多元函数拟合。如 电视机和收音机价格多销售额的影响,此时自变量有两个。
python 解法:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd #import statsmodels.api as sm #方法一 import statsmodels.formula.api as smf #方法二 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D df = pd.read_csv('http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~gareth/ISL/Advertising.csv', index_col=0) X = df[['TV', 'radio']] y = df['sales'] #est = sm.OLS(y, sm.add_constant(X)).fit() #方法一 est = smf.ols(formula='sales ~ TV + radio', data=df).fit() #方法二 y_pred = est.predict(X) df['sales_pred'] = y_pred print(df) print(est.summary()) #回归结果 print(est.params) #系数 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') #ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.scatter(X['TV'], X['radio'], y, c='b', marker='o') ax.scatter(X['TV'], X['radio'], y_pred, c='r', marker='+') ax.set_xlabel('X Label') ax.set_ylabel('Y Label') ax.set_zlabel('Z Label') plt.show()
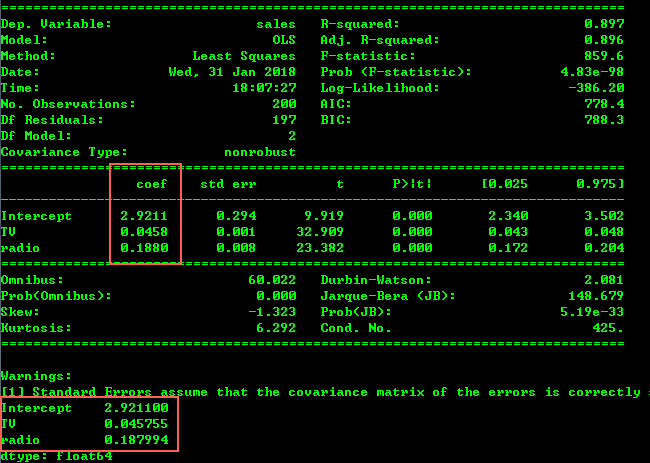
拟合的各项评估结果和参数都打印出来了,其中结果函数为:
f(sales) = β0 + β1*[TV] + β2*[radio]
f(sales) = 2.9211 + 0.0458 * [TV] + 0.188 * [radio]

图中,sales 方向上,蓝色点为原 sales 实际值,红色点为拟合函数计算出来的值。其实误差并不大,部分数据如下。

同样可拟合一元函数;
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import statsmodels.formula.api as smf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D df = pd.read_csv('http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~gareth/ISL/Advertising.csv', index_col=0) X = df['TV'] y = df['sales'] est = smf.ols(formula='sales ~ TV ', data=df).fit() y_pred = est.predict(X) print(est.summary()) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.scatter(X, y, c='b') ax.plot(X, y_pred, c='r') plt.show()


Ridge Regression:(岭回归交叉验证)
岭回归(ridge regression, Tikhonov regularization)是一种专用于共线性数据分析的有偏估计回归方法,实质上是一种改良的最小二乘估计法,通过放弃最小二乘法的无偏性,以损失部分信息、降低精度为代价获得回归系数更为符合实际、更可靠的回归方法,对病态数据的拟合要强于最小二乘法。通常岭回归方程的R平方值会稍低于普通回归分析,但回归系数的显著性往往明显高于普通回归,在存在共线性问题和病态数据偏多的研究中有较大的实用价值。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import linear_model from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D df = pd.read_csv('http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~gareth/ISL/Advertising.csv', index_col=0) X = np.asarray(df[['TV', 'radio']]) y = np.asarray(df['sales']) clf = linear_model.RidgeCV(alphas=[i+1 for i in np.arange(200.0)]).fit(X, y) y_pred = clf.predict(X) df['sales_pred'] = y_pred print(df) print("alpha=%s, 常数=%.2f, 系数=%s" % (clf.alpha_ ,clf.intercept_,clf.coef_)) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.scatter(df['TV'], df['radio'], y, c='b', marker='o') ax.scatter(df['TV'], df['radio'], y_pred, c='r', marker='+') ax.set_xlabel('TV') ax.set_ylabel('radio') ax.set_zlabel('sales') plt.show()
输出结果:alpha=150.0, 常数=2.94, 系数=[ 0.04575621 0.18735312]