2);
array=(int**)malloc(n1*sizeof(int*)); //第一维
for(i=0;i<n1; i++)
{
array[i]=(int*)malloc(n2* sizeof(int));//第二维
}
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
array[i][j]=i*n2+j+1;
printf("%d\t",array[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
free(array[i]);//释放第二维指针
}
free(array);//释放第一维指针
return 0;
}
3维
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n1,n2,n3;
int ***array;
int i,j,k;
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的第一维长度:");
scanf("%d",&n1);
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的第二维长度:");
scanf("%d",&n2);
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的第三维长度:");
scanf("%d",&n3);
array=(int***)malloc(n1*sizeof(int**));//第一维
for(i=0; i<n1; i++)
{
array[i]=(int**)malloc(n2*sizeof(int*)); //第二维
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
array[i][j]=(int*)malloc(n3*sizeof(int)); //第三维
}
}
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n3;k++)
{
array[i][j][k]=i+j+k+1;
printf("%d\t",array[i][j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
free(array[i][j]);//释放第三维指针
}
}
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
free(array[i]);//释放第二维指针
}
free(array);//释放第一维指针
return 0;
}
更多的维度也能照此写出来
使用recolloc进行数组的扩大或者缩小:
扩大
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int*n,*p;
int i,n1,n2;
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的长度:");
scanf("%d",&n1);
n=(int*)calloc(n1,sizeof(int));
printf("请输入所要扩展的动态数组的长度:");
scanf("%d",&n2);
p=(int*)realloc(n,(n2)*sizeof(int));//动态扩充数组
for(i=0;i<n2;i++)
{
p[i]=i+1;
if(i%5==0)
printf("\n");
printf("%d\t",p[i]);
}
free(p);
return 0;
}
缩小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int*n,*p;
int i,n1,n2;
printf("请输入所要创建的动态数组的长度:");
scanf("%d",&n1);
n=(int*)calloc(n1,sizeof(int));
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
n[i]=i+1;
if(i%5==0)
printf("\n");
printf("%d\t",n[i]);
}
printf("\n请输入所要缩小的动态数组的长度:");
scanf("%d",&n2);
p=(int*)realloc(n,(n2)*sizeof(int));
for(i=0;i<n2;i++)
{
if(i%5==0)
printf("\n");
printf("%d\t",p[i]);
}
printf("\n");
free(p);
return 0;
}
4. sizeof()
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//linux内核链表里的一个宏
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)4)->MEMBER)
typedef struct stu1
{
int a;
int b;
}stu1;
void print()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
}
int print2()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 1;
}
#pragma pack (1) /*指定按1字节对齐*/
typedef union stu
{
char str[10];
int b;
}stu;
#pragma pack () /*取消指定对齐,恢复缺省对齐*/
typedef union stu2
{
char str[10];
int b;
}stu2;
int main()
{
int i;
//sizeof可以对一个表达式求值,编译器根据表达式的最终结果确定大小
//但是不会对表达式进行计算,不会对函数进行执行
printf("sizeof(i):\t%d\n",sizeof(i));
printf("sizeof(4):\t%d\n",sizeof(4));
printf("sizeof(4+2.5):\t%d\n",sizeof(4+2.5));
printf("sizeof(int):\t%d\n",sizeof(int));
printf("sizeof 5:\t%d\n",sizeof 5);
cout << "============================" << endl;
//对于void类型,其长度为1
cout << sizeof(print()) << endl;
//int型的返回值,其长度为4(都是在32位机器)
cout << sizeof(print2()) << endl;
cout << "============================" << endl;
printf("offsetof(stu1,a):%d\n",offsetof(stu1,a)-4);
cout << "ofsetof(stu1,a):" << offsetof(stu1,a) - 4 << endl;
printf("offsetof(stu1,b):%d\n",offsetof(stu1,b)-4);
cout << "============================" << endl;
printf("sizeof(stu) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu));
printf("sizeof(stu2) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu2));
return 0;
}
对于结构体:
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct stu1
{
char array[7];
}stu1;
typedef struct stu2
{
double fa;
}stu2;
typedef struct stu3
{
stu1 s;
char str;
}stu3;
typedef struct stu4
{
stu2 s;
char str;
}stu4;
typedef struct stu5
{
double d1;
int i1;
char c1;
}stu5;
typedef union stu6
{
double d1;
int i1;
char c1;
}stu6;
typedef struct stu7
{
char c1;
int i1;
double d1;
}stu7;
typedef struct stu8
{
int i1;
char c1;
double d1;
}stu8;
int main()
{
printf("sizeof(stu1) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu1));
printf("sizeof(stu2) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu2));
printf("sizeof(stu3) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu3));
printf("sizeof(stu4) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu4));
printf("sizeof(stu5) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu5));
printf("sizeof(stu6) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu6));
printf("sizeof(stu7) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu7));
printf("sizeof(stu8) :\t%d\n",sizeof(stu8));
return 0;
}
size_t ,对于大小的比较,或者其他计算,会变成其补码形式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
size_t a = -1;
size_t b = 10;
if(a<b)
cout << "a < b" << endl;
else
cout << "a !< b" << endl;
return 0;
}
答案是 a !< b
5 一道堆栈指针问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//指针的地址是在栈中(首地址除外),但是指针指向的内容却在堆中,
//所以并没有被清除
char* get_str()
{
char* str = {"abcd"};
return str;
}
//栈里面的变量都是临时的。当前函数执行完成时,
//相关的临时变量和参数都被清除了,所以返回的指针指向的已经是随机的了
//但是str[]首地址被当成指针来处理,存放在堆中。
char* get_str2()
{
char str[] = {"abcd"};
return str;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char* p = get_str();
cout << *p << endl;
cout << *(p+1) << endl;
cout << p << endl;
cout << "========================" << endl;
char *p2 = get_str2();
//第1次执行 *p2的时候,由于p2指针的首地址被返回了,还是可以取到*p2的内容的
/*
可以试试取*(p2+1),也是可以取到的
*/
cout << *p2 << endl;
//第一次调用*p2的时候还是有数据的,但是第2次就没有了,
//说明cout之后指针已经被破坏了
cout << *p2 << endl;
cout << *(p2+1) <<endl;
cout << *p2 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
return 0;
}
参考:整理自互联网
http://blog.csdn.net/bizhu12/article/details/6668834