个人信息:
姓名:张越
班级:计算1811
学号;201821121006
编写程序:
在服务器上用Vim编写程序:创建一个命名管道,创建两个进程分别对管道进行读fifo_read.c和写fifo_write.c。给出源代码。
fifo2_write.c
#include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <signal.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int main(){ int fifo=mkfifo("fifo",0662); if((fifo == -1)){ if((errno!=EEXIST)){ perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); } } char buffer[1024]; int fd = open("fifo",O_WRONLY); //打开管道文件fifo if(fd == -1){ printf("Open failure "); exit(-1); } while(1){ printf("write : "); scanf("%s",buffer); int fkwrite=write(fd,buffer,(strlen(buffer)+1)); printf("Successful: %s ",buffer); } close(fd); return 0; }
fifo2_read.c
#include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <signal.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int main(){ int fifo=mkfifo("fifo",0662); if((fifo == -1)){ if((errno!=EEXIST)){ //排除文件已存在这个报错 perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); } } char buffer[1024]; int fd=open("fifo",O_RDONLY); if(fd == -1){ printf("Error! "); exit(-1); } while(1){ if(read(fd,buffer,1024) > 0) printf("Successful: %s ",buffer); } return 0; }
执行结果:
执行.fifo2_write
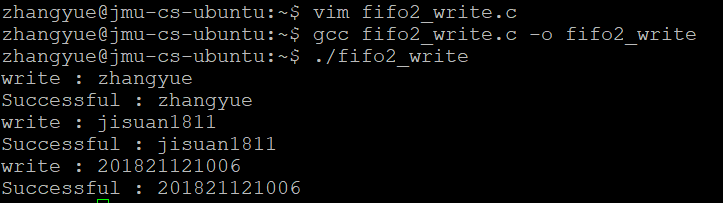
执行./fifo2_read
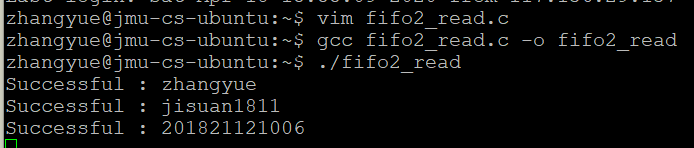
分析:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> 用于管道的命名头文件
首先创建fifo2_read.c文件作为读端,用于从管道中读取数据。然后创建fifo2_write.c为文件的写端,用于向管道中写入数据。
在通信的时候,读端打开写端菜可以有效的使用写。并且在每次写入之后,可以回馈消息在写入端(读端是否读取成功)。
如果直接打开写端没有打开读端,那么会造成堵塞。
通过实验产生的疑问跟解答:
一.关于mkfifo命令:用于创建一个fifo的特殊文件,是一个命名管道(可以用于做进程之间的通信的桥梁)
二.关于短管道的方向:管道是单方向的。
三.命名管道跟无名管道的区别是什么:
1.FIFO 在文件系统中作为一个特殊的文件而存在,但 FIFO 中的内容却存放在内存中。
2、当使用 FIFO 的进程退出后,FIFO 文件将继续保存在文件系统中以便以后使用。
3、FIFO 有名字,不相关的进程可以通过打开命名管道进行通信。
四.O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, O_RDWR分别代表什么:
读写方式(O_RDWR)
只读方式(O_RDONLY)
写方式(O_WRONLY)