JDBC连接数据库的方式
方式一:
public void test1() {
try {
Driver driver = new Driver(); //获得一个驱动
//连接数据看所需url,其中myemployees是所要连接的数据库
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myemployees";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root"); //user:用户名
properties.setProperty("password", "123456"); //password:密码
Connection conn = driver.connect(url,properties);
System.out.println(conn);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
方式二
public void test1() {
try {
//1.获取driver,通过反射实现
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
//2.连接数据库
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myemployees";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
Connection conn = driver.connect(url,properties);
System.out.println(conn);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
方式三
public void test1() {
try {
//通过DriverManager类获得connection
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myemployees";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,properties);
System.out.println(conn);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
方式四(推荐)
编写jdbc.properties配置文件
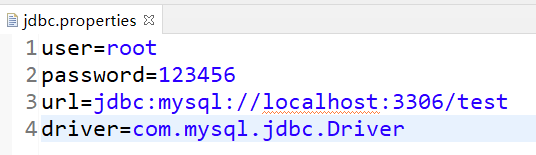
//通过配置文件方式
public void test1() {
try {
//通过当前类 获得类加载,进而加载文件
InputStream is = Conn.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
// 读取配置文件信息
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
// 加载驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
增删改查(CRUD)
所用表

编写连接数据库的工具类
public class CRUDUtils {
//获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
//1.加载文件
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(is);
//2. 读取配置文件,获取数据
String user = pro.getProperty("user");
String password = pro.getProperty("password");
String url = pro.getProperty("url");
String driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
// 3.加载驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//4.获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
//关闭资源
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, PreparedStatement ps) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
增加数据的写法
/**
* 增加用户
*/
public void addUser() {
// 1. 获取连接
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
// 2. INSERT INTO USER VALUES(4,'user4','123',NOW())
String sql = "INSERT INTO USER VALUES(?,?,?,NOW())"; //所有字段
String sql2 = "INSERT INTO USER(id, birthday) values(?,?)"; //选择两个字段
try {
// PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// ps.setInt(1, 4);
// ps.setString(2, "user4");
// ps.setString(3, "123");
// ps.execute();
//3. 获取prepareStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
//4. 设置值
ps.setInt(1, 4); //插入id
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = sdf.parse("2000-1-1");
//插入birthday,涉及java.util.date和java.sql.date日期转换
ps.setDate(2, new java.sql.Date(date.getTime()));
//5.提交
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6.关闭
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
}
修改数据的写法
public void updateUser() {
//1. 获取连接
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//2.预编译SQL语句,返回preparedStatement实例
String sql = "update user set username=? where id=?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
ps.setString(1, "abc");
ps.setInt(2, 1);
//4.提交
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//资源关闭
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
}
查询数据
编写一个Use人类
import java.sql.Date;
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String username, String password, Date birthday) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", birthday=" + birthday + "]";
}
}
通用查询
/**
通用查询
Java属性和数据库列不一致时,可以为数据库列起别名
同时获取列的别名时可以用md.getColumnLabel()方法。
*/
public User queryUser(String sql, Object... args) {
// 1.获取连接
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 2.预编译sql,获取preparedStatement实例
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 填充占位符
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) {
ps.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
// 3. 执行,并返回结果集
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData md = rs.getMetaData(); //获取结果集中的元素据
int columnCount = md.getColumnCount(); //获取结果集中列数
if (rs.next()) { //rs.next()查看是否存在下一条记录,类比iterate迭代器
//将数据封装到user对象中
User user = new User();
for(int i=0;i<columnCount;i++) {
//通过反射 给user字段赋值
//String columnName = md.getColumnName(i+1);//获取列名
String columnLabel = md.getColumnLabel(i+1); //获取列的别名
Field field = User.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true); //访问
field.set(user,rs.getObject(i+1));
}
return user;
}
return null;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.关闭
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
@Test //需要有Junit包
public void test2() {
String sql = "select id,username,password,birthday from user "
+ "where username=? and password=?";
User queryUser = queryUser(sql, "user3", "1234");
System.out.println(queryUser);
}
preparedstatement相较于statement的好处
SQL注入问题,SQL语句写法不繁琐PreparedStatement操作B1ob的数据,而Statement做不到。PreparedStatement可以实现更高效的批量操作。
存储blob类型数据
- Blob:二进制对象。用于存储图片视频等
public void blob() {
//1.获取连接
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//2.获取PreparedStatement对象
String sql = "insert into user(id,username,password,photo)"
+ "values(?,?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
ps.setInt(1, 5);
ps.setString(2, "aaa");
ps.setString(3, "123");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("1.jpg"));
ps.setBlob(4, fis); // 该方法存储二进制对象
//提交
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, null);
}
}
批量操作
mysql默认不支持批量操作需要在url后面加上代码:rewriteBatchedStatements=true
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
/*
* 批量操作
*/
public void batch() {
//获取连接
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
//获取 实例
String sql = "insert into test1(name) values(?)";
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(false); //设置不允许自动提交
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
ps.setString(1, "name"+i);
ps.addBatch(); //添加批量
if (i % 2000 == 0) {
ps.executeBatch(); //一次性送走2000条记录让SQL执行
ps.clearBatch(); //结束批量操作,下一波执行
}
ps.execute();
}
conn.commit(); //最后一次性提交,大大节省了时间
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, null);
}
}
事务的处理
DDL:数据定义语言,(创建create,删除truncaate/drop,修改alter表)
set autocommit=false不起作用DML:数据操作语言,(增insert,删delete,改update记录)
天然的自动提交事务,一旦执行就提交,可以通过SQL语句:set autocommit=false,设置 不需要自动提交- 默认关闭连接 数据也会自动提交
/**
* 操作score表,实现AA向BB转账100
*/
public void updateMoney(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//获取PreparedStatement实例
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) {
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]); //填充占位符
}
ps.execute(); //执行
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
CRUDUtils.closeResource(null, ps, null); //关闭PreparedStatement资源
}
}
// A 转账给 B,转账完毕则关闭资源,中间阻塞,则数据回滚
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection conn = CRUDUtils.getConnection(); //获取Connection连接
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(false); //设置 不自动提交
String sqlA = "UPDATE score SET balance=balance-100 WHERE id=?";
updateMoney(conn, sqlA, 1); //A 取出100
System.out.println(10/0); //模拟阻塞
sqlA = "UPDATE score SET balance=balance+100 WHERE id=?";
updateMoney(conn, sqlA, 2);//B 得到100
conn.commit(); //事务提交
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
conn.rollback(); //回滚
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
CRUDUtils.closeResource(conn, null, null); //转账完毕则关闭Connection资源
}
}
事务并发问题
- 脏读:对于两个事务T1,T2,T1读取了已经被T2更新但还没有被提交的字段。之后,若T2回滚,T1读取的内容就是临时且无效的。
- 不可重复读:对于两个事务T1,T2,T1读取了一个字段,然后T2更新了该字段。之后,T1再次读取同一个字段,值就不同了。
- 幻读:对于两个事务T1,T2,T1从一个表中读取了一个字段,然后T2在该表中插入了一些新的行。之后,如果T1再次读取同一个表,就会多出几行。
隔离级别
- ①
READ UNCOMMITTED(读而未提交数据): - ②
READ COMMITED(读已提交数据): 解决了脏读问题 - ③
REPEATABLE READ(可重复读): 解决了脏读和不可重复读问题 - ④
SERIALIZABLE(串行化): 解决了脏读,不可重复读,幻读的问题,但是性能十分低下。
Oracle 只支持②和④的隔离级别,默认是②,而MySQL支持①,②,③,④的隔离级别,默认③
数据库连接池
看文档写代码
//获取c3p0连接池
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//设置基本信息
cpds.setDriverClass( "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); //loads the jdbc driver
cpds.setJdbcUrl( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" );
cpds.setUser("root");
cpds.setPassword("123456");
//获取连接
Connection connection = cpds.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection); //com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.NewProxyConnection@75412c2f