一 概述
Thread类是java中的线程类,Java所有多线程的实现,均通过封装Thread类实现,Thread类实现了Runnable接口:
public class Thread implements Runnable {
二 Runnable接口
Runnable是一个函数式接口,接口里面只有一个run方法,用来执行线程运行的代码逻辑
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
三 ThreadGroup类
线程组是一个父子结构,一个线程组可以属于其他线程组,也可以拥有自己的子线程组,如果你一直向上追溯的话,会发现所有的线程组都在一个根线程组里面— System 线程组
线程组的出现可不是为耍酷用的,它是为了更方便的管理线程而存在的.比如设置线程最大优先级,销毁线程等等,添加线程,移除线程组等
还继承了Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler,用来处理默认的线程异常捕获处理,如果线程没有设置处理器,默认走的是group的处理方法
其中大部分方法都是递归操作方法
public class ThreadGroup implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
// 所属的父ThreadGroup
private final ThreadGroup parent;
// 线程组名称
String name;
// 最大优先级
int maxPriority;
/*是否被销毁*/
boolean destroyed;
// 是否是守护线程
boolean daemon;
//未启动线程数
int nUnstartedThreads = 0;
// 线程总数
int nthreads;
// 线程数组
Thread threads[];
// 线程组数量
int ngroups;
// 所拥有线程组数组
ThreadGroup groups[];
private ThreadGroup() { // called from C code
this.name = "system";
this.maxPriority = Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;
this.parent = null;
}
// 指定名字,父group为当前线程的线程组
public ThreadGroup(String name) {
this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);
}
// 指定父group和name的线程组
public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);
}
// 处理线程未检查异常异常,默认走这里,单独设置了走自己的
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
if (parent != null) {
parent.uncaughtException(t, e);
} else {
// 获取默认的异常处理
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh =
Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler();
// 如果有设置,则进行处理,否则直接打印System.err
if (ueh != null) {
ueh.uncaughtException(t, e);
} else if (!(e instanceof ThreadDeath)) {
System.err.print("Exception in thread ""
+ t.getName() + "" ");
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
}
}
// 设置最大优先级,递归
public final void setMaxPriority(int pri) {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
checkAccess();
if (pri < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || pri > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
return;
}
// 设置最大优先级不能超过 父group的最大优先级
maxPriority = (parent != null) ? Math.min(pri, parent.maxPriority) : pri;
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
// 递归调用该线程组的每个线程组
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
groupsSnapshot[i].setMaxPriority(pri);
}
}
// 递归获取线程总数
public int activeCount() {
int result;
// Snapshot sub-group data so we don't hold this lock
// while our children are computing.
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return 0;
}
// 线程总数
result = nthreads;
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
result += groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount();
}
return result;
}
.......add,remoev等其他方法
四 源码分析
属性
// 线程名称
private volatile String name;
// 线程优先级
private int priority;
// 是否是守护线程,默认false
private boolean daemon = false;
/* JVM state */
private boolean stillborn = false;
// 要执行的任务
private Runnable target;
// 所属的线程群组
private ThreadGroup group;
// 每个线程实例都引用一个ThreadLocal的map,每个线程在向ThreadLocal里塞值的时候,其实都是向自己所持有的ThreadLocalMap里塞入数据
// 读数据同理,根据ThreadLocal引用作为key取出value,实现线程隔离
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal,自父线程集成而来的ThreadLocalMap,
* 主要用于父子线程间ThreadLocal变量的传递,实现类是InheritableThreadLocal类
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
/* 用于自动编号匿名线程 */
private static int threadInitNumber;
// 同步方法,编号唯一
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() { return threadInitNumber++; }
// 线程栈大小
private long stackSize;
// 线程ID
private long tid;
// 用于生成线程ID的序列号
private static long threadSeqNumber;
private volatile int threadStatus = 0;
// 获取下一个线程ID,同步
private static synchronized long nextThreadID() { return ++threadSeqNumber; }
// 线程最低优先级
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
// 线程默认分配的优先级
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
// 线程最高优先级
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
构造器
// 线程无法克隆
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
throw new CloneNotSupportedException();
}
public Thread() {
init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
// 线程初始化
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize) {
init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true);
}
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
// 线程名字不能为null
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
// 每个线程都必须在一个线程组中,如果g为null,则设置为当前线程或者SecurityManager的线程组
if (g == null) {
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
g.checkAccess();
// 检查是否具有需要的权限
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
// 增加线程组中未启动线程的数量
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
// 设置优先级与是否是守护线程,与ThreadGroup相同
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
// 如果父线程的inheritableThreadLocals不为null,则将父线程inheritableThreadLocals传递至子线程
// 实现类是InheritableThreadLocal,
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
// 调用ThreadLocal的createInheritedMap方法,复制父线程table到当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals
this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
// 设置指定的栈大小,如果未指定大小,将在jvm 初始化参数中声明:Xss参数进行指定
this.stackSize = stackSize;
// 设置线程ID
tid = nextThreadID();
}
// 设置优先级
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
ThreadGroup g;
checkAccess();
if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) {
// 如果线程的优先级大于所属线程组的优先级,则设置为线程组的优先级
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
setPriority0(priority = newPriority);
}
}
// 设置线程优先级
private native void setPriority0(int newPriority);
// 构造器,所有构造器都调用init方法,每个线程都有所属的线程组
public Thread(Runnable target) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc, false);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) { init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); }
public Thread(String name) { init(null, null, name, 0); }
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { init(group, null, name, 0); }
public Thread(Runnable target, String name) {init(null, target, name, 0); }
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) { init(group, target, name, 0); }
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(group, target, name, stackSize); }
核心方法
interrupt
/**
* 中断线程,设置中断标志位(并不会立即停止线程):
*
* 1 如果当前线程阻塞在Object.wait(),Thread.join(),Thread.sleep()上,那么该线程会收到InterruptedException,且线程的打断标志会被清除;
* 2 如果当前线程阻塞在InterruptibleChannel上,那么该InterruptibleChannel会被关闭,线程的打断标志会被置位,且当前线程会收到ClosedByInterruptException;
* 3 如果当前线程阻塞在Selector上,那么该Selector的selection操作将会立即返回一个非0的结果,且Selector.wakeup()会被调用,线程的打断标志会被置位,
* 4 如果上述情况均不存在,将当前线程的打断标志置位,并不会马上停止线程
* 5 打断一个isAlive()返回false的线程没有效果,isInterrupted()仍然会返回false;
*/
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
// Interruptible 是一个只有interrupt方法的接口
Interruptible b = blocker;
// 在Interruptible上阻塞
if (b != null) {
// 只是设置中断标志,并没有停止线程
interrupt0();
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}
private native void interrupt0();
// 判断当前线程是否中断,传入true,会清除中断标志位,即重新置为false(默认是false)
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}
//判断线程是否终端 传入false,不会清除中断标志位
public boolean isInterrupted() {
return isInterrupted(false);
}
/**
* 返回线程是否被打断(打断标志是否被置位)
* 传入的参数决定是否该方法是否会清除终端标志位
*/
private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted);
start 与 run
// strat 同步方法,启动线程
public synchronized void start() {
// 如果调用时不是在线程状态不是NEW,则抛出IllegalThreadStateException, 0 表示NEW状态
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
// 将当前线程加入所属线程组数组,并维护线程总数(+1)和未启动数量(-1)
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
// 启动线程
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
// 启动失败,会移除线程组并还原未启动数量+1
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
private native void start0();
// 执行runable的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
setName
// 线程名称可以修改
public final synchronized void setName(String name) {
checkAccess();
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
if (threadStatus != 0) {
setNativeName(name);
}
}
public final String getName() {
return name;
}
sleep与join
/**
* 当前执行线程休眠指定毫秒在休眠期间,不释放任何当前线程持有的锁;
*/
public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
sleep(millis);
}
// 当前执行线程休眠指定毫秒在休眠期间,不释放任何当前线程持有的锁
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* 当前执行线程等待指定线程(也就是该调用发生的Thread对象)死后再继续执行;
* 可以设置超时,如果设置超时为0,则为不设置超时;
* 线程结束时(terminate),将会调用自身的notifyAll(),唤醒在该Thread对象上wait()的方法;
* 如果该线程被打断,该方法将抛出InterruptedException,并将打断标志位清除
*/
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
// 返回当前线程是否还活着
// start()后且还没有死亡的线程均视为活着的线程
public final native boolean isAlive();
// 同步方法,需要锁
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
// 为防止虚假唤醒,使用while循环方式来检查条件
while (isAlive()) {
// wait会释放锁,其他线程就可以调用join,
// 当一个线程正在某一个对象的同步方法中运行时调用了这个对象的wait()方法,那么这个线程将释放该对象的独占锁并被放入这个对象的等待队列
// 比如主线程里调用了线程A的wait(进入join会获取锁,join是同步方法),主线程就会释放锁,并进入这个对象的等待队列,等待notify通知之后才能继续运行,notify等代码写在本地实现里面
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
线程轨迹
// 静态方法,打印当前线程的栈轨迹(StackTrace),通过新建一个异常的方式实现
public static void dumpStack() {
new Exception("Stack trace").printStackTrace();
}
private static final StackTraceElement[] EMPTY_STACK_TRACE
= new StackTraceElement[0];
/**
* 获得栈轨迹,返回的是一个数组
* 数组的第0个栈轨迹为最近调用的栈轨迹
*/
public StackTraceElement[] getStackTrace() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread()) {
// check for getStackTrace permission
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkPermission(
SecurityConstants.GET_STACK_TRACE_PERMISSION);
}
// 线程死亡,返回空
if (!isAlive()) {
return EMPTY_STACK_TRACE;
}
StackTraceElement[][] stackTraceArray = dumpThreads(new Thread[] {this});
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = stackTraceArray[0];
// a thread that was alive during the previous isAlive call may have
// since terminated, therefore not having a stacktrace.
if (stackTrace == null) {
stackTrace = EMPTY_STACK_TRACE;
}
return stackTrace;
} else {
// Don't need JVM help for current thread
return (new Exception()).getStackTrace();
}
}
// 返回所有线程的栈轨迹
public static Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> getAllStackTraces() {
// check for getStackTrace permission
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkPermission(
SecurityConstants.GET_STACK_TRACE_PERMISSION);
security.checkPermission(
SecurityConstants.MODIFY_THREADGROUP_PERMISSION);
}
// 获取所有线程列表的快照
Thread[] threads = getThreads();
StackTraceElement[][] traces = dumpThreads(threads);
Map<java.lang.Thread, StackTraceElement[]> m = new HashMap<>(threads.length);
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = traces[i];
if (stackTrace != null) {
m.put(threads[i], stackTrace);
}
// else terminated so we don't put it in the map
}
return m;
}
private native static StackTraceElement[][] dumpThreads(Thread[] threads);
private native static Thread[] getThreads();
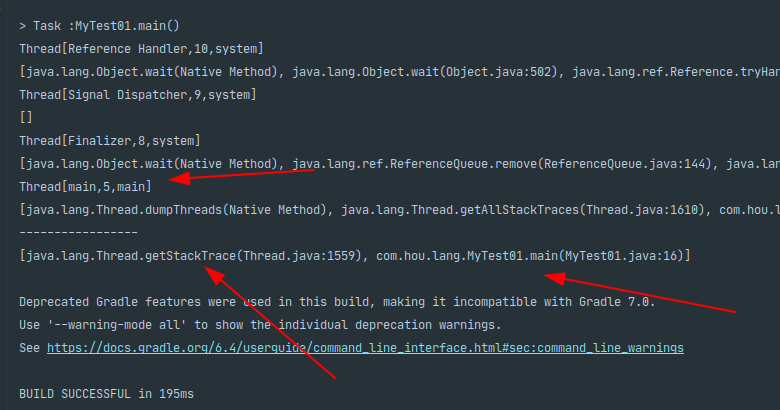
使用:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取所有线程轨迹,key线程,value轨迹map,即执行方法倒序,最后执行方法的在最前面
Thread.getAllStackTraces().forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(value));
});
// 获取当前线程轨迹
System.out.println("-----------------");
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stackTrace));
}
查看打印:
UncaughtExceptionHandler
// 对于未检查异常,如果在run()方法中运行出现了未检查异常,那么默认的行为是将堆栈跟踪信息写到控制台中(或者记录到错误日志文件中),然后退出程序
// 此函数式接口,用来捕获并处理在一个线程对象中抛出的未检查异常,以避免线程终止
@FunctionalInterface
public interface UncaughtExceptionHandler {
void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e);
}
// null unless explicitly set
private volatile Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler;
// 所有线程共享默认的,如果线程不设置,默认取这个,如果等于null,直接程序终止,不等于处理逻辑
private static volatile Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler;
//..... 两个属性 get,set
private void dispatchUncaughtException(Throwable e) {
getUncaughtExceptionHandler().uncaughtException(this, e);
}
使用,可以直接捕获到线程中的异常
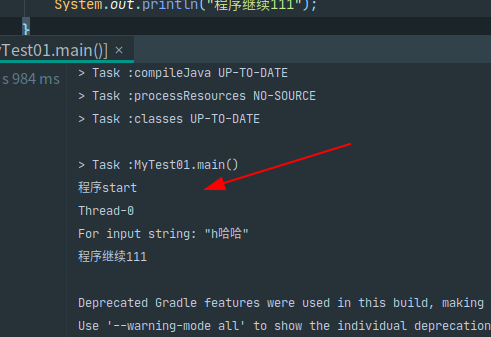
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 设置所有线程
// Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new MyUncaughtExceptionHandler());
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("程序start");
//每个线程单独设置,如果没有,默认获取所有默认的
Thread.currentThread().setUncaughtExceptionHandler((x, y) -> {
System.out.println(x.getName());
System.out.println(y.getMessage());
});
// 这种就是未检查异常,并没有trycatch,是代码逻辑问题,直接抛异常会导致程序结束
Integer.parseInt("h哈哈");
});
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("程序继续111");
}
捕捉: