Java NIO 简介
JAVA NIO有两种解释:一种叫非阻塞IO(Non-blocking I/O),另一种也叫新的IO(New I/O),其实是同一个概念。它是一种同步非阻塞的I/O模型,也是I/O多路复用的基础,已经被越来越多地应用到大型应用服务器,成为解决高并发与大量连接、I/O处理问题的有效方式。
NIO是一种基于通道和缓冲区的I/O方式,它可以使用Native函数库直接分配堆外内存(区别于JVM的运行时数据区),然后通过一个存储在java堆里面的DirectByteBuffer对象作为这块内存的直接引用进行操作。这样能在一些场景显著提高性能,因为避免了在Java堆和Native堆中来回复制数据。
Java NIO组件
NIO主要有三大核心部分:Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器)。传统IO是基于字节流和字符流进行操作(基于流),而NIO基于Channel和Buffer(缓冲区)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。Selector(选择区)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接打开,数据到达)。因此,单个线程可以监听多个数据通道。
Buffer
Buffer(缓冲区)是一个用于存储特定基本类型数据的容器。除了boolean外,其余每种基本类型都有一个对应的buffer类。Buffer类的子类有ByteBuffer, CharBuffer, DoubleBuffer, FloatBuffer, IntBuffer, LongBuffer, ShortBuffer 。
Channel
Channel(通道)表示到实体,如硬件设备、文件、网络套接字或可以执行一个或多个不同 I/O 操作(如读取或写入)的程序组件的开放的连接。Channel接口的常用实现类有FileChannel(对应文件IO)、DatagramChannel(对应UDP)、SocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel(对应TCP的客户端和服务器端)。Channel和IO中的Stream(流)是差不多一个等级的。只不过Stream是单向的,譬如:InputStream, OutputStream.而Channel是双向的,既可以用来进行读操作,又可以用来进行写操作。
Selector
Selector(选择器)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接打开,数据到达)。因此,单个的线程可以监听多个数据通道。即用选择器,借助单一线程,就可对数量庞大的活动I/O通道实施监控和维护。
注:
写就绪相对有一点特殊,一般来说,你不应该注册写事件。写操作的就绪条件为底层缓冲区有空闲空间,而写缓冲区绝大部分时间都是有空闲空间的,所以当你注册写事件后,写操作一直是就绪的,选择处理线程全占用整个CPU资源。所以,只有当你确实有数据要写时再注册写操作,并在写完以后马上取消注册。
基于阻塞式I/O的多线程模型中,Server为每个Client连接创建一个处理线程,每个处理线程阻塞式等待可能达到的数据,一旦数据到达,则立即处理请求、返回处理结果并再次进入等待状态。由于每个Client连接有一个单独的处理线程为其服务,因此可保证良好的响应时间。但当系统负载增大(并发请求增多)时,Server端需要的线程数会增加,对于操作系统来说,线程之间上下文切换的开销很大,而且每个线程都要占用系统的一些资源(如内存)。因此,使用的线程越少越好。
但是,现代的操作系统和CPU在多任务方面表现的越来越好,所以多线程的开销随着时间的推移,变得越来越小了。实际上,如果一个CPU有多个内核,不使用多任务可能是在浪费CPU能力。
传统的IO处理方式,一个线程处理一个网络连接
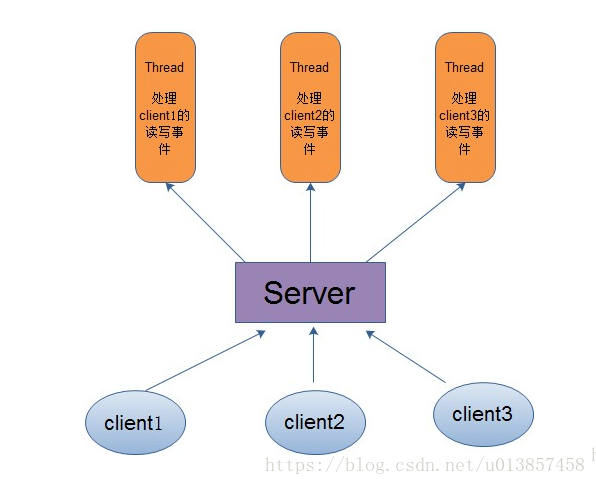
NIO处理方式,一个线程可以管理过个网络连接
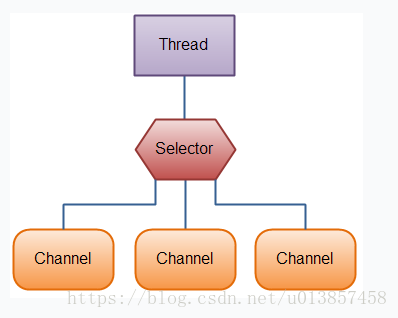
NIO服务器端如何实现非阻塞?
服务器上所有Channel需要向Selector注册,而Selector则负责监视这些Socket的IO状态(观察者),当其中任意一个或者多个Channel具有可用的IO操作时,该Selector的select()方法将会返回大于0的整数,该整数值就表示该Selector上有多少个Channel具有可用的IO操作,并提供了selectedKeys()方法来返回这些Channel对应的SelectionKey集合(一个SelectionKey对应一个就绪的通道)。正是通过Selector,使得服务器端只需要不断地调用Selector实例的select()方法即可知道当前所有Channel是否有需要处理的IO操作。注:java NIO就是多路复用IO,jdk7之后底层是epoll模型。
Java NIO的简单实现
服务端
package com.github.sources.network.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
*
*/
public class NioServer {
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public static void main(String[] args){
new NioServer(8080).start();
}
public NioServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void init() {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = null;
try {
ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("NioServer started ......");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
public void accept(SelectionKey key) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("accept a client : " + sc.socket().getInetAddress().getHostName());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void start() {
this.init();
while (true) {
try {
int events = selector.select();
if (events > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectionKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = selectionKeys.next();
selectionKeys.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
accept(key);
} else {
service.submit(new NioServerHandler(key));
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class NioServerHandler implements Runnable{
private SelectionKey selectionKey;
public NioServerHandler(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
this.selectionKey = selectionKey;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("收到客户端"+socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress().getHostName()+"的数据:"+new String(buffer.array()));
//将数据添加到key中
ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer.array());
socketChannel.write(outBuffer);// 将消息回送给客户端
selectionKey.cancel();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端
package com.github.sources.network.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
*
*/
public class NioClient {
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
private static final int port = 8080;
private Selector selector;
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i=0;i<3;i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
NioClient client = new NioClient();
client.connect(host, port);
client.listen();
}
}).start();
}
}
public void connect(String host, int port) {
try {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
this.selector = Selector.open();
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void listen() {
while (true) {
try {
int events = selector.select();
if (events > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectionKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKeys.next();
selectionKeys.remove();
//连接事件
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if (socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) {
socketChannel.finishConnect();
}
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("Hello this is " + Thread.currentThread().getName()).getBytes()));
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
sc.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("收到服务端的数据:"+new String(buffer.array()));
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}